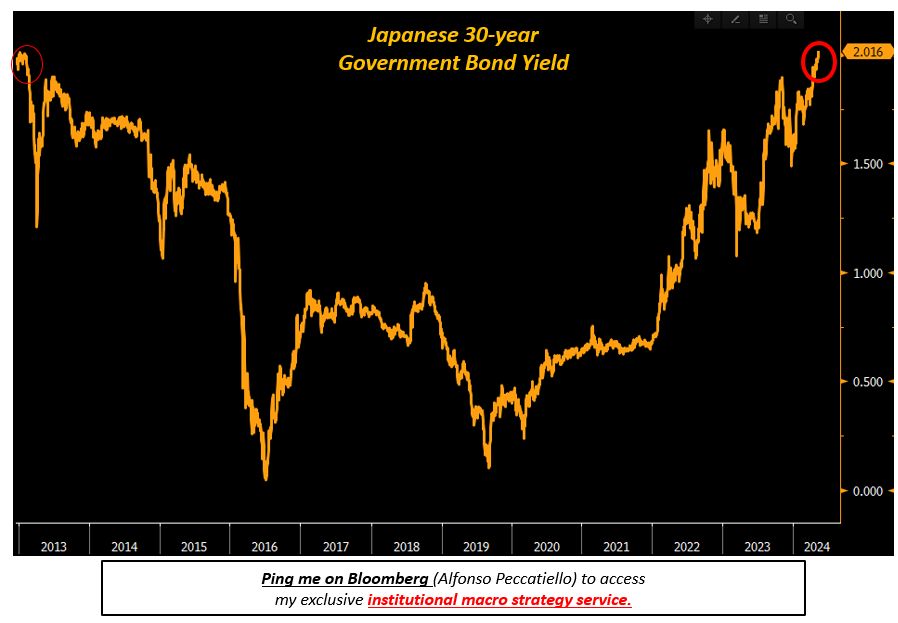
Japan government bond yields have recently surged to 1.965%, marking the highest level since June 2007 and bringing attention to the dynamics of the Japan bond market. As investors closely monitor the Bank of Japan’s monetary policy, this yield increase highlights rising expectations surrounding inflation and economic growth in the region. The sentiment surrounding government debt Japan plays a critical role in shaping these yields, prompting experts to analyze the implications for both domestic and international investors. This shift reflects a broader trend in the global economy, where rising interest rates are becoming increasingly prevalent. Consequently, the fluctuations in Japan’s bond yields serve as a significant indicator of the market’s health and future monetary policy expectations.
The recent uptick in Japan’s bond yields signals a pivotal moment in the nation’s fiscal landscape, particularly concerning the substantial interest in its 10-year government bonds. As the Bank of Japan re-evaluates its strategies in the face of economic recovery and potential inflationary pressures, analysts are paying keen attention to the implications for investors. The increase in government bond yields not only impacts the yield curve but also illuminates the overarching narrative surrounding Japan’s financial stability. Understanding the nuances of government debt in Japan is crucial, as these trends could influence everything from individual investment strategies to macroeconomic policies. With the evolving financial climate, the significance of Japan’s bond market is poised to grow, warranting further exploration into its economic ramifications.
Current Trends in Japan Government Bond Yields
The yield on Japan’s 10-year government bonds has recently surged to 1.965%, marking a pivotal moment in the Japan bond market. This rise is the highest seen since June 2007, reflecting heightened investor sentiment about both inflation and economic prospects. In the face of increasing yield trends, analysts are closely monitoring how this could influence the broader financial landscape within Japan, particularly as it pertains to investor strategies.
This uptick in bond yields is indicative of a significant shift in market perception, especially regarding the Bank of Japan’s monetary policy. As expectations grow for adjustments to interest rates, the bond market reacts accordingly, leading to increased volatility. Investors are now more focused on potential ramifications for government debt Japan, interpreting these yield movements as either threats or opportunities, depending on their long-term forecasts.
