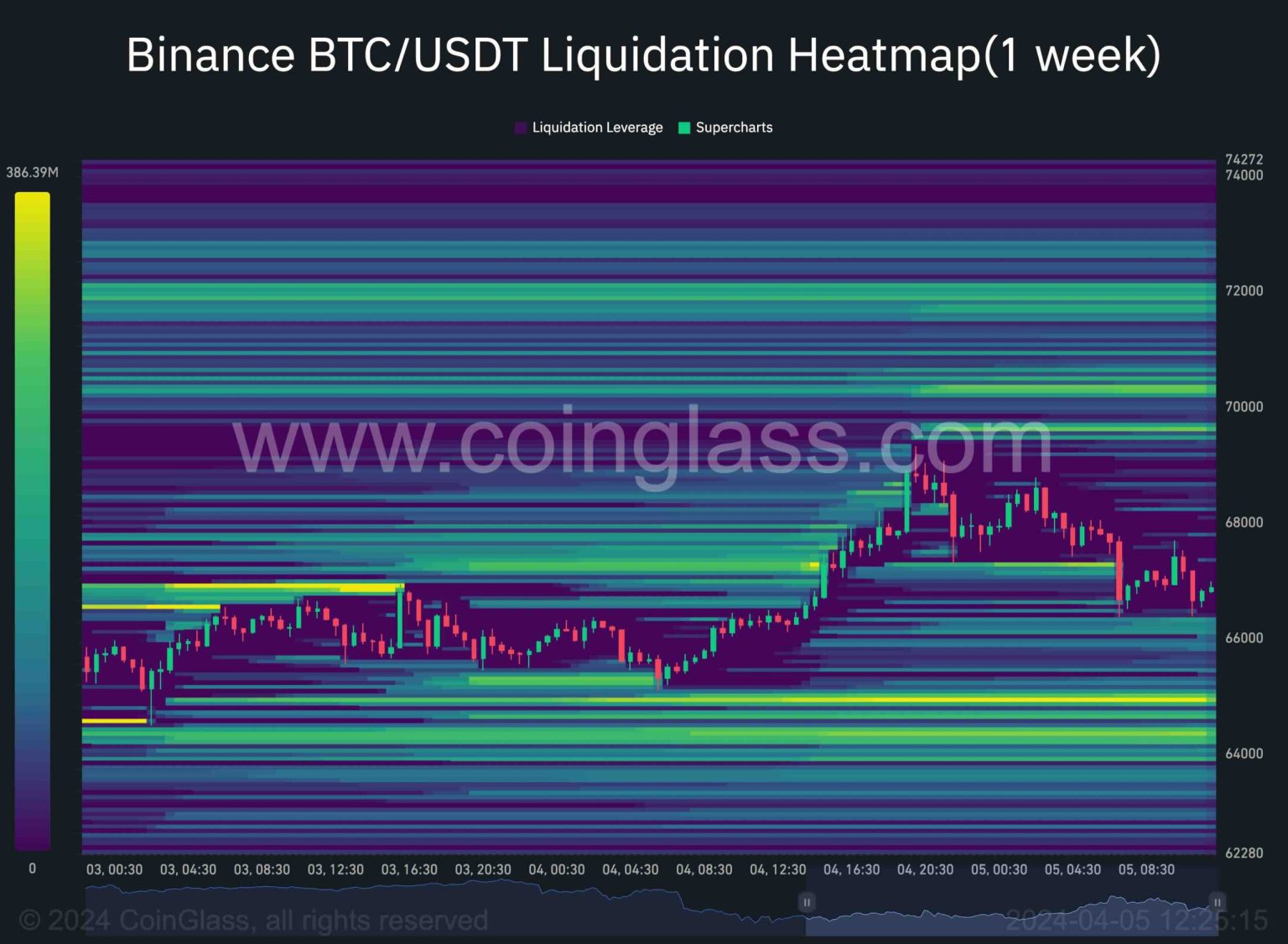
The phenomenon known as the “Bitcoin liquidation treadmill” has emerged as a crucial aspect of the cryptocurrency trading landscape, where traders’ risky positions face relentless scrutiny and forced unwinding. As Bitcoin futures and perpetual contracts continue to command the market, the volatility surrounding these instruments exemplifies the liquidation mechanics at play. This week alone, approximately $794 million in Bitcoin long positions were liquidated, highlighting the dangers of crowded trades and the chilling influence of funding rates. The intricate relationship between open interest analysis and price movements underscores how leverage and liquidation can create cycles of forced selling, thereby impacting the overall market. Understanding this treadmill is essential for anyone involved in Bitcoin trading, as it dramatically influences decision-making and pricing patterns in the cryptocurrency market.
