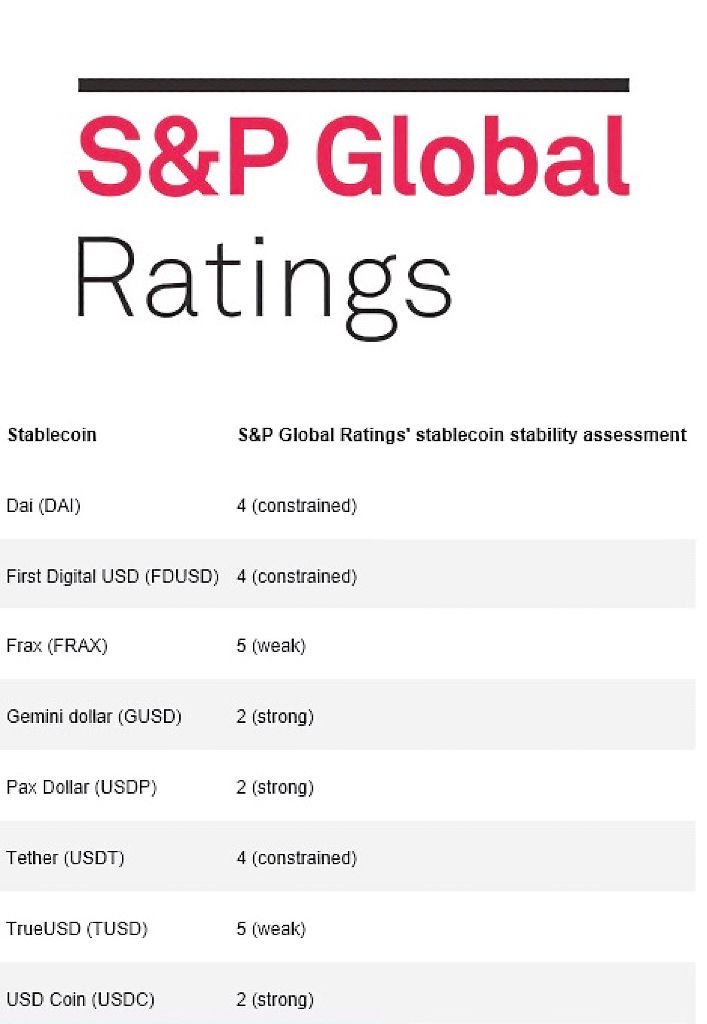
The Tether S&P Rating has sparked significant discussion within financial circles, as the S&P downgrades Tether’s stability rating to unprecedented lows. In a bold response, Tether CEO Paolo Ardoino expressed pride in the critique from the rating agency, asserting that traditional financial systems are riddled with flaws. His comments highlight the growing skepticism surrounding financial rating agencies, which often fail to accurately assess the true stability of companies. Amid these challenges, Tether stands out as a capital-surplus company, defying conventional models and maintaining profitability without toxic asset reserves. This situation further emphasizes the urgent need for a re-evaluation of how the financial sector measures trustworthiness and stability in the face of industry upheavals.
The recent evaluation of Tether by S&P has raised alarms though many now question the reliability of such financial assessments. The Tether CEO’s remarks illuminate a broader issue concerning the efficacy of conventional rating systems, which are often seen as outdated in a rapidly evolving financial landscape. By constructing a financially robust framework, Tether exemplifies a new direction for companies seeking to escape the pitfalls of traditional financial narratives. This reevaluation comes at a time when investors are becoming increasingly wary of the practices employed by financial rating agencies. The conversation surrounding Tether’s financial integrity is just the beginning of a larger dialogue about redefining trust in our economic systems.
Understanding Tether’s S&P Rating: A CEO’s Perspective
Tether CEO Paolo Ardoino recently addressed the S&P downgrading of Tether’s credit rating, suggesting that this action reflects a deeper issue within traditional financial systems rather than a failure on Tether’s part. Ardoino’s statement emphasized a prevailing dissatisfaction with how conventional rating agencies operate, arguing that they’ve often misled investors by issuing investment-grade ratings to companies that later collapse. He pointed out that Tether, while facing scrutiny, is challenging this outdated system that prioritizes traditional models over innovative financial practices.
Further defending Tether, Ardoino claimed that despite the negative rating from S&P, the company operates with a capital surplus and does not engage in risky asset reserves, which he refers to as ‘toxic assets’. This contrasts with the practices of many firms within the traditional financial ecosystem that consistently make poor investments. Through Tether’s structure, a healthier alternative is presented, one that not only questions the validity of financial rating agencies but also suggests a model of sustainability that could potentially reshape investor confidence in decentralized finance.
