In recent years, quantum computing progress has captured the imagination of technologists, academics, and the general public alike, often leading to significant quantum computing hype. While advancements in quantum algorithms and quantum cryptography have been noteworthy, the reality is that we are still several decades away from realizing the full potential of quantum computers. Current quantum devices struggle with tasks as simple as factoring small numbers, something that even the most basic classic computers can handle effortlessly. For instance, even with the ideal application of Grover’s algorithm, quantum machines can only reduce the security parameters of hash functions like SHA-256 security from 256 to 128, which still remains effectively unbreakable. As enthusiasts await the age of quantum computers explained through groundbreaking applications, it’s crucial to ground our expectations in reality and understand the lengthy journey ahead in quantum computing advancement.
The ongoing evolution of next-generation computational systems has sparked considerable interest, especially regarding their application in cryptography and algorithm development. Often referred to as the frontier of information technology, these advanced methodologies, rooted in quantum mechanics, hold the promise of revolutionizing data security and processing speeds. Despite this immense potential, the current capabilities of these systems are still limited, casting doubt on soon-to-be-released models that promise unprecedented power. Many are excited about how these technologies might transform our cyber landscape, but practical implementation remains a challenge, undermining the sensational narratives often portrayed in the media. Therefore, understanding the intricacies surrounding these computing technologies is essential for informed dialogue on their future impact.
Understanding Quantum Computing Progress
Quantum computing is an area that has captured the imaginations of technologists and futurists alike. However, there exists a significant discrepancy between the quantum computing progress that is being achieved in research labs and the lofty expectations often portrayed in media. Many people assume that breakthroughs are just around the corner, yet experts like Shaw caution that we may be decades away from realizing the full potential of quantum computers. This hype can create misconceptions about what these machines can actually do and when we can expect those capabilities.
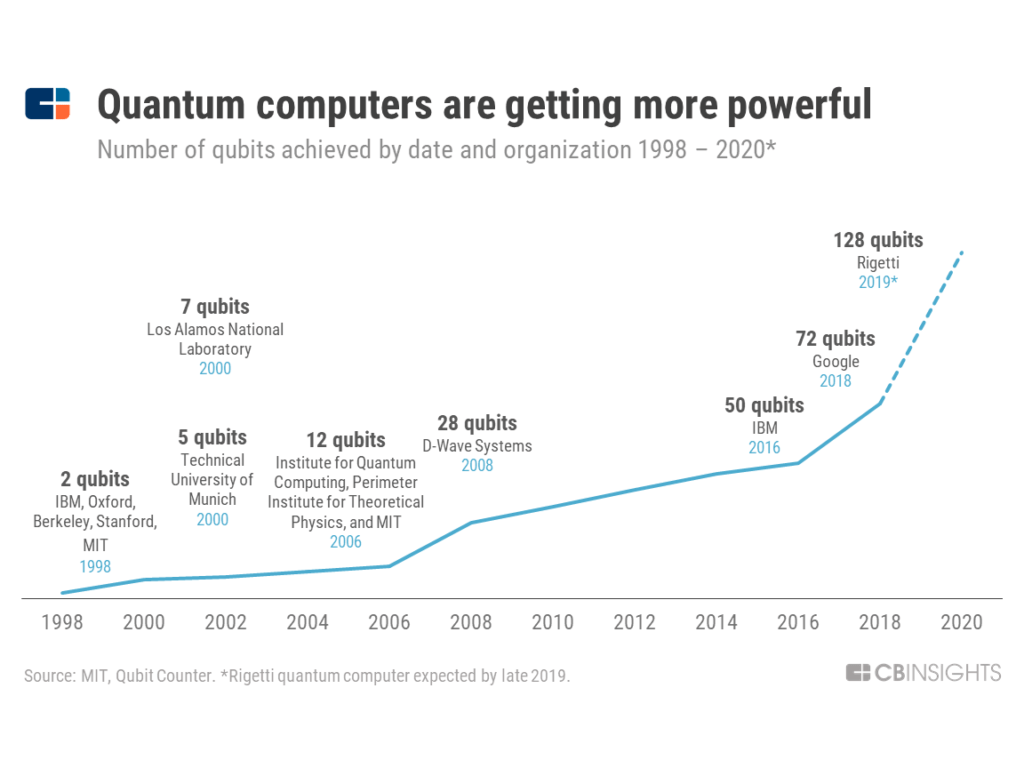
Despite substantial investments and rapid advancements in quantum algorithms, the practical applications of quantum computing remain limited at this stage. For instance, while some quantum systems are currently operational, they are far from being able to solve complex problems such as breaking cryptographic codes or performing extensive calculations in real-time network scenarios. The current quantum computers still struggle to effectively manage basic mathematical tasks like factoring simple numbers, which serves as a stark reminder of how much development is still needed before quantum capabilities can match public expectations.