Impact of Bank of Japan’s Monetary Policy on Bond Yields
The Bank of Japan’s monetary policy plays a crucial role in shaping the landscape of government bond yields. With the recent rise in yields on Japan’s 10-year government bonds, speculation is rife regarding how the bank might adjust its current strategies in response to market shifts. As the nation grapples with inflationary pressures and a recovering economy, observers are eager to see if the BoJ will pivot from its historically low interest rates.
Furthermore, the financial implications of the Bank of Japan’s actions extend beyond the immediate effects on bond yields. An increase in government bond yields not only indicates a response to economic conditions but also affects overall government debt Japan strategies. The potential for a more aggressive stance from the Bank could mean higher borrowing costs for the government, influencing fiscal policy decisions going forward.
Analyzing the Implications of Rising Japan Bond Yields
The notable rise in Japan bond yield, particularly the 10-year government bonds, signals increasing confidence among investors regarding the future of Japan’s economy. As yields approach levels not seen in over a decade, market analysts suggest that this trend could lead to a reassessment of government debt strategies and fiscal measures. The implications are profound, potentially steering Japan towards a fiscal path that could incorporate more spending to bolster growth.
Simultaneously, elevated bond yields attract foreign investors, a factor that could foster greater interest in Japan’s financial markets. This influx can contribute to a stability narrative for the Japan bond market, as international stakeholders seek to navigate a complex global economy. However, with the backdrop of uncertainty, the sustainability of this yield increase remains a discussion point for economists.
Inflation Expectations and Their Influence on Japan’s Bond Market
As inflation expectations rise, so too do the yields on Japan’s 10-year government bonds, illuminating a direct correlation between the two factors. Investors are increasingly wagering that rising costs will compel the Bank of Japan to adjust its ultra-loose monetary policy. Such anticipations have historically driven yields upward, as higher inflation often results in increased interest rates.
The current inflationary environment suggests that the Bank of Japan may need to reconsider its approach to monetary easing. With bond yields reflecting market sentiments on future inflation, this becomes a critical point for stakeholders within the Japan bond market. Navigating inflation expectations becomes paramount, especially as it translates directly into the government’s cost of borrowing and its broader economic strategies.
Government Debt Considerations in Light of Bond Yield Increases
The surge in Japan government bond yields underscores the urgent need for discussions around government debt management. As yields rise, the cost of servicing existing debt also becomes a pressing issue for policymakers. The potential increase in borrowing costs necessitates a reevaluation of strategies aimed at maintaining fiscal sustainability without stifling growth.
Moreover, with the uncertainty in the global economy and the rising yields, Japan’s government must tread carefully to manage public finances. Prolonged periods of elevated yields could adversely affect Japan’s ability to finance its debt comfortably, pushing the government to explore innovative fiscal policies or adjustments to existing frameworks. This dynamic will be a focal point as stakeholders assess the viability of Japan’s fiscal future.
The Relationship Between Economic Recovery and Bond Yields
The ongoing economic recovery in Japan plays a vital role in the context of rising bond yields. As the economy shows signs of improvement, investors are more inclined to expect that the Bank of Japan will adjust its policies to combat potential inflation. Consequently, the relationship between economic health and Japan bond yields becomes significant, highlighting the interplay of market predictions and government measures.
Additionally, this recovery sparks debates on how robust it truly is and its sustainability in the face of mounting inflation pressures. A more resilient economy may support higher bond yields, signaling investor confidence, but it also raises questions about the longevity of growth projections. The Government must ensure that while fostering economic recovery, it does not overlook the implications of rising bond yields on fiscal policy.
Foreign Investment Dynamics in Japan’s Bond Market
Recent trends suggest that an increase in Japan bond yields has begun to attract more foreign investment within the nation’s bond market. As yields rise, international investors view Japanese government bonds as more appealing compared to other alternatives, especially in a low-interest-rate environment globally. This dynamic could facilitate increased liquidity within Japan’s financial system, contributing to greater economic stability.
