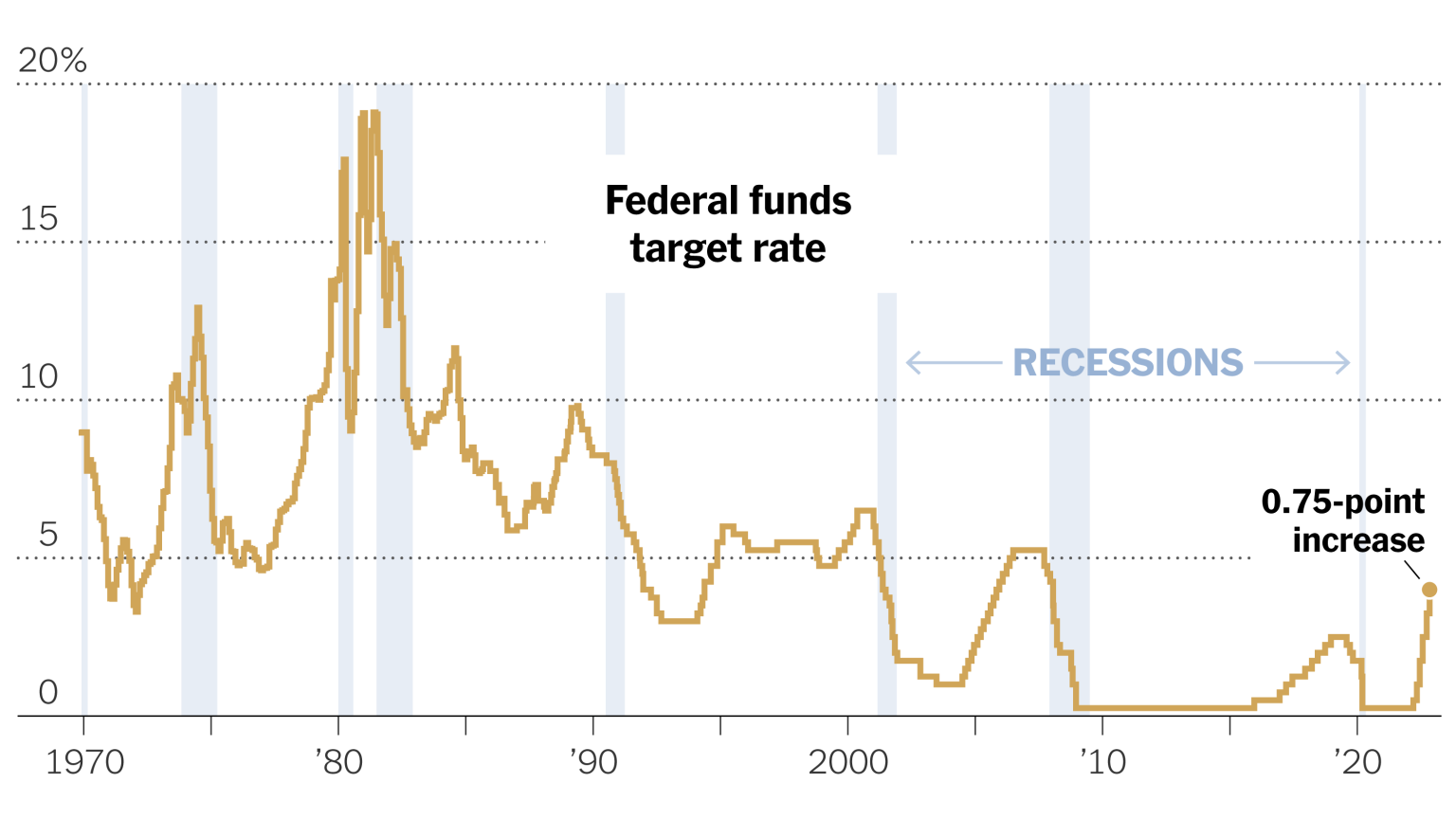
Federal Reserve interest rates play a crucial role in shaping economic dynamics in the United States. In recent comments, Philadelphia Federal Reserve President Paulson suggested that if inflation cools as predicted, the Federal Reserve might consider further interest rate cuts. This insight underscores the delicate balance that the Fed maintains in responding to economic indicators, especially in terms of inflation and growth. The latest Federal Reserve news reveals cautious optimism regarding inflation cooling predictions, paving the way for potential economic policy adjustments later this year. As the market awaits clarity on these developments, the implications of interest rate cuts loom large for consumers and investors alike.
In navigating the complexities of U.S. monetary policy, the adjustments to the Federal Reserve’s benchmark rates are pivotal. Recent evaluations echoed by officials like Paulson indicate that a decrease in inflation may enable the central bank to modify its current interest rates downward. This discussion aligns with broader economic forecasts and sentiments surrounding inflation stabilization and its effects on financial markets. The ongoing interplay of labor market signals and inflation rates highlights the intricacies involved in forming a robust economic strategy. As policymakers deliberate, the potential for rate adjustments remains at the forefront of economic discussions.
