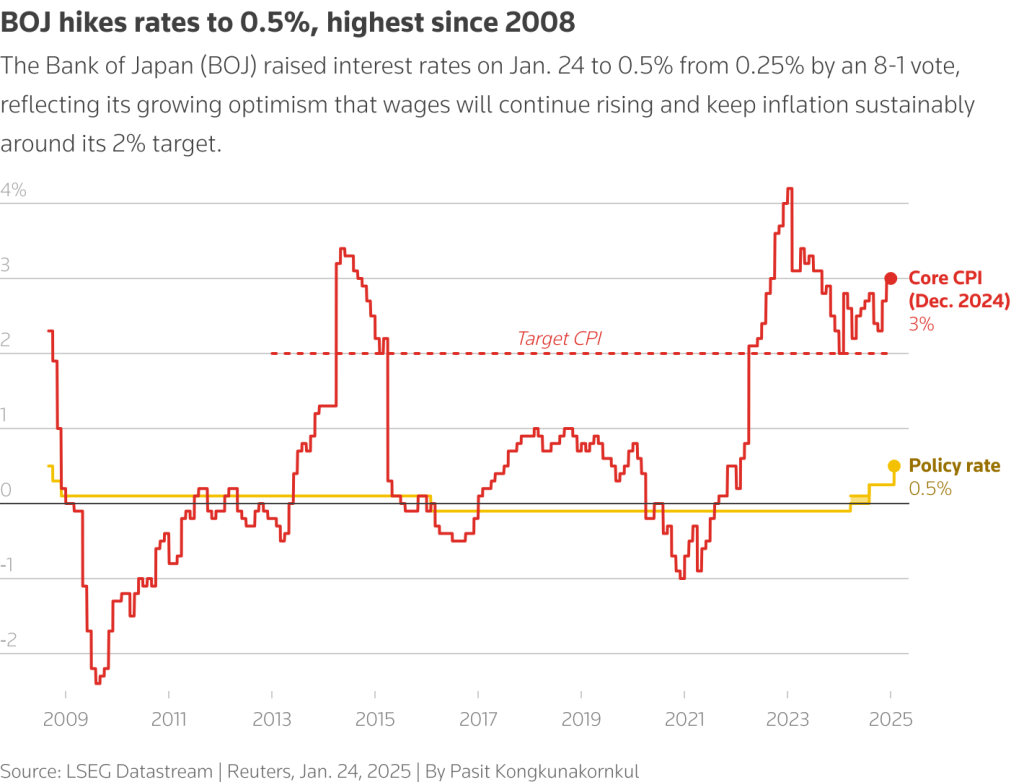
The recent announcements from the Bank of Japan regarding interest rate hikes have captured significant attention, particularly as Governor Kazuo Ueda outlines expectations for the country’s monetary policy. As the central bank evolves its strategies based on shifting economic indicators, market analysts eagerly discuss interest rate predictions and their potential implications for the Japan economy outlook. A careful examination of the Bank of Japan news reveals a delicate balance between stimulating growth and curbing inflation. The world is watching closely as these interest rate shifts could redefine the landscape of the Japanese financial sector. Understanding the future trajectory of the BoJ’s monetary policy will be crucial for investors and businesses alike as they navigate this changing economic environment.
Recent developments at Japan’s central bank highