| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
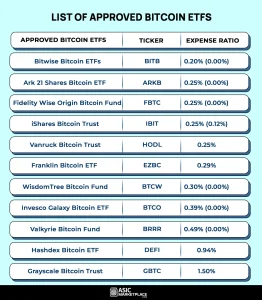
| Exclusive Bank Partnerships | South Korea is reviewing the ‘one exchange–one bank’ model for crypto exchanges, evaluating its impact on market competition. |
| Regulatory Collaboration | The Financial Services Commission and Fair Trade Commission are assessing if linking exchanges to single banks promotes market concentration. |
| Anti-Money Laundering Compliance | Current practices stem from AML regulations, leading exchanges to rely on banks for fiat transaction facilitation. |
| Market Research | A government-funded study points out that the exchange-bank model may hinder competition and services for smaller exchanges. |
| Centralization Issues | The study reveals that South Korea’s crypto market is highly centralized, favoring larger platforms over newcomers. |
| Digital Asset Basic Act | Regulations are being finalized for a framework to govern stablecoin issuance, with legislation affected by ongoing regulatory discussions. |
Summary
South Korea crypto regulations are under close examination as the nation assesses exclusive bank partnerships for cryptocurrency exchanges. The objective is to foster a more competitive landscape while addressing concerns of market concentration that currently benefit larger platforms. With new legislation on the horizon, the focus will be on structuring a fair regulatory environment that encourages participation from all market players, ensuring that smaller exchanges can compete effectively and access necessary banking services.
South Korea crypto regulations are entering a critical phase as the government evaluates bank partnerships for cryptocurrency exchanges. The Financial Services Commission (FSC), along with the Fair Trade Commission, is scrutinizing the impact of these exclusive relationships on market concentration within the digital asset landscape. With the upcoming Digital Asset Basic Act aiming to reshape the framework for cryptocurrency regulations, there’s growing concern about the potential monopolistic tendencies created by the one exchange–one bank model. This regulatory review comes in the wake of a comprehensive study highlighting how such practices limit access to financial services for newer exchanges, thereby stifling competition. As South Korea continues to navigate this complex arena, the implications of these regulations could redefine the operational dynamics for crypto exchanges operating in a market increasingly focused on fostering fair competition and innovation.
In recent developments regarding South Korea’s digital currency governance, regulatory bodies are examining the intricate ties between cryptocurrency platforms and financial institutions. This inquiry, spearheaded by the FSC and the Fair Trade Commission, is pivotal to understanding the implications of current banking partnerships that could be contributing to market imbalances. As discussions surrounding the proposed Digital Asset Basic Act gain momentum, there’s a significant focus on how existing frameworks influence competition and innovation among virtual asset exchanges. These regulatory considerations are essential, given that the concentration of market power could hinder the participation of emerging players in this evolving sector. Consequently, the future of South Korea’s crypto landscape hinges on how effectively these challenges are addressed, potentially reshaping the dynamics of the digital asset ecosystem.
Understanding South Korea’s Crypto Regulations
South Korea’s regulatory landscape for cryptocurrencies is evolving rapidly, driven by the urgent need to establish a robust framework that addresses the unique challenges of digital assets. The Financial Services Commission (FSC) is at the forefront of these changes, as it seeks to implement comprehensive cryptocurrency regulations under the forthcoming Digital Asset Basic Act. This legislation is expected to set foundational rules for how digital currencies and tokens can be managed, ensuring transparency and fostering investor confidence. As such, the FSC’s collaboration with the Fair Trade Commission is pivotal in assessing current practices, particularly the reliance on exclusive bank partnerships for crypto exchanges.
Currently, the South Korean market is characterized by a ‘one exchange–one bank’ paradigm, which, although not formally codified, has emerged to adhere to Anti-Money Laundering (AML) standards and other compliance guidelines. This model has raised concerns about market concentration, with a small number of exchanges dominating the landscape. The implications of these concentrated practices point to significant barriers for new entrants, thereby stifling competition and innovation within the sector. As regulators fine-tune their approach, clarity around these regulations will be essential for fostering a more equitable and diverse trading environment.
The Role of Bank Partnerships in Crypto Exchanges
Exclusive bank partnerships play a crucial role in the operational framework of South Korean cryptocurrency exchanges. By aligning with designated banks, exchanges are able to offer customers effective fiat transaction solutions, making it easier for users to engage with digital assets. This strategic collaboration also helps mitigate potential compliance risks associated with various banking laws. Nevertheless, the dependence on a select group of banking partners raises critical issues regarding market access and competition, particularly when smaller platforms struggle to secure similar banking relationships.