The Implications of S&P Downgrades on Tether’s Reputation
The S&P downgrades Tether’s stability rating, a move that has been met with both criticism and support within financial circles. While traditionalists may view the downgrade as a sign of instability, ardent supporters of Tether argue that such actions highlight the failings of the traditional financial system that has systematically misrepresented the viability of certain investment opportunities. This situation underscores the growing rift between traditional financial institutions and cryptocurrency enterprises, where transparency and capital surplus usage, as seen in Tether, demand a paradigm shift in how these organizations are assessed.
Additionally, Tether’s steadfastness in maintaining a capital surplus strategy without resorting to dangerous asset holdings positions it uniquely amid ongoing criticism. The financial rating agencies, often trusted by investors as objective assessors, can sometimes perpetuate inaccuracies that lead investors to overlook healthier financial structures. As Tether continues to grow and thrive within a shadowed financial landscape, this becomes a pivotal moment for assessing how ratings influence public perception and investor decisions.
Tether’s Capital-Surplus Model: A New Benchmark?
Unlike traditional companies that may suffer from liquidity crises due to mismanagement or toxic asset holdings, Tether represents a break from these missteps with its capital-surplus model. This innovation allows Tether to maintain robustness in its financial health, setting a new benchmark for how cryptocurrency companies can operate sustainably. In Ardoino’s view, this model not only secures investors’ confidence but also promotes a more transparent ecosystem that stands in stark contrast to the traditional financial sector’s historical practices.
Moreover, the capital-surplus model is not merely a defensive strategy; it positions Tether as a frontrunner in financial technology innovation. By prioritizing financial stability over traditional metrics, Tether may well inspire other financial entities to rethink their practices and come up with more resilient and sustainable models. This shift could herald a new era in the financial landscape, where the value of companies is measured not just by conventional metrics but also by their ability to adapt and serve their customer’s needs effectively.
Challenging Traditional Finance: Tether’s Place in the Market
Tether’s rise as a significant player in the cryptocurrency market reflects a broader challenge to the legacy systems of finance. Ardoino’s controversial remarks regarding the traditional financial system shed light on the inherent weaknesses often masked by outdated norms and reliance on flawed rating methodologies. By succeeding in an environment that is increasingly resistant to change, Tether embodies a revolutionary spirit aimed at disrupting entrenched financial practices that have historically proven unreliable.
This paradigm shift not only boosts Tether’s credibility among crypto investors but also invites scrutiny on larger financial institutions and their reliance on antiquated models. As more businesses question the validity of S&P and similar ratings, they may begin to embrace Tether’s approach as a beacon of potentiality for a more equitable financial future. This entrenchment of digital assets could very well signal the end of a monolithic dependency on traditional finance, heralding new possibilities.
The Role of Financial Rating Agencies in Crypto Markets
Financial rating agencies play a vital role in shaping the perceptions of investors towards both traditional and emerging financial instruments, including cryptocurrencies. The recent S&P downgrade of Tether has sparked discussions on the reliability of these agencies, particularly in an evolving market where conventional assessment methods struggle to keep pace with rapid innovations. As the CEO of Tether expressed, such ratings are often questionable, prompting a re-evaluation of what credibility means in the context of digital finance.
With the rise of blockchain technology, financial rating agencies face a unique challenge: how to adapt their models to assess new and often volatile forms of assets. As Tether’s CEO posits, traditional financial systems filled with ‘naked emperors’ may be losing their grip on relevancy as digital currencies like Tether offer a transparent alternative. Therefore, the future role of these agencies may hinge on their ability to accurately evaluate the innovative structures that cryptocurrencies present, or risk becoming obsolete in the process.
Investors’ Perspective on Tether and Financial Stability
From an investor’s standpoint, understanding Tether’s approach to financial stability is crucial in a climate dominated by uncertainty. Many look to Tether as a safe harbor, especially when compared with traditional financial offerings that often fall victim to market whims and flawed ratings. Ardoino’s call for a reevaluation of how we understand stability in finance resonates strongly with investors who have suffered losses due to agency misratings of safer, yet poorly performing institutions.
As more investors embrace the decentralized finance narrative championed by Tether, the demand for transparent and reliable financial structures will likely grow. This shift could inspire a new generation of investors to prioritize firms that not only promise growth but also demonstrate tangible financial responsibility. Tether’s capital-surplus model stands as a significant case study in attracting these investors, emphasizing the narrative that stable, ethical business practices can ultimately lead to sustained profitability.
