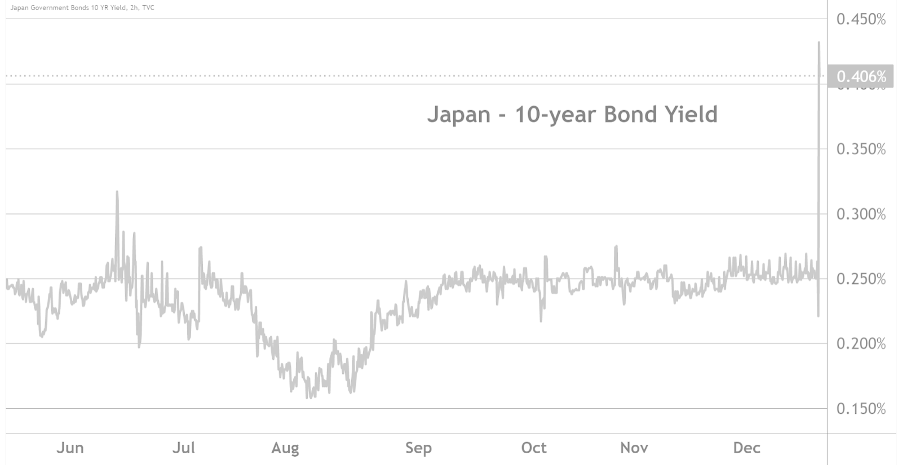
Japan government bond yields are in the spotlight as they continue to rise, reflecting significant shifts in the country’s economic landscape. Recently, the yield on Japan’s 2-year government bonds reached a notable 1%, marking its highest level since June 2008. Meanwhile, the 20-year bond yield also saw an increase, climbing by 3 basis points to 2.855%, a peak not seen since November 2020. This upward trend in yields has sparked considerable interest in the Japan bond market, prompting analysts to conduct a detailed government bonds analysis. As investors reassess their strategies, understanding the dynamics of Japanese treasury yields becomes essential for navigating this evolving financial environment.
The recent fluctuations in yields of Japan’s public debt instruments have generated a buzz among market participants. With the 2-year bonds showing a significant increase to 1%, investors are taking notice of the changing landscape surrounding government securities. The long-term outlook, represented by the 20-year bond yield rising to 2.855%, further emphasizes the evolving nature of fixed-income investment in Japan. As stakeholders engage in comprehensive evaluations of the Japan bond market, the analysis of government bonds is becoming increasingly crucial. Appreciating the implications of Japanese treasury yields can provide valuable insights into future economic trends.
Understanding Japan Government Bond Yields
In recent months, the yield on Japan’s 2-year government bonds has surged to unprecedented levels, hitting 1%—a milestone not seen since June 2008. This rise reflects a significant shift in market dynamics, influenced by various factors including changes in monetary policy and investor sentiment. The increase in short-term yields is closely monitored by analysts as it often indicates expectations for future economic growth and inflation.
Additionally, the yield on longer-term bonds, such as the 20-year government bonds, has also seen upward pressure, reaching 2.855% recently. This increment signifies a growing belief in the potential for increasing interest rates in the long term. Investors are recalibrating their strategies in light of these shifts, as changes in Japan’s bond market can have significant implications for both domestic and global economies.
The Role of Japanese Treasury Yields in the Global Market
Japanese treasury yields, particularly those of the 2-year and 20-year government bonds, play a crucial role in the global bond market. As one of the largest holders and issuers of government debt, movements in Japanese yields can influence international interest rates and investment flows. This interconnectedness highlights how domestic fiscal policies and economic conditions in Japan can impact global financial markets.
For instance, when Japan’s 2-year bond yield rises, it not only affects local investors but also attracts foreign investment while potentially leading to a reevaluation of risk in other markets. This ripple effect is essential for bondholders and policymakers alike, as they navigate their investment strategies and economic forecasts in response to shifting yields in Japan.
Analysis of Japan’s Bond Market Performance
The recent performance of Japan’s bond market, particularly the notable increase in the yields of government bonds, speaks volumes about the evolving economic landscape. Analysts observe that the rise in yields—both short and long-term—could be indicative of tighter monetary policy expectations by the Bank of Japan. This anticipation plays a significant role in shaping investor confidence and demand for bonds.
Moreover, the current trends in the Japan bond market provide a wealth of data for government bonds analysis. By examining the variances in yields, investors can better gauge market sentiment and economic forecasts. Understanding these shifts provides insight into the health of the economy, as rising yields may suggest a recovery, prompting investors to reassess their portfolios and expectations for future returns on government securities.
Key Factors Influencing Yields on 2-Year and 20-Year Bonds
Several key factors influence the yields on Japan’s 2-year and 20-year bonds, prominently monetary policy, inflation trends, and investor behavior. As the Bank of Japan communicates its policy intentions, market responsiveness becomes evident, showing a correlation between its announcements and yield movements. Investors closely monitor these policies to predict shifts in the bond landscape.
Additionally, inflation expectations play a pivotal role in determining the appetite for government bonds. If inflation is anticipated to rise, yields on government securities typically increase, reflecting the need for higher returns to compensate for potential erosion of purchasing power. Therefore, understanding these intertwined factors is crucial for investors navigating Japan’s complex bond market.