The implications of these exclusive partnerships can be profound, reinforcing existing market dominance among well-established exchanges while potentially leaving newer players at a disadvantage. In light of ongoing discussions about the regulatory structure, the FSC is tasked with balancing the need for stringent compliance with the necessity of a competitive market landscape. The regulatory review aiming to level the playing field will determine whether the current banking partnership model will continue or if changes are necessary to promote a more equitable distribution of market power.
Impact of the Digital Asset Basic Act on Market Dynamics
The Digital Asset Basic Act represents a significant evolution in the regulatory framework governing cryptocurrencies in South Korea. As it unfolds, the act aims to clarify the rules governing transactions, trading, and the overall supervision of digital assets. This legislative move is seen as a critical step in fostering a transparent and secure environment for investment while addressing concerns related to market concentration and liquidity. Of particular note is the proposed introduction of asset reserve requirements for stablecoin issuers, which aims to enhance consumer protection and stabilize the crypto market.
Additionally, the act is expected to tackle the complexities of oversight for domestic stablecoin issuers, a topic ripe for discussion among regulatory bodies. As South Korea continues to navigate the intricate landscape of digital assets, the evolution of the Digital Asset Basic Act can significantly reshape the competitive dynamics of the crypto market. This will not only influence existing exchanges but will also open avenues for new market participants to engage without the overwhelming barriers that dominate the current setup.
The Future of Market Competition in South Korea’s Crypto Sector
As South Korea’s regulatory framework evolves, the prospect of increased competition in the crypto sector becomes more tangible. The potential for changes in exclusive bank partnerships and the overarching regulatory landscape could foster a healthier, more diversified marketplace for digital assets. By mitigating current monopolistic practices, the Financial Services Commission’s efforts could unleash the potential of smaller exchanges, empowering them to compete more effectively against established players. This shift could lead to improved liquidity, pricing efficiency, and a wider array of services for consumers.
Moreover, a future with more equitable access to banking services for cryptocurrency exchanges may also spur innovation. With a fairer competitive environment, exchanges can differentiate themselves not just through volume and liquidity but by offering innovative products and services that cater to an evolving clientele. Such developments would not only enrich the South Korean crypto ecosystem but could also position it as a leader in the global digital asset market, attracting both local and international investors.
Regulatory Challenges Associated with Market Concentration
Regulatory challenges associated with market concentration in South Korea’s crypto sector cannot be overstated. As identified in several studies, the current model of exclusive partnerships leads to a highly centralized market that tends to favor a few dominant exchanges. This scenario poses significant challenges to regulators, as they must address how competition can be improved without compromising the stability of the financial system. The emphasis on stringent compliance and risk management must balance the need for an inclusive market.
Furthermore, the regulatory approach must consider the implications of following a ‘one exchange-one bank’ strategy, especially as it hampers the ability of smaller players to thrive. Without effective regulatory intervention, the same players will continue to dominate, narrowing consumer choice and stultifying overall market dynamism. As South Korean regulators develop the Digital Asset Basic Act, it is crucial that they implement mechanisms that prevent market concentration while promoting a competitive environment robust enough to attract new participants.
The Importance of AML Regulations in Cryptocurrency Transactions
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations are a critical component of the cryptocurrency framework in South Korea, specifically in how they shape exchanges’ operations and partnerships with banks. These guidelines are designed to prevent illicit activities and protect the integrity of the financial system. However, they also play a pivotal role in determining how effectively exchanges can interact with customers in a fiat capacity. As recognized by the FSC, striking the right balance between regulatory compliance and facilitating market access is vital to achieving a healthy cryptocurrency ecosystem.
As regulators work to define the parameters of the Digital Asset Basic Act, AML considerations will undoubtedly influence the future of bank partnerships with crypto exchanges. Enhanced due diligence measures could evolve from the current model, addressing not only compliance risks but also fostering trust in digital asset transactions. By implementing more comprehensive and nuanced AML regulations, regulators can pave the way for a more inclusive and diverse market.
Evaluating Competition through Research and Regulation
The ongoing evaluation of competition within South Korea’s cryptocurrency market is underpinned by in-depth research initiatives aimed at understanding current dynamics and regulatory efficacy. Government-funded studies are shedding light on how market concentration affects both consumer choices and the operational capabilities of smaller exchanges. These insights are instrumental for the Financial Services Commission as it formulates policies to promote a competitive and transparent marketplace.
In essence, the research is a critical feedback loop that helps regulators assess the impact of existing bank partnerships and the broader implications of upcoming legislation. By prioritizing empirical findings in their decision-making processes, regulators can create a framework that promotes healthy competition without idealizing any single model, thus paving the way toward a more reliable and expansive crypto environment.