Within the realm of cryptocurrency trading, the term “liquidation treadmill” refers to an ongoing cycle that traders encounter when their positions are systematically hunted and forced to close. This cycle is particularly relevant when discussing perpetual futures, which are increasingly shaping Bitcoin’s price discovery amidst high volatility. Liquidation mechanics, driven by the funding rates and open interest analysis, reveal the fragility of leveraged positions that can quickly turn into substantial sell-offs. As traders navigate this rugged terrain, their actions can feed back into the market, creating further price fluctuations and solidifying this concept. To comprehend the implications of such a treadmill is vital for anyone attempting to leverage positions in the ever-evolving cryptocurrency landscape.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Bitcoin Liquidation Treadmill | Bitcoin is undergoing a systematic liquidation process where leveraged positions are actively hunted. |
| Perpetual Futures Influence | Perpetual futures dominate Bitcoin’s short-term price discovery and can quickly transform crowded longs into forced selling. |
| Price Fluctuations | BTC’s price fluctuates around the $80,000 mark, influenced by futures positioning and significant liquidation events. |
| Liquidation Hot Zones | Recent data indicated about $794 million in liquidations close to ~$87,800, highlighting areas of risk around $80,000. |
| Mechanics of Liquidation | Liquidation occurs when collateral dips below the maintenance margin, causing forced sales and triggering further selling pressure. |
| Market Sensitivity | Leveraged positions are sensitive to minor price declines, increasing the likelihood of cascading liquidations. |
| Indicators of Risk | Reading data such as heatmaps, open interest, and funding rates can indicate where liquidations may cluster. |
| Breaking the Treadmill | To stop the treadmill, there must be a reduction in leverage, lower open interest, and a solid spot market presence to absorb sales. |
Summary
The concept of the Bitcoin liquidation treadmill emphasizes the precarious balance within the cryptocurrency market, where leveraged trading can lead to rapid and severe price corrections. Understanding this cycle is crucial for traders looking to navigate the volatile waters of Bitcoin. As the market continues to be influenced heavily by derivatives such as perpetual futures, the need for a stable spot market presence becomes ever more critical to mitigate the adverse effects of forced liquidations.
Understanding the Liquidation Treadmill in Bitcoin Trading
Bitcoin’s current trading environment can be aptly described as a “liquidation treadmill,” a phenomenon where traders with risky positions are systematically targeted and subsequently liquidated. As Bitcoin’s price fluctuates, particularly within the $80,000 range, these liquidations become a pronounced factor influencing market dynamics. Approximately $794 million in Bitcoin longs were liquidated within a week as prices approached ~$87,800, showcasing the immense pressure that leveraged positions exert on both the market and individual traders. This situation reflects the mechanics of Bitcoin futures, especially in a landscape where traders leverage their positions in anticipation of further price moves.
In essence, the liquidation treadmill represents a feedback loop within the market, whereby the liquidation of positions leads to further downward pressure on prices. This undesirable cycle becomes more pronounced when traders utilize high levels of leverage in their positions, which increases their susceptibility to forced sales when prices dip. Therefore, understanding these liquidation mechanics is crucial for traders looking to navigate Bitcoin’s volatile environment effectively. By analyzing liquidation trends, traders can gain insights into potential price movements and the risk characteristics of their positions.
The Role of Perpetual Futures in Bitcoin’s Price Discovery
Perpetual futures have significantly altered Bitcoin’s price discovery process, making them a central instrument for traders. With the overwhelming dominance of perpetuals—comprising around 68% of Bitcoin’s trading volume—the dynamics of how Bitcoin’s price is set have shifted dramatically. These derivatives allow for infinite time to hold positions, providing the potential for enhanced gains or losses. As traders use perpetual contracts for speculation and hedging, the influence they wield over the market grows, leading to volatile price action that does not always correspond with broader market trends.
Moreover, the funding mechanism intrinsic to perpetual futures plays a crucial role in sustaining this liquidation treadmill. Positive funding pressures long positions to maintain their leverage, while negative funding creates incentives for short positions. Thus, the perpetual contracts not only serve as a vehicle for price discovery but also generate self-reinforcing cycles where crowded long positions can quickly become the target of forced liquidity events. As traders navigate the complexities of perpetual futures, awareness of these mechanisms is vital for managing risk in a market that is increasingly dominated by derivatives.
