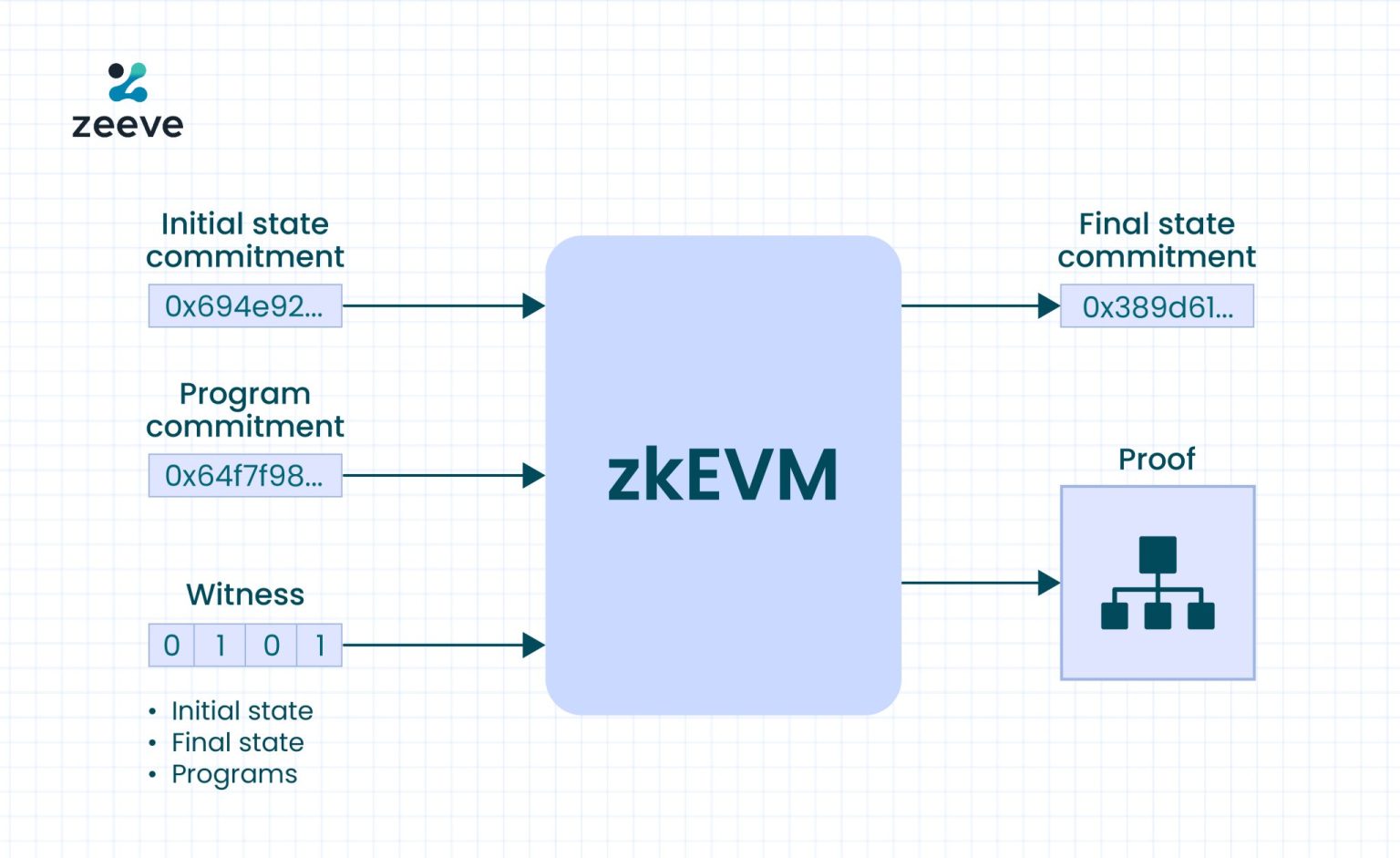
The ZK-EVM, a cutting-edge advancement in blockchain technology, recently entered its alpha phase, showcasing production-level performance as highlighted by Vitalik Buterin. This innovative aspect of Ethereum is set to revolutionize the Ethereum mainnet by introducing mechanisms for improved decentralization, consensus, and efficiency. With the launch of PeerDAS, which leverages data availability sampling, Ethereum is transforming into a robust P2P network capable of handling high throughput while maintaining security and performance. Buterin emphasizes that this evolution isn’t just about gradual improvements; it represents a significant shift in how networks operate, echoing the advantages of both BitTorrent’s bandwidth and Bitcoin‘s consensus. As ZK-EVM and PeerDAS forge ahead, the potential for Ethereum to truly solve the trilemma of efficiency, decentralization, and scalability becomes increasingly tangible.
Introducing ZK-EVM, or Zero-Knowledge Ethereum Virtual Machine, offers a glimpse into the future of blockchain scalability and security. Vitalik Buterin’s insights define this emerging technology’s impact on the Ethereum mainnet, particularly highlighting its alpha phase advancements and production-ready capabilities. Alongside PeerDAS, which denotes a new strategy for data accessibility in network operations, these developments are expected to significantly enhance the way Ethereum manages decentralization and consensus. This innovative architecture promises high bandwidth similar to what is found in P2P networks, thus providing a competitive edge over traditional blockchain solutions. The synergy of these technologies aims to redefine the landscape of decentralized applications while simultaneously addressing the critical challenges of data availability and network integrity.
Understanding ZK-EVM and Its Role in Ethereum’s Future
The ZK-EVM, or Zero-Knowledge Ethereum Virtual Machine, is currently in its alpha phase, demonstrating impressive production-level performance. This advancement signifies a pivotal shift for the Ethereum ecosystem, as it not only enhances security but also opens the door for various decentralized applications (dApps) to flourish. With ZK-EVM, Ethereum aims to combine high throughput with robust security measures, addressing long-standing challenges in decentralized networks. As Vitalik Buterin pointed out, the emergence of ZK-EVM positions Ethereum to transcend traditional limitations associated with P2P networks.
The introduction of ZK-EVM is particularly notable as it integrates with new mechanisms like PeerDAS, which leverages data availability sampling to optimize Ethereum’s operational efficiency. This synergy is vital for realizing a truly decentralized P2P infrastructure capable of handling the increasing demands of users and applications. As Ethereum evolves, the ZK-EVM is anticipated to play a crucial role in facilitating smoother interactions within the network while concurrently maintaining data integrity and availability.
As Ethereum progresses, the expectations surrounding ZK-EVM are high, especially with its anticipated implementation as a primary method for block validation by 2027. This transition is expected to enhance Ethereum’s functionality, allowing for an increase in gas limits and providing real, scalable solutions for decentralized operations. With such innovations, Ethereum is shifting away from traditional constraints, heralding a new era of blockchain technology.
In summary, the ZK-EVM stands as a cornerstone in Vitalik Buterin’s vision for a more efficient Ethereum network. Its evolution through phases of development underscores the commitment to improving consensus mechanisms and bandwidth utilization within the ecosystem. With ZK-EVM, Ethereum is set to not only compete but excel in delivering decentralized solutions that meet the growing needs of users globally.
PeerDAS and Its Impact on Ethereum’s Mainnet
The PeerDAS initiative, which has officially launched on the Ethereum mainnet, represents a significant advancement in addressing data availability issues within the blockchain. By utilizing data availability sampling, PeerDAS can enhance the efficiency of Ethereum’s P2P network, ensuring that data is accessible when needed by nodes throughout the network. This is particularly crucial as the demand for transaction throughput continues to escalate, and decentralized applications require reliable access to blockchain data.
Vitalik Buterin’s emphasis on PeerDAS aligns with Ethereum’s broader goal of establishing a resilient decentralized network. The integration of PeerDAS is not just about enhancing transaction speeds; it is also about bolstering the overall trust in the Ethereum ecosystem by decentralizing data access. As developers are able to deploy more complex dApps, PeerDAS will play a vital role in ensuring data integrity, which is essential for application performance and user experience.
PeerDAS is indicative of a larger trend towards improving the scalability of blockchain networks. While traditional systems may struggle under heavy loads, the intelligent data availability mechanisms introduced by PeerDAS can help Ethereum efficiently manage this demand. As a result, we can expect to see further innovations in how decentralized networks operate and interact, paving the way for more robust applications and services.