Understanding Federal Reserve Interest Rate Cuts
The Federal Reserve’s interest rates play a crucial role in shaping the economic landscape in the United States. Interest rate cuts are typically implemented to stimulate the economy by making borrowing cheaper for consumers and businesses. In recent discussions, Federal Reserve President Paulson has indicated that if inflation cools, there is a possibility of further reductions in rates. This is a pivotal moment as it reflects an understanding of the delicate balance the Fed must maintain between fostering economic growth and managing inflationary pressures.
It is important for investors and policymakers to stay updated on Federal Reserve news, particularly regarding interest rate adjustments. Market reactions to any announcements can significantly sway economic indicators. When interest rates are lowered, it can lead to increased spending and investment, which can help maintain economic momentum. However, the timing of these cuts is critical, as premature reductions may lead to overheating the economy, while delayed cuts might stifle growth.
Paulson’s Predictions for Inflation and Economic Policy Adjustments
Paulson’s recent comments about the potential for inflation cooling has sparked discussions about necessary economic policy adjustments. With inflation at the forefront of economic concerns, the Fed is weighing the implications of its current monetary policy. If inflation shows signs of lowering, it may allow the Fed to implement more aggressive interest rate cuts, potentially leading to a more favorable environment for consumers and businesses alike. Market players are keenly watching these developments as they shape their strategies for investment and resource allocation.
As the Federal Reserve navigates through these mixed signals regarding the economy, Paulson’s cautious optimism underscores the need for data-driven decisions. While the potential for inflation cooling provides a glimmer of hope, it also necessitates careful monitoring of the economic situation to avoid unintended consequences from policy adjustments. This delicate interplay reflects the complexities of modern economic management and the vital role the Federal Reserve plays in maintaining stability.
The Impact of Inflation Cooling on Federal Reserve Policy
The prospect of inflation cooling may have significant implications for the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy direction. If inflation rates start to decline, it gives the Fed more flexibility to consider interest rate cuts, which could stimulate economic activity. However, Paulson has reiterated that further cuts will not be immediate, emphasizing a cautious approach to avoid destabilizing the economy. This aligns with the Fed’s broader strategy of gradual adjustments based on concrete economic indicators rather than speculative forecasts.
Moreover, the potential for economic policy adjustments in light of cooling inflation underscores the intricacies of managing price stability and economic growth. A calm inflation environment can bolster consumer confidence and encourage spending, which is critical for recovery. The Federal Reserve must balance the need for stimulating the economy while maintaining a vigilant stance against the risk of inflation resurgence, showcasing the complexities of their decision-making process.
Market Reactions to Federal Reserve Announcements
Financial markets are highly responsive to news from the Federal Reserve, particularly regarding interest rates and inflation outlooks. Investors closely analyze any statements from notable figures like Paulson to gauge the future path of monetary policy. Anticipation of interest rate cuts can lead to market rallies, while uncertainty can result in volatility. Understanding how the market reacts to Federal Reserve announcements is essential for investors seeking to make informed decisions in an ever-evolving economic landscape.
Given the recent discussions around potential interest rate cuts due to easing inflation, market analysts are closely monitoring the collective sentiment and trends. If the Fed commits to a cut during an economic upswing, it could validate current market optimism and enhance asset valuations. Conversely, if inflation remains stubborn, that could lead to a tightening of monetary policy, prompting investors to shift their strategies accordingly. Staying attuned to these dynamics can offer investors the predictive advantage they need.
The Significance of Labor Market Indicators in Monetary Policy
The labor market serves as a vital indicator for the Federal Reserve when assessing economic health and making monetary policy decisions. Paulson mentioned the mixed signals within the labor market, highlighting that while there are pressures, it is not in a state of collapse. Such insights inform the Fed’s approach to adjusting interest rates, as a strong labor market typically correlates with inflationary pressures. Therefore, economists must carefully analyze these labor trends when predicting the Fed’s potential actions.
Moreover, the connection between labor market conditions and inflation cannot be overstated. If unemployment remains low and wage growth accelerates, inflation could rise, prompting the Fed to reconsider its stance on interest rates. Thus, understanding labor market indicators not only provides a glimpse into the current economic climate but also assists in forecasting necessary policy adjustments by the Federal Reserve. This interconnectedness is critical for stakeholders examining the future landscape of economic policy.
Economic Policy Adjustments in Response to Inflation
Economic policy adjustments are often a response to shifts in inflation rates. As Paulson indicated, if inflation cools, the Federal Reserve may contemplate appropriate changes in the federal funds rate. This proactive approach is essential for maintaining economic stability, ensuring that monetary policy remains responsive to inflationary trends. If adjustments are made effectively, they can stimulate economic growth without introducing new inflationary pressures.
In addition, policy adjustments might also involve more than just interest rate cuts; they can include other tools such as quantitative easing or tightening measures. The overall goal of these adjustments is to create a conducive environment for growth while managing inflation expectations. As such, the Fed’s strategy must remain flexible and adaptable in response to economic indicators, including inflation cooling predictions, to safeguard against economic fluctuations.