However, this influx of foreign capital also presents challenges, particularly regarding exchange rate fluctuations and potential volatility. The government and the Bank of Japan must consider how foreign investment dynamics will shape the market, especially as bond yields rise. Ensuring that Japan remains an attractive destination for foreign investors requires careful navigation of these economic undercurrents.
Long-term Predictions for Japan’s Bond Market
With the current trajectory of Japan bond yields, long-term predictions about the bond market are becoming increasingly critical. While some analysts forecast further yield increases due to anticipated changes in monetary policy, others caution that unsustainable growth might lead to market corrections. The complexity of these predictions is compounded by global economic conditions, which directly influence investor sentiment.
Regardless of the uncertainty, the need for acute awareness in the bond market remains paramount. Investors must evaluate long-term strategies to align with macroeconomic trends, while regulators must ensure that the market remains stable against potential downturns in yield. As such, the future of Japan’s bond market hinges on a delicate balance between growth, inflation management, and fiscal discipline.
The Role of Japan’s Economic Indicators in Yield Fluctuations
Japan’s economic indicators serve as significant determinants of government bond yield fluctuations. Recent data signaling economic recovery has coincided with rising yields, substantiating the link between macroeconomic performance and bond market reactions. These indicators not only guide government policy but also shape investor expectations, thereby impacting the overall climate of Japan’s bond market.
Monitoring such indicators—like GDP growth rate, unemployment levels, and inflation metrics—is crucial for developing a nuanced understanding of yield movements. As Japan navigates recovery amidst a volatile global economy, these economic indicators will become increasingly vital in shaping investors’ confidence and expectations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What factors are contributing to the increase in Japan government bond yields?
The increase in Japan government bond yields, particularly the yield on 10-year government bonds Japan, is primarily driven by market expectations for the Bank of Japan’s future monetary policy. Investors are anticipating rising inflation and potential economic recovery, which are influencing the uptick in yields.
How does the Bank of Japan’s monetary policy affect Japan bond market yields?
The Bank of Japan’s monetary policy plays a critical role in influencing Japan bond market yields. Changes in policy, including interest rate adjustments or quantitative easing measures, can lead to fluctuations in government bond yields, such as the recent rise in the yield of 10-year government bonds Japan.
Why is the latest rise in Japan government bond yields significant for investors?
The recent rise in Japan government bond yields to 1.965%, the highest since June 2007, is significant for investors as it signals heightened expectations of inflation and economic improvement. This trend indicates potential risks and returns associated with investing in the Japan bond market.
What does the increase in Japan’s government bond yields indicate about government debt?
The increase in Japan’s government bond yields suggests a growing concern regarding government debt sustainability and reflects investor sentiment about Japan’s economic outlook. Rising yields can indicate a perceived risk in holding Japan’s government debt, impacting future borrowing costs for the government.
How might global economic factors influence Japan bond yield trends?
Global economic factors, including inflation rates and central bank policies from other countries, can significantly influence Japan bond yield trends. The interconnectedness of global markets means that investor sentiment abroad can impact the Japan government bond market and yields.
What should investors consider when monitoring Japan government bond yields?
Investors should consider various factors, such as the Bank of Japan’s monetary policy changes, economic indicators, and global market conditions, when monitoring Japan government bond yields. Understanding these elements can provide insights into potential investment opportunities in the Japan bond market.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Current Yield | 1.965%, highest since June 2007. |
| Market Expectations | Expectations for Bank of Japan’s monetary policy are rising. |
| Investor Sentiment | Reflects expectations of rising inflation and economic recovery. |
| Significance | Indicates the condition of Japan’s government debt amidst global economic uncertainties. |
Summary
Japan government bond yields are a crucial indicator of economic health, and the recent rise to 1.965% is significant. This increase signals heightened expectations for inflation and economic recovery, alongside intensifying market expectations for the Bank of Japan’s monetary policy. As global economic conditions remain uncertain, monitoring Japan’s government bond yields will be vital for investors and policymakers alike.