Ultimately, the successful deployment of PeerDAS on Ethereum’s mainnet represents a significant leap forward. By addressing the trilemma of decentralization, security, and scalability, PeerDAS, alongside ZK-EVM, positions Ethereum to handle the challenges of a growing ecosystem, making it a leader in the blockchain technology landscape.
The Future of Ethereum: Innovations from 2026 to 2030
Vitalik Buterin envisions a transformative phase for Ethereum stretching from 2026 to 2030, during which critical innovations such as BAL and ePBS are expected to mature. These mechanisms aim to increase gas limits and improve the overall efficiency of the network. As Ethereum fine-tunes its state architecture and execution loads, we can anticipate a significant undertaking to integrate ZK-EVM nodes into the ecosystem. This evolution is transformative, poised to solidify Ethereum’s centrality in the blockchain space.
As these advancements take shape, the significance of decentralized block construction becomes increasingly evident. By distributing the task of block creation across different nodes and locations, Ethereum can mitigate risks associated with centralization, ensuring that power does not reside in the hands of a few. This strategy is crucial in enhancing regional fairness and promoting a genuinely decentralized network. The successful adoption of the ZK-EVM during this period signifies Ethereum’s commitment to fostering innovation while adhering to the principles of decentralization.
The anticipated changes from 2026 to 2030 mark a profound shift in Ethereum’s capabilities. With ZK-EVM as a cornerstone for block validation, users can expect higher transaction throughput and more responsive decentralized applications. Furthermore, this period will likely witness the emergence of new business models and opportunities as developers leverage these technical enhancements.
In conclusion, Vitalik Buterin’s roadmap for Ethereum is ambitious and far-reaching. As Ethereum gears up for the transformations between 2026 and 2030, the synergy between PeerDAS, ZK-EVM, and distributed block construction will shape the platform’s trajectory, ultimately enhancing user experience and cementing its status as a leader in the blockchain domain.
Decentralization vs Centralization: The Ethereum Paradigm Shift
The ongoing shift in the Ethereum ecosystem highlights the critical dialogue surrounding decentralization and centralization. Vitalik Buterin points out that Ethereum’s evolution, particularly through innovations like ZK-EVM and PeerDAS, represents a concerted effort to overcome the limitations of centralization inherent in previous blockchain infrastructures. In traditional systems, especially those that rely on full replication, issues such as latency and inefficiency often arise, challenging the very essence of decentralization. However, with the newly introduced mechanisms, Ethereum aims to find a sustainable balance that maximizes both decentralization and performance.
The transparency and risk management offered by a decentralized approach are essential for building trust among users. By ensuring that no single entity can dominate the block construction process, Ethereum fortifies its alignment with decentralized principles. This paradigm shift not only strengthens security protocols but also enhances the network’s resilience against attacks and promotes inclusivity among its participants. Vitalik’s focus on achieving decentralized consensus while maintaining high bandwidth is a game-changer for the future of Ethereum, emphasizing quality along with egalitarian access.
As Ethereum continues its journey towards improved decentralization through innovations like ZK-EVM and PeerDAS, the emphasis on distributed block construction becomes increasingly central. This approach seeks to diminish centralized control, fostering a more collaborative environment where power and influence are shared among a wider array of participants. This is not merely an ideological endeavor; it has practical implications on the security and efficiency of the network, allowing Ethereum to scale effectively while upholding its foundational principles.
In essence, the ongoing transition towards decentralization within Ethereum offers insights into the future of blockchain technology as a whole. By prioritizing equitable access and distributed governance, Ethereum sets a powerful precedent for other platforms aiming to navigate the complexities of blockchain networks and user interactions.
Examining Ethereum’s Trilemma: Security, Scalability, and Decentralization
The blockchain trilemma remains a persistent challenge, comprising the pillars of security, scalability, and decentralization. Vitalik Buterin’s remarks on the advancements of ZK-EVM and PeerDAS reveal a deep commitment to addressing these complexities effectively. The traditional compromises often demand sacrifices in one area to bolster another; however, the ongoing innovations within the Ethereum network suggest a potential resolution. By implementing ZK-EVM, Ethereum seeks to enhance its scalability and throughput, all while maintaining robust security mechanisms.