Shifts in Consumer Behavior Towards Cryptocurrency
Consumer behavior towards cryptocurrency in South Korea is evolving in tandem with regulatory developments and burgeoning interest in digital assets. As increasingly sophisticated product offerings and services emerge amidst regulatory clarity, consumers are becoming more engaged and confident in their investment decisions. The financial markets’ receptiveness to new crypto products, particularly stablecoins, reflects a growing trend towards adopting digital assets as mainstream investment vehicles.
Moreover, this shifting landscape creates an opportunity for exchanges and related businesses to tailor their offerings to meet the demands of an evolving consumer base. Transparency and reliability in transactions will become paramount as consumers navigate more complex products. By understanding these behavioral shifts, stakeholders in the South Korean crypto market can strategically position themselves to meet the rising expectations of a more informed and security-conscious generation of investors.
The Global Context of South Korea’s Crypto Legislation
The discussions surrounding South Korea’s cryptocurrency regulations must be understood within a global context, particularly as other nations also refine their approaches to digital assets. The actions taken by the Financial Services Commission, especially with the impending Digital Asset Basic Act, are reflective of broader trends where countries are grappling with the challenges and opportunities presented by cryptocurrencies. By aligning local regulations with international standards, South Korea can maintain its competitive edge in the global market.
Furthermore, engagement with global regulatory trends may facilitate collaborations with other nations, promoting standards that can enhance market integrity and consumer protection across borders. As South Korea navigates its regulatory landscape, it stands at the intersection of innovation and compliance, which places it in a unique position to be a leader in establishing best practices for cryptocurrency governance on a global scale.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the current South Korea crypto regulations regarding bank partnerships for exchanges?
South Korea’s crypto regulations currently allow exchanges to form exclusive partnerships with banks for facilitating fiat transactions. Although this ‘one exchange–one bank’ model is not codified in law, it has emerged due to Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations. The Financial Services Commission (FSC) and Fair Trade Commission are reviewing these structures to assess their impact on market concentration and competition within the crypto sector.
How does the Digital Asset Basic Act affect cryptocurrency regulations in South Korea?
The Digital Asset Basic Act is pivotal to South Korea’s evolving cryptocurrency regulations. Although its final submission has been delayed to 2026, the act aims to regulate digital assets comprehensively, including measures like mandatory reserve requirements for stablecoin issuers. This legislative framework is intended to introduce greater oversight and clarify the relationship between crypto exchanges and banks in response to market concentration issues.
Will South Korea’s evaluation of crypto exchange bank partnerships impact market concentration?
Yes, South Korea’s evaluation of the exclusive bank partnerships for crypto exchanges is aimed at addressing market concentration. The FSC’s review seeks to determine if the current ‘one exchange–one bank’ practice limits competition and restricts access for smaller or emerging exchanges, potentially leading to a more balanced and competitive crypto market.
What role does the Financial Services Commission (FSC) play in South Korea’s cryptocurrency regulations?
The Financial Services Commission (FSC) plays a crucial role in shaping South Korea’s cryptocurrency regulations. It collaborates with other agencies to evaluate bank partnerships with exchanges, analyze market concentration, and oversee the implementation of laws like the Digital Asset Basic Act. The FSC’s decisions significantly influence the operational environment for cryptocurrency exchanges and their relationships with banking institutions.
How are South Korean cryptocurrency exchanges adapting to current regulations?
South Korean cryptocurrency exchanges are adapting to current regulations by securing exclusive partnerships with banks to provide fiat transaction services. This model is largely influenced by compliance requirements, such as AML directives. However, as the regulatory framework evolves with the anticipated Digital Asset Basic Act, exchanges may need to adjust their operational structures to align with regulatory changes and mitigate risks associated with market concentration.
What challenges do new cryptocurrency exchanges face under South Korean regulations?
New cryptocurrency exchanges in South Korea face significant challenges due to existing regulations that favor larger, established platforms. The exclusive bank partnership model can restrict access to essential banking services, making it difficult for new entrants to compete effectively. Additionally, the ongoing regulatory reviews pertaining to market concentration may influence the landscape they must navigate.
How does market concentration in South Korea’s crypto sector impact liquidity?
Market concentration in South Korea’s crypto sector leads to liquidity issues, as the dominance of a few major exchanges limits transactions and trading options for users. This concentration benefits established platforms, creating barriers for smaller exchanges and hindering overall market efficiency. With the ongoing regulatory assessments, authorities are working towards balancing competition and liquidity in the crypto market.