Impact of Rising Interest Rates on Government Bonds
The rising interest rates seen in Japan’s bond markets are having profound implications for government bonds. As yields climb, the cost of borrowing increases, affecting various sectors of the economy. For investors, this scenario presents challenging decisions, as higher yields may result in depreciation of existing bond holdings, influencing strategies around investment and risk management.
Furthermore, future interest rate hikes could lead to enhanced volatility in the bond market. With the yields on government bonds like the newly elevated 2-year and 20-year securities fluctuating, traders must adapt their strategies to mitigate risks. Analyzing these trends is essential for both institutional and retail investors, as they seek to optimize returns amid shifting economic conditions.
Investment Opportunities in Japanese Bonds
In light of the rising yields on instruments like the 2-year and 20-year government bonds, investors are re-evaluating their portfolios to capitalize on potential investment opportunities available through Japanese bonds. Higher yields often attract a diverse range of investors looking for fixed-income securities that offer better returns compared to lower-yielding assets elsewhere.
Moreover, the shift in the bond market can create unique investment prospects in sectors connected to the bond economy. Yield fluctuations signal broader economic trends, resulting in opportunities for savvy investors to position themselves advantageously by exploring different maturities and bond types. This strategic reallocation can help maximize gains amid market uncertainties.
Forecasting Future Trends in Government Bond Yields
Forecasting future trends in Japan’s government bond yields requires a multi-faceted approach that considers both domestic and global economic indicators. As yields continue to rise, analysts are keenly observing the Bank of Japan’s monetary policy moves and how these may react to global economic developments. Expectations for inflation, economic recovery, and geopolitical events all factor into the complex yield forecast equations.
Additionally, investor sentiment plays a vital role in predicting future trends. With rising yields on the 2-year and 20-year bond, analysts speculate that continued demand for Japanese government bonds may shift towards short-term securities as investors balance risk and return. Monitoring these dynamic behaviors provides crucial insights into future market directions.
The Shift from Short-Term to Long-Term Yields
The ongoing increase in the yields on both short-term (like the 2-year bond yield) and long-term (like the 20-year bond yield) government bonds suggests a strategic shift currently occurring within Japan’s bond market. Investors are gradually moving their focus from shorter maturities to longer-term securities, driven by expectations of sustained economic growth and potential inflationary pressures.
This evolving trend highlights the necessity for investors to evaluate their strategies cautiously. While short-term bonds may offer immediate returns, the attractiveness of long-term securities is heightened due to the potential for accumulating better yields over time. Understanding this shift helps investors navigate their decisions effectively amidst economic fluctuations.
Government Bonds Analysis in Changing Economic Conditions
The current environment of rising interest rates compels an in-depth government bonds analysis, particularly within the context of Japan’s government securities. Analysts must meticulously assess how the 2-year and 20-year bond yields will respond to shifting economic circumstances—such as fluctuations in inflation rates and changes in monetary policy.
A comprehensive analysis will also need to address the challenges faced by investors holding existing bonds as yields rise. Strategies may include diversifying portfolios or considering shorter-duration investments to minimize exposure to widening yield spreads. Keeping abreast of economic indicators will be crucial for making informed decisions in the bond market moving forward.
Frequently Asked Questions
What factors influence Japan government bond yields, particularly the 2-year bond yield Japan?
The yields on Japan’s government bonds, including the 2-year bond yield Japan, are influenced by various factors such as domestic monetary policy, inflation expectations, and global economic conditions. Recent data indicates a rise in the 2-year bond yield to 1%, highlighting investor sentiment and possible shifts in the Bank of Japan’s monetary policy.
How does the 20-year bond yield in Japan impact the overall Japan bond market?
The 20-year bond yield, which recently increased to 2.855%, plays a significant role in the Japan bond market by influencing long-term borrowing costs and investor expectations. It reflects market perceptions about future interest rates and economic growth, thereby affecting the pricing of other government bonds and financial instruments.
What is the current trend in Japanese treasury yields and what does it indicate?
Recent trends indicate an upward movement in Japanese treasury yields, including the notable rise in the 2-year and 20-year bond yields. This trend suggests a potential shift in economic outlook, with investors bracing for inflation or changes in monetary policy, which could lead to higher borrowing costs and impacts on the government bond market.
How can I analyze government bonds analysis in relation to Japan’s economic landscape?
Government bonds analysis in Japan involves examining yields, monetary policy changes, and economic indicators such as GDP growth and inflation. Analyzing these aspects helps investors understand the risk-return profile of Japan government bonds and the implications for the broader economy, especially given the recent rise in the 2-year and 20-year bonds.
What are the implications of rising Japan government bond yields for investors?
Rising Japan government bond yields, especially for the 2-year and 20-year bonds, signal changing market conditions that investors should consider. Higher yields often indicate increased borrowing costs and may impact funding for businesses and consumers, potentially influencing overall economic activity in Japan.
| Bond Type | Current Yield | Change | Previous High |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2-Year Government Bonds | 1% | Highest since June 2008 | June 2008 |
| 20-Year Government Bonds | 2.855% | +3 basis points | November 2020 |
Summary
Japan government bond yields have recently seen significant increases, with the 2-year bond yield rising to 1%, the highest level since June 2008. This surge reflects market adjustments and economic indicators influencing government bond rates, while the 20-year bond yield also rose to 2.855%, a new high since November 2020. The trends in Japan government bond yields indicate shifts in investor sentiment and projections about future economic activity.
Related: More from Market Analysis | Related Box Test | Crypto Worries Over Iranian Oil Supply: Is It Overhyped? in Crypto Market