The recent adjustments to the Ethereum blob limit mark a significant step towards enhancing Ethereum scalability. Developers have raised the blob limit for the second time in just weeks, facilitating a greater capacity for transaction batching through advanced rollup technology. This improvement is part of a broader initiative following the recent BPO hard fork aimed at reducing gas fees stability while accommodating more data in each block. With this upgrade, the blob target has also increased, allowing Ethereum to effectively manage higher transaction volumes. As the Ethereum ecosystem continues to evolve, these enhancements are crucial for promoting efficient and cost-effective transactions.
In the rapidly evolving landscape of blockchain, the term “Ethereum blob limit” refers to the maximum capacity for data transactions that can be processed in a single block. This limit is critical for improving the overall scalability of the Ethereum network by enabling transaction batching and reducing network congestion. Known formally as the BPO hard fork, this update brings forth substantial changes to Ethereum’s infrastructure, ensuring that as demand grows, the system can handle increased loads effectively. Additionally, advancements in rollup technology play a vital role in compressing transactions, thereby stabilizing gas fees and promoting seamless operations across the Ethereum protocol. Essentially, this blob capacity expansion represents a pivotal move towards enhancing user experience and operational efficiency on the Ethereum blockchain.
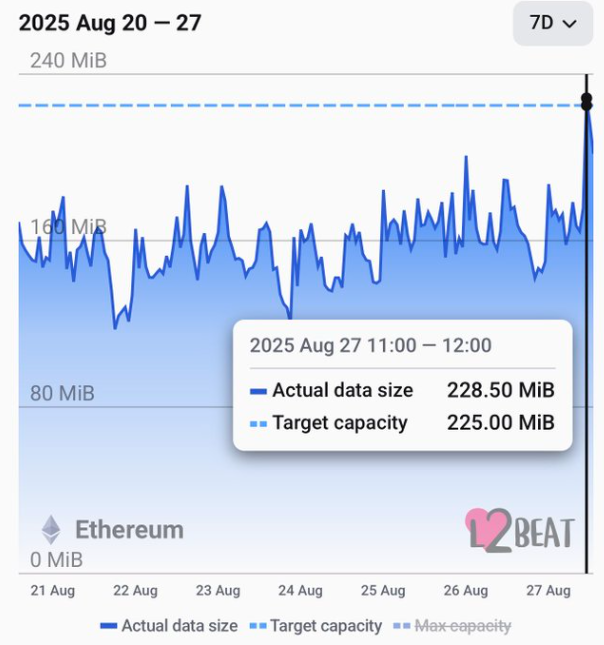
Understanding Ethereum’s Blob Limit Enhancements
The recent increase in Ethereum’s blob limit from 15 to 21 is a significant step towards improving scalability within the Ethereum network. This upgrade, which occurred during the second Blob Parameter-Only (BPO) hard fork, allows for a greater volume of transactions to be batched through rollups. By accommodating larger data packages in each blob, Ethereum is setting the stage for a more efficient transaction system that can handle increased demand without compromising on speed or reliability.
As Ethereum seeks to optimize its scalability, understanding the implications of the blob limit is crucial. Each blob now holds 128 kilobytes of data, enabling a total of up to 2,688 KB to be stored in a single block. This enhancement is not merely about throughput; it also influences gas fees stability by helping to mitigate network congestion. Ultimately, these changes strive to fortify the performance of Ethereum as it evolves.
The Impact of the BPO Hard Fork on Transaction Batching
The implementation of the BPO hard fork on December 9, 2025, marked a pivotal moment in Ethereum’s approach to transaction batching. This upgrade allows developers to group multiple transactions into a single batch, significantly improving efficiency. The latest additions, particularly the raise in blob targets from 10 to 14, indicate a focused effort to enhance data processing and transaction logistics within this decentralized network.
This batching capability is synonymous with the rollup technology, which plays a vital role in ensuring that Ethereum can manage a higher transaction load without exhibiting signs of strain or excessive delays. As the network continues to adopt rollups more extensively thanks to these hard forks, it sets a foundation for ensuring that gas fees remain stable and manageable for users, thereby maintaining trust and usability within the Ethereum ecosystem.