Liquidation Mechanics and Their Market Impact
The mechanics behind liquidation are foundational to understanding Bitcoin’s price movements. On platforms like Binance, liquidation occurs when a trader’s collateral drops below the required maintenance margin, leading exchanges to liquidate positions to mitigate risk. This process generates downward pricing pressure and can trigger cascading liquidations among other leveraged players in the market. Consequently, as prices fall, the market becomes increasingly sensitive, resulting in a feedback loop that perpetuates the liquidation treadmill.
Furthermore, the impact of liquidation mechanics extends beyond individual positions; it influences overall market sentiment and trading strategies. Traders often find themselves caught in the cycle of liquidations, where fear and uncertainty lead to rapid sell-offs, further amplifying price swings. With Bitcoin’s price action closely tied to these liquidation events, the ability to interpret and anticipate these mechanics becomes indispensable for traders aiming to capitalize on market movements while avoiding the pitfalls of excessive leverage.
Utilizing Liquidation Heatmaps for Strategic Trading
Liquidation heatmaps emerge as a valuable tool for traders looking to visualize and anticipate potential market shifts due to forced sales. By mapping liquidation points based on trading data and leverage levels, heatmaps highlight areas where liquidations may cluster, providing traders with insight into where support and resistance may lie. This analytical approach helps traders position themselves more strategically, especially in volatile markets where liquidation threats loom large due to concentrated leverage.
While heatmaps do not predict future prices with certainty, they offer a framework for understanding trader behavior in relation to liquidation zones. By incorporating data-driven methods alongside traditional technical analysis, traders can refine their strategies to navigate the complexities of Bitcoin trading more effectively. Recognizing liquidations as a core aspect of market dynamics is essential for identifying opportunities while managing risks associated with high-leverage positions.
The Interplay of Open Interest and Liquidation Dynamics
Open interest represents the total value of outstanding futures contracts within the Bitcoin market, serving as a crucial metric for assessing market sentiment and positioning. By analyzing open interest alongside price movements and funding dynamics, traders can glean critical insights into the health of leveraged positions. A rising open interest amid increasing prices might indicate stronger momentum and the buildup of leverage, while declining open interest during price drops may suggest market participants are unwinding positions, often through liquidations.
Importantly, open interest does not function in isolation; it requires contextual understanding through the lenses of price direction and funding levels. For instance, a decline in open interest during a significant sell-off might signal that traders are actively reducing risk exposure, while stable open interest may indicate underlying fragility that can lead to deeper liquidation events. Thus, traders must integrate open interest analysis into their strategies to mitigate the risks associated with levered positions and potential liquidation cascades.
Breaking the Liquidation Treadmill Cycle
To escape the continuous loop of liquidation, market participants must recognize a few critical factors. A sustained reduction in leverage is essential for moving away from the liquidation treadmill, which can be indicated by lower open interest and less extreme funding rates. This not only helps stabilize prices but also creates a healthier environment for market growth. When the demand for spot Bitcoin strengthens, it can effectively absorb the pressure from forced liquidations, allowing the market to regain composure and establish new price levels.
Changes in market volatility can also provide an opportunity to disrupt the cycle. When volatility decreases, the incentives to engage in high-leverage trading diminish, which can lead to a more balanced trading environment. Understanding how perpetual futures and spot trading interact helps traders discern when risk exposure moves from being detrimental to beneficial. Ultimately, differentiating between derivative-driven intraday volatility and longer-term spot influences is critical for navigating Bitcoin’s market conditions.
Market Signals: Funding, Open Interest, and Liquidation Trends
Three core signals—funding, open interest, and liquidation intensity—work collaboratively to indicate the market’s health and potential direction. Funding measures how overcrowded a trading position has become, while open interest provides context to the overall market sentiment. If funding shows a persistent shift towards high rates while open interest remains elevated during downturns, it may indicate a fragile basis for upward price movements, signaling potential for further liquidations.
Conversely, a decline in funding in conjunction with a fall in open interest often signals a constructive transition within the market. This scenario implies a reduction in leverage, which could facilitate a more sustainable recovery in prices if the market can withstand the influences of forced selling. Understanding how these signals interplay among themselves not only bolsters traders’ capacity to anticipate market movements but also enhances their decision-making when executing trades in a leveraged environment.
Strategies for Navigating Bitcoin’s Volatility
Navigating Bitcoin’s volatile landscape requires a blend of strategic planning and risk management. Traders should consider employing techniques like setting stop-loss orders, utilizing hedging strategies, and actively monitoring liquidation heatmaps to minimize exposure during high-risk periods. Additionally, focusing on long-term trends rather than short-term fluctuations can help mitigate the emotional responses that often lead to impulsive trading decisions. This approach not only cultivates a disciplined trading practice but also increases the potential for capital preservation during tumultuous market phases.