Debunking the Quantum Computing Hype
The media often exaggerates the capabilities of quantum computing, leading to widespread misconceptions and elevated public expectations. The sensationalized discussions typically center around topics like quantum cryptography, hinting at a future where quantum computers can crack secure systems with ease. However, Shaw emphasized that the realities of quantum computing do not nearly live up to the hype that surrounds them. Current quantum computers are not equipped to challenge
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the current state of quantum computing progress compared to media hype?
The current state of quantum computing progress indicates a substantial gap between reality and the media hype surrounding it. While there are advancements in the field, experts like Shaw suggest that achieving the claimed capabilities of quantum computers will take 40 to 50 years. This highlights the need for realistic expectations regarding the pace and impact of quantum computing technology.
How does quantum computing affect quantum cryptography advancements?
Quantum computing progress plays a crucial role in the development of quantum cryptography. As quantum computers advance, so does the necessity for cryptographic systems that can withstand their computational power. However, current quantum algorithms like Grover’s offer only incremental improvements in breaking cryptographic functions such as SHA-256, suggesting that many existing systems remain secure against today’s quantum capabilities.
What are the implications of quantum algorithms on traditional cryptography like SHA-256?
Quantum algorithms significantly impact traditional cryptography by challenging its security frameworks. For instance, even the optimal Grover algorithm reduces the SHA-256 security from 2^256 to 2^128, which still remains unbreakable by current standards. This underlines the need to rethink cryptographic strategies in light of potential future quantum computing progress.
Can current quantum computers break Bitcoin‘s SHA-256 encryption?
Currently, quantum computers cannot effectively break Bitcoin’s SHA-256 encryption. Despite theoretical algorithms, such as those proposed by Grover, allowing for reductions in search space, the capacity to perform the repeated calculations necessary to crack Bitcoin in real-time exceeds the current capabilities of advanced quantum systems. This reinforces that concerns about breaking Bitcoin cryptography with quantum computing are largely speculative at this point.
Why is there skepticism about the rapid advancements in quantum computing?
Skepticism about rapid advancements in quantum computing arises from a disconnect between perceived media narratives and actual technological progress. Experts, including Shaw, emphasize that the current capabilities of quantum computers are limited, pointing out they cannot even perform basic operations like factoring the number 21 without prior knowledge. This indicates that claims of immediate revolutionary impacts on computing and cryptography need to be tempered with an understanding of current technological limitations.
What are the challenges faced by quantum computers in performing calculations?
Quantum computers face several challenges in performing calculations, particularly due to issues related to quantum decoherence and error rates. Currently, the most advanced machines struggle with simple tasks such as factoring small numbers without prior knowledge, indicating that they are far from achieving the formidable capabilities touted in media narratives. Understanding these limitations is crucial as we assess the true progress of quantum computing technology.
What is the significance of quantum computing progress for the future of technology?
The significance of quantum computing progress lies in its potential to revolutionize various fields, including cryptography, optimization problems, and complex simulations. However, the reality of this progress indicates that while advancements are promising, they come with expectations that must be grounded in achievable timelines. As scientists continue to explore and develop quantum computing technologies, a balanced perspective on its capabilities will be vital.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Gap in Progress | There is a significant gap between actual progress in quantum computing and the media hype. |
| Long Timeline to Functionality | Quantum computers won’t achieve claimed functions for another 40 to 50 years. |
| Limitations of Algorithms | Even the ideal Grover algorithm only reduces SHA-256 search space to 2^128. |
| Current Quantum Capabilities | Current quantum computers struggle with basic tasks, like factoring 21. |
| Challenges with Bitcoin Cracking | To crack Bitcoin, a quantum computer would need substantial speed improvements. |
| Foundation of Modern Cryptography | Modern cryptography is designed with future computational advancements in mind. |
| Lack of Factual Support for Fears | Current fears about quantum computing capabilities lack factual basis. |
Summary
Quantum computing progress has been a topic of much discussion, but it’s important to recognize the reality versus the hype. Despite ongoing advancements, we are still decades away from quantum technologies delivering on their initial promises. Current limitations highlight the challenges that need to be overcome before quantum computers can perform tasks that threaten existing cryptographic systems.