PeerDAS plays an instrumental role in this equation, addressing data availability in a way that reinforces both security and scalability. By promoting efficient data sharing across the network, PeerDAS allows Ethereum to handle increased user demand without jeopardizing the integrity of the information being processed. This underscores the notion that improvements in one aspect of the trilemma can significantly enhance the other two, creating a harmonious balance that contributes to the overall health of the network.
Ethereum’s ongoing efforts to stabilize this trilemma are set against a backdrop of rapid technological evolution. As developers innovate and optimize performance, the iterative nature of these enhancements reinforces the notion that the trilemma is indeed manageable. The synergy between mechanisms like ZK-EVM and PeerDAS highlights a pathway for Ethereum to realize an ecosystem that is both scalable and secure, fostering confidence among its users and attracting a broader audience to decentralized applications.
In conclusion, the dialogue surrounding Ethereum’s trilemma reflects a broader understanding of how blockchain technology can evolve. The innovations being introduced today serve as a robust foundation for ongoing improvements, building towards a future where security, scalability, and decentralization coexist without compromise.
The Importance of Gas Limits in Ethereum’s Performance
Gas limits play a crucial role in regulating operations within Ethereum, directly affecting how transactions are executed and how dApps interact across the network. As Vitalik Buterin notes, emerging mechanisms like BAL and ePBS are set to gradually increase gas limits, paving the way for greater operational efficiency. A well-structured gas limit ensures that network activity remains fluid while preventing congestion, creating an optimal environment for developers and users alike.
Higher gas limits contribute to Ethereum’s scaling ambitions, particularly in relation to supporting ZK-EVM nodes. As more complex applications emerge, the ability to process increased transaction volumes becomes critical. Optimizing gas limits aligns with Ethereum’s vision of transforming into a high-capacity decentralized platform, where various applications can thrive without being hindered by limitations of the underlying blockchain.
Ultimately, understanding the dynamics of gas limits is essential for fostering a healthy ecosystem. With anticipations set for 2026 and beyond, Ethereum is firmly on the path to achieving a balance that accommodates growth while ensuring security and efficiency in transaction processing. These developments will undoubtedly strengthen Ethereum’s position in the broader cryptocurrency and blockchain landscape.
In conclusion, gas limits serve as both a stabilizing factor and a potential growth enabler within the Ethereum network. Through the anticipated innovations, Ethereum aims to navigate the complexities of scalability while ensuring its foundational principles remain intact, thereby fostering sustainable growth and user engagement.
Revisiting Consensus Mechanisms in the Ethereum Ecosystem
Consensus mechanisms are foundational to blockchain networks, determining how transactions are validated and blocks are confirmed. In Ethereum, Vitalik Buterin has expressed a commitment to evolving these mechanisms to enhance efficiency and scalability simultaneously. Ethereum’s transition to more decentralized protocols aims to foster a greater sense of trust and security among users while enabling rapid transaction processing. As developments such as ZK-EVM and PeerDAS take hold, the way consensus is achieved could undergo significant changes.
The ongoing focus on distributed block construction speaks to the importance of ensuring that validation processes are not overly centralized. By promoting a broader stakeholder participation in consensus, Ethereum can mitigate risks associated with potential single points of failure. This decentralized approach to consensus not only reinforces security but also addresses concerns regarding fairness and regional representation within the Ethereum network.
As Ethereum evolves, the mechanisms of consensus will be tested and refined, impacting how the network operates overall. These advancements are likely to catalyze fresh perspectives on decentralized governance and network management. The lessons learned during this evolution may influence other blockchain ecosystems, setting standards for future innovations in consensus mechanisms.
In summary, consensus mechanisms are at the heart of Ethereum’s functions, and their evolution will determine the network’s capabilities moving forward. With innovations aimed at decentralizing and improving efficiency, Ethereum is charting a course that encourages widespread participation and robust resilience against disruptions.
Scaling Solutions and Their Importance for DeFi Applications
Scaling solutions are critical in addressing the increasing demands of decentralized finance (DeFi) applications built on the Ethereum blockchain. Vitalik Buterin’s insights into ZK-EVM and PeerDAS underscore a commitment to pioneering methods that enhance throughput and efficiency. As DeFi continues to grow, the necessity of scalable solutions becomes more pronounced, ensuring that users can transact without the delays or high costs historically associated with Ethereum’s busy periods.