Long-term Outlook for Federal Reserve Policy
The long-term outlook for Federal Reserve policy is closely tied to inflation dynamics and overall economic health. As rates are a primary tool for managing inflation, any indications of easing inflation can reshape the Fed’s strategic framework. Paulson’s insights suggest that a careful approach will govern the Fed’s decision to lower rates, considering both short-term and long-term economic projections.
Market participants are particularly interested in how the Federal Reserve’s interest rate policy will evolve over the coming years. If inflation continues to show signs of cooling, investors may anticipate a series of gradual cuts, fostering an optimistic economic environment. However, the potential for unexpected inflationary pressures necessitates ongoing vigilance and adaptability from the Federal Reserve, ensuring that the long-term economic stability is prioritized.
Investor Strategies Amidst Rate Uncertainty
In an environment of uncertain interest rates, investor strategies need to be dynamic and adaptable. With recent discussions surrounding potential interest rate cuts based on Paulson’s insights, investors are advised to reassess their portfolios. Depending on their risk tolerance, some may choose to capitalize on lower borrowing costs by increasing investments in growth-oriented sectors, while others might opt for more conservative strategies.
Moreover, staying informed about Federal Reserve news is critical for making timely adjustments to investment strategies. As inflation figures evolve and economic indicators fluctuate, having a solid understanding of the underlying factors at play can give investors a competitive edge. Therefore, a proactive approach in monitoring key developments—like interest rate cuts or inflation trends—can help them navigate the complexities of the current economic landscape effectively.
Future Implications of Federal Reserve Decisions
The future implications of Federal Reserve decisions on interest rates can have widespread effects on both domestic and global economies. As Paulson suggests, should inflation cool, the Fed may consider rate cuts that could affect consumer spending, business growth, and investment patterns. Understanding these potential implications is crucial for businesses strategizing for future growth in relation to economic conditions set by the Fed.
Additionally, changes in Federal Reserve interest rates can lead to fluctuations in foreign exchange markets and global trade dynamics. As interest rates lower, capital may flow into emerging markets, altering the competitive landscape across various regions. Therefore, assessing the long-term consequences of Federal Reserve decisions will be vital for global investors and policymakers, enabling them to make informed forecasts and adapt to the evolving economic climate.
Frequently Asked Questions
What insights did Paulson share about future Federal Reserve interest rates?
In her recent speech, Philadelphia Federal Reserve President Paulson indicated that further Federal Reserve interest rate cuts could be possible if inflation cools and the economy remains stable. She emphasized that while the current interest rate range of 3.5% to 3.75% is tight enough to help control inflation, any adjustments may not be immediate.
How could inflation cooling affect Federal Reserve interest rates?
If inflation cools, as per Paulson’s comments, the Federal Reserve interest rates may be lowered further. This is contingent on continued economic stability and the health of the labor market, which are essential for implementing any rate cuts.
What does Paulson mean by ‘slightly tight’ in relation to Federal Reserve interest rates?
Paulson described the existing target interest rate range as ‘slightly tight,’ which implies that while it effectively curtails inflation, it still allows for the potential of further adjustments in the Federal Reserve interest rates if market conditions improve.
Why is the Federal Reserve considering potential interest rate cuts?
The Federal Reserve is contemplating potential interest rate cuts as a response to mixed signals in the economy. If inflation eases and economic conditions show positive signs, further adjustments to Federal Reserve interest rates could be deemed appropriate.
What factors are influencing Paulson’s outlook on Federal Reserve interest rate adjustments?
Paulson’s outlook on Federal Reserve interest rate adjustments is primarily influenced by inflation trends, economic stability, and the labor market’s health. She is closely monitoring these elements before supporting any further economic policy adjustments.
When might the Federal Reserve implement additional interest rate cuts?
While Paulson expressed optimism about potential interest rate cuts, she cautioned that such decisions would not occur immediately. The timing will depend on observing further data related to inflation and overall economic performance.
How does Paulson view the current economic environment regarding interest rate policy?
Paulson conveyed a cautious optimism in her assessment of the current economic environment, noting that while the economy faces pressures, it is not collapsing, which leaves room for thoughtful economic policy adjustments by the Federal Reserve.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Federal Reserve Interest Rates | Philadelphia Fed President Paulson stated that if inflation decreases, the Federal Reserve may lower interest rates further. |
| Current Rate Range | The current target interest rate range is 3.5% to 3.75%, which Paulson finds ‘slightly tight’. |
| Future Rate Cuts | Further rate cuts may occur if inflation eases, but they might not happen immediately. |
| Economic Indicators | Paulson noted ‘mixed signals’ from the labor market, indicating a cautious outlook. |
| Additional Evidence | She wants more data on the economy before supporting further policy adjustments. |
Summary
Federal Reserve interest rates are poised for potential adjustments as outlined by President Paulson. If inflation starts to cool, there may be opportunities for the Federal Reserve to reduce these rates further. However, Paulson emphasizes the need for caution and thorough evaluation of economic indicators before making any decisions. As the economic landscape evolves, close attention will be paid to inflation trends and labor market signals, guiding future monetary policy directions.