Moreover, staying informed about macroeconomic factors influencing Bitcoin and broader cryptocurrency markets can provide traders with a comprehensive perspective on potential risk scenarios. Understanding fundamental trends allows traders to align their strategies more closely with market conditions, fostering a balanced approach to leveraging positions while being cognizant of liquidation risks. Engaging with community resources, educational platforms, and professional insights can further equip traders to navigate Bitcoin’s challenging environment proficiently.
The Future of Bitcoin Trading and Liquidation Mechanisms
Looking ahead, the landscape of Bitcoin trading, particularly concerning liquidation mechanics, is poised for evolution. As institutional investors continue to grow their presence in the cryptocurrency space, the dynamics of futures trading and liquidations may undergo a transformation. The interaction between regulated markets and offshore perpetual trading will likely influence how liquidity is managed and how liquidation events unfold, potentially leading to a more stable trading environment.
Furthermore, innovations in trading technology and analytic tools will play a crucial role in shaping trader behavior and the broader market context. Enhanced risk management tools that leverage artificial intelligence and machine learning could provide greater clarity and predictability around liquidation scenarios. Ultimately, as the market matures, the ongoing balance between derivatives-driven trading and spot demand will dictate Bitcoin’s price trajectory, emphasizing the importance of adapting trading strategies to meet evolving market conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Bitcoin liquidation treadmill and how does it affect cryptocurrency trading?
The Bitcoin liquidation treadmill refers to a cycle of forced selling triggered by liquidation mechanics in cryptocurrency trading, particularly with perpetual futures. When the price of Bitcoin approaches liquidation thresholds for heavily leveraged positions, it can lead to a rapid sell-off as traders are forced to close positions, escalating further downward pressure on prices.
How do perpetual futures contribute to the Bitcoin liquidation treadmill?
Perpetual futures contribute to the Bitcoin liquidation treadmill by creating a feedback loop through liquidation mechanics. When perpetual futures prices exceed the spot price, it leads to positive funding rates, encouraging bullish positions. If the price declines, it triggers liquidations that exacerbate the drop, pulling more traders into forced selling.
What are the liquidation mechanics involved in Bitcoin futures trading?
In Bitcoin futures trading, liquidation mechanics come into play when a trader’s collateral falls below the maintenance margin, initiating forced selling by exchanges to reduce risk. This process creates a domino effect, as one liquidation can lead to further liquidations among other leveraged positions, forming the liquidation treadmill.
Why are liquidation heatmaps important in the context of Bitcoin trading?
Liquidation heatmaps are crucial as they help traders visualize potential points where forced liquidations may occur. By analyzing trading data and leverage levels, these heatmaps reveal areas of heightened liquidation risk, enabling traders to strategize accordingly and avoid typical liquidation zones.
What role does open interest analysis play in understanding the Bitcoin liquidation treadmill?
Open interest analysis offers insight into the positioning within Bitcoin futures. A rising open interest combined with increasing prices suggests growing leverage, while a decreasing open interest during price declines indicates positions are being closed, often through liquidation, which feeds into the liquidation treadmill.
How can traders break the Bitcoin liquidation treadmill cycle?
To break the Bitcoin liquidation treadmill cycle, traders can look for a sustained reduction in leverage indicated by lower open interest and funding rates. Additionally, strong spot market support can absorb forced selling, preventing the cycle from continuing and allowing stabilization in prices.
What market indicators should traders monitor for Bitcoin liquidation trends?
Traders should monitor funding rates, open interest levels, and liquidation intensity. An increase in forced liquidations coupled with high open interest can signal a heightened liquidation risk, while changes in funding can provide insights into market sentiment and trader positioning relative to the Bitcoin price.
How does the volatility of Bitcoin prices influence the liquidation treadmill?
The volatility of Bitcoin prices significantly influences the liquidation treadmill by intensifying the risk of forced liquidations. In highly volatile markets, leveraged positions carry lower margins for error, making them highly susceptible to liquidations, which creates a cyclical pattern of selling pressure.
What is the significance of $794 million in Bitcoin long liquidations this week?
The $794 million in Bitcoin long liquidations this week serves as a benchmark for the extent of forced selling within the liquidation treadmill. It highlights the high level of leverage in the market and the potential for rapid price declines when liquidation hot zones are breached, impacting overall market dynamics.
How do traders utilize data to navigate the Bitcoin liquidation treadmill effectively?
Traders can effectively navigate the Bitcoin liquidation treadmill by utilizing data analysis, including identifying liquidation heatmaps, monitoring open interest shifts, and tracking funding rates. This analytical approach allows traders to gauge market sentiment, when to enter or exit trades, and anticipate potential liquidation cascades.