The Future of Tether in a Digital Economy
Looking ahead, Tether is poised to play a critical role in shaping the landscape of digital economies. With growing acceptance of cryptocurrency as a legitimate asset class, Tether’s resilience against traditional market oscillations suggests that it may serve as a critical stabilizing force for investors navigating these waters. The company’s innovative practices, including its capital-surplus strategy, signal a potential blueprint for success in the increasingly digital-centric economy.
As financial systems globally begin to incorporate more technologies, Tether may become a frontrunner in advocating for methodologies that prioritize financial stability and sustainability. This forward-thinking approach could not only bolster Tether’s market position but also inspire other companies within blockchain and traditional finance alike to reconsider their operational models. The influence of Tether extends beyond mere market performance; it challenges existing notions of fiscal responsibility, setting a precedent for what the future of financial health could resemble.
Conclusion: Evaluating Tether’s Impact on Financial Ratings
In conclusion, the dialogue surrounding Tether and its S&P rating raises critical questions about the efficacy and reliability of financial rating agencies in evaluating cryptocurrency entities. Tether CEO’s defiant stance against traditional financial institutions invites a broader reevaluation of what constitutes sound investment metrics in a world that is increasingly shifting towards decentralized finance. By challenging existing norms, Tether has proven that celebrated terms like ‘sustainability’ and ‘financial reliability’ can be redefined in the context of emerging technologies.
As Tether continues to innovate and redefine its strategies amidst the scrutiny of S&P and traditional financial norms, it will be interesting to observe how the landscape evolves. Investors, regulators, and financial ratings agencies alike will need to reconsider their approaches, not just to Tether, but to a growing class of companies that challenge the status quo. Ultimately, Tether serves as a catalyst for change, highlighting the urgent need for evaluative frameworks that are robust enough to incorporate the complexities of modern financial practices.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does the S&P downgrade of Tether mean for its stability rating?
The S&P downgrade of Tether’s stability rating signifies a reassessment of its financial reliability. Tether’s CEO, Paolo Ardoino, emphasizes that despite the downgrade, the company operates as a capital-surplus entity without toxic asset reserves, challenging conventional financial perceptions.
How does Tether’s capital-surplus status impact its S&P rating?
Tether’s capital-surplus status indicates that it holds more assets than liabilities, which the CEO argues should provide a level of stability that differs from traditional financial institutions. This distinction raises questions about the relevance of S&P’s rating methodologies in assessing Tether’s actual financial health.
What was the Tether CEO’s response to the S&P downgrade?
Tether CEO Paolo Ardoino expressed pride in the scrutiny from S&P, suggesting that such ratings stem from outdated models that have failed in traditional finance. He argues that these ratings do not reflect Tether’s unique position and success as a capital-surplus company in a fragmented financial system.
How do financial rating agencies impact Tether’s reputation in the market?
Financial rating agencies like S&P play a crucial role in shaping market perceptions. Tether’s CEO believes that the negative ratings reflect concerns over innovation in financial practices, suggesting that such agencies may not fully understand Tether’s operational model and its departure from traditional systems.
What issues does Tether face from the traditional financial system according to its CEO?
According to Tether’s CEO, the traditional financial system is fraught with failures and systemic issues. He claims that Tether’s attempt to operate outside of these norms has made it a target for criticism, particularly from established financial institutions threatened by its unconventional approach.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| S&P Downgrading Tether | S&P has downgraded Tether’s stability rating to the lowest level. |
| CEO’s Response | Tether CEO Paolo Ardoino expressed pride in the company’s criticism from S&P, suggesting it reflects the flaws of traditional financial systems. |
| Critique of Traditional Ratings | He criticized traditional financial rating models that have misled investors and led to bankruptcies despite high ratings. |
| Regulatory Concerns | Ardoino highlighted global regulatory bodies questioning the objectivity of major rating agencies. |
| Tether’s Unique Position | Tether is positioned as a capital-surplus company with no toxic assets, maintaining profitability. |
| Traditional System Vulnerabilities | Tether claims the traditional financial system is flawed and fears the emergence of alternative financial models. |
Summary
Tether S&P Rating has raised significant discussions in the financial community following its recent downgrade. Tether’s CEO, Paolo Ardoino, responded by asserting that the criticism from S&P highlights the vulnerabilities of traditional financial structures. He emphasized that rating agencies have historically misled investors, leading to disastrous financial outcomes. Despite the downgrade, Tether maintains its profitability without relying on inherently risky asset reserves, showcasing the effectiveness of its model in contrast to traditional financial systems.