With the rollout of innovations like ZK-EVM, Ethereum positions itself as a frontrunner in the DeFi space. The ability to scale efficiently will not only facilitate more transactions but also attract a wider audience eager to engage in decentralized finance. By promoting accessibility through advanced scaling techniques, Ethereum is poised to create an ecosystem where financial services are available to everyone, regardless of their technical expertise.
The integration of PeerDAS further enhances this scalability, allowing for efficient data handling across a decentralized network. By addressing data availability issues, PeerDAS complements ZK-EVM’s focus on throughput, ensuring robust interaction between DeFi applications and the Ethereum blockchain. This holistic approach aims not just to meet current demands but also to anticipate the future growth of the DeFi ecosystem.
In conclusion, the success of DeFi applications on Ethereum is closely tied to the implementation and effectiveness of scaling solutions. By continually innovating and refining these technologies, Ethereum will maintain its leadership position in the blockchain landscape, fostering an environment conducive to inclusion and financial empowerment across global markets.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is ZK-EVM and how does it relate to Ethereum?
ZK-EVM, or Zero-Knowledge Ethereum Virtual Machine, is a new technology that enhances the Ethereum blockchain’s efficiency and scalability. It utilizes zero-knowledge proofs to allow smart contracts to execute off-chain while still ensuring security and validity on the Ethereum mainnet. This technology aims to improve Ethereum’s throughput while maintaining decentralization.
How does PeerDAS enhance the functionality of ZK-EVM on the Ethereum mainnet?
PeerDAS, or Peer-to-Peer Data Availability Sampling, complements ZK-EVM by improving data availability on the Ethereum mainnet. By implementing data availability sampling, it ensures that data required for transactions is widely distributed among nodes, which enhances the performance and security of ZK-EVM operations by enabling efficient data access without compromising decentralization.
What are the key phases and expected advancements for ZK-EVM according to Vitalik Buterin?
As of the latest updates, ZK-EVM has entered the alpha phase and is achieving production-level performance. Vitalik Buterin anticipates that from 2026 to 2028, there will be significant advancements including gas limits increase, adjustments in state structure, and more opportunities for running ZK-EVM nodes. These enhancements are expected to solidify ZK-EVM as the primary method for validating blocks on Ethereum.
How does ZK-EVM address the trilemma of scalability, decentralization, and security in Ethereum?
ZK-EVM addresses Ethereum’s trilemma by integrating mechanisms such as PeerDAS that facilitate high throughput, decentralization, and security simultaneously. By allowing real code to execute on the Ethereum mainnet while utilizing zero-knowledge proofs, ZK-EVM achieves a balance that resolves the typical trade-offs seen in blockchain technology.
What long-term impacts can we expect from the implementation of ZK-EVM and PeerDAS?
The implementation of ZK-EVM and PeerDAS is expected to transform Ethereum into a more efficient and decentralized P2P network. Over the next decade, enhancements in gas limits, block construction decentralization, and advanced data availability mechanisms will likely promote fairer participation across the network, reduce centralized intervention risks, and improve overall Ethereum performance.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| ZK-EVM Phase | The ZK-EVM has entered the alpha phase and is achieving production-level performance, with a focus on improving security. |
| Launch of PeerDAS | PeerDAS has been launched on the Ethereum mainnet, transforming Ethereum into a new type of P2P network. |
| Ethereum’s Transformation | The combination of PeerDAS and ZK-EVM aims to solve the decentralization, consensus, and bandwidth challenges of Ethereum. |
| Future Projections | From 2026 to 2030, significant advancements are expected, including increased gas limits and block validation methods involving ZK-EVM. |
| Distributed Block Construction | The long-term aim is to decentralize block construction to reduce risks of centralization and improve fairness. |
Summary
ZK-EVM is currently paving the way for a more advanced Ethereum by combining state-of-the-art technologies like PeerDAS and aiming for a decentralized framework that incorporates high performance and security. The shift towards these innovations represents a significant step in resolving longstanding challenges within blockchain technology, positioning Ethereum for enhanced scalability and efficiency in the upcoming years.