Enhancing Ethereum Scalability Through Future Forks
Looking ahead, Ethereum has ambitious plans for future scalability upgrades, particularly with the anticipated Glamsterdam hard fork. Expected to be implemented in 2026, this upgrade is projected to increase the gas limit significantly from 60 million up to 200 million. Such a move would not only enhance transaction throughput but also provide developers with increased flexibility to deploy more complex smart contracts seamlessly.
The anticipated introduction of ‘perfect parallel processing’ is a game-changer for Ethereum’s transaction capabilities. This fundamental improvement is made possible through Ethereum Improvement Proposal-7928, which aims to facilitate multi-lane transaction processing. By transitioning from a single-lane highway of transaction processing to a more multi-lane structure, Ethereum will greatly reduce bottlenecks and enhance overall throughput.
Rollback Technology: The Backbone of Ethereum’s Scalability
Rollup technology has emerged as a cornerstone for improving the scalability of the Ethereum network. By batching transactions and processing them off-chain, rollups dramatically decrease the computational burden on individual nodes. As the second BPO hard fork widens the blob limits, the efficiency of rollups becomes increasingly vital to sustaining low gas fees and enhanced transaction speeds.
The capacity to process a higher volume of transactions through rollups directly correlates to the network’s overall health. As more users flock to Ethereum and engage with decentralized applications, the presiding efficiency offered by rollups ensures that Ethereum can accommodate this surge without succumbing to the sluggishness often associated with growing networks. This scalability path is essential for maintaining Ethereum’s position as a leading player in the decentralized finance space.
Gas Fees Stability Post-Hard Fork: What It Means for Users
Following the first and second BPO hard forks, there has been a notable stabilization in gas fees on the Ethereum mainnet. Data from YCharts illustrates how these recent upgrades have contributed to reduced network congestion, resulting in more predictable and manageable transaction fees for users. The increased blob limit means that Ethereum has more leeway to handle transactions during peak times without resorting to exorbitant fees.
For users, this stability in gas fees translates to a more user-friendly experience when interacting with the Ethereum network. Whether sending ETH, executing smart contracts, or using decentralized applications, the reduced variability in costs bolsters consumer confidence, attracting a broader audience to the Ethereum ecosystem. It is crucial for the long-term viability of decentralized finance that Ethereum continues to address these challenges in gas costs.
Future Considerations for Ethereum’s Gas Limit Regulations
The discussion surrounding the potential raise of Ethereum’s gas limit from 60 million to 80 million highlights the proactive measures that developers are considering for future scalability. By allowing more transactions and smart contract executions within each block, Ethereum is not only improving its efficiency but also providing a framework that can adapt to rising demands. Such foresight is crucial as Ethereum positions itself to accommodate increasing user engagement and transaction complexity in the coming years.
Moreover, the prospect of increasing the gas limit further with upcoming forks like Glamsterdam demonstrates the commitment to enhancing transaction capabilities. The multi-lane processing changes proposed will enhance the overall efficiency, making it imperative for the community to track these developments closely. Each increment in gas limit pushes the envelope for what Ethereum might achieve, lending credence to its future as a robust platform for digital transactions.
Analyzing the Ripple Effects of Ethereum’s Scalability Upgrades
Every upgrade in Ethereum’s blob capacity and gas limit has profound ripple effects across the entire blockchain ecosystem. Stakeholders, from developers to end-users, will notice immediate changes in transaction speeds, fee structures, and the general efficiency of the network. These enhancements not only streamline operational capabilities but also position Ethereum as a prime choice for decentralized applications and financial transactions, especially as competition escalates across blockchain platforms.
As Ethereum continues to scale and optimize transaction protocols, its capability to integrate with innovative solutions like rollups will define its success. The focus on maintaining low gas fees and enabling quick transactions will attract larger user bases and foster wider adoption of decentralized finance products. The ongoing dialogue around Ethereum’s scalability reflects an eagerness within the community to enhance and enrich the user experience, ensuring that Ethereum remains at the forefront of blockchain technology.
Ethereum’s Commitment to Long-Term Scalability Solutions
Ethereum’s drive toward long-term scalability is underscored by its consistent evolution through timely hard forks. These structural updates are critical to aligning with a burgeoning user base and accommodating the rising number of transactions in a rapidly changing digital landscape. As seen with the latest blob limit adjustments and gas fee management efforts, Ethereum is strategically positioning itself to meet future demands head-on.
The roadmap sketched out with enhancements from the BPO hard fork to future proposals like those in Glamsterdam showcases a carefully orchestrated plan to address both short-term limitations and long-term growth needs. This tenacity in pursuing scalability solutions is a testament to Ethereum’s understanding of the market dynamics and its obligation to provide a sustainable and efficient blockchain experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of the Ethereum blob limit increase?
The recent increase in the Ethereum blob limit from 15 to 21 blobs significantly enhances the network’s scalability, allowing for more transactions to be batched through rollup technology. This change reduces costs and improves the efficiency of transactions on the Ethereum blockchain.
How does the blob limit affect Ethereum transaction batching?
With the Ethereum blob limit raised, more transactions can now be batched together using rollups, which leads to improved Ethereum scalability. This batching capacity helps lower gas fees and manage network congestion, making transactions more cost-effective for users.
What is the connection between the Ethereum blob limit and gas fees stability?
The blob limit increase plays a critical role in stabilizing gas fees on the Ethereum mainnet. As more transaction data is accommodated, the resulting decrease in network congestion leads to more predictable and lower gas fees for users, ultimately improving the overall transaction experience.
How does the second BPO hard fork impact Ethereum scalability?
The second BPO hard fork has positively impacted Ethereum’s scalability by raising the blob target and limit. By allowing more data to be processed in batches, it contributes to reducing transaction costs and enhancing throughput capabilities on the Ethereum network through advanced rollup technology.
What future changes are anticipated for Ethereum’s gas limit?
Future enhancements, including an increase in the Ethereum gas limit from 60 million to 80 million and later to 200 million, are expected following the second BPO hard fork. These adjustments will promote higher transaction volumes and better scaling solutions, including the implementation of ‘perfect parallel processing’ through Block Access Lists.
When will the Glamsterdam hard fork be implemented and what will it accomplish?
The Glamsterdam hard fork is anticipated to take place later in 2026, aiming to further enhance Ethereum scalability by increasing the gas limit to 200 million. This upgrade will utilize Block Access Lists, enabling perfect parallel processing and transforming transaction processing into a multi-lane system.
What role do blobs play in Ethereum’s rollup technology?
Blobs are a crucial component of Ethereum’s rollup technology as they allow for increased data capacity within individual blocks. Each blob accommodates 128 kilobytes of transaction data, which enhances the efficiency of batching multiple transactions, ultimately reducing costs and improving user experiences.
How does the increase in blob limit relate to Ethereum’s overall transaction throughput?
The increase in the blob limit is directly related to Ethereum’s transaction throughput. By allowing more data to be processed per block, the Ethereum network can handle a higher volume of transactions, which alleviates pressure on mainnet gas fees and enhances the overall performance of the blockchain.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Blob Limit Increase | The blob limit on Ethereum has been raised from 15 to 21 as part of the second BPO hard fork. |
| Data Capacity Enhancement | This change allows more transactions to be batched, reducing costs and improving scalability. |
| Blob Target Raised | The blob target has increased from 10 to 14, a critical metric for monitoring network performance. |
| System Capacity | Each blob accommodates 128 KB, allowing up to 2,688 KB in a single block. |
| Impact on Gas Fees | Transaction fees on Ethereum have stabilized post the first BPO hard fork due to reduced network congestion. |
| Future Enhancements | The Glamsterdam hard fork is expected in 2026, planning to raise the gas limit to 200 million. |
Summary
The Ethereum blob limit has been significantly increased, enhancing the network’s ability to process transactions more efficiently. This recent adjustment, part of the strategy to improve scalability by 2026, focuses on not just increasing the blob limit but also optimizing gas fees by allowing more transactions to be effectively batched. As a result, these updates mark a pivotal progression in Ethereum’s ongoing efforts to navigate congestion and enhance transaction throughput.
Related: More from Ethereum News | Google Cloud, MoneyGram Join New Privacy Network Bank Initiative | Ethereum Network Transactions Hit New Record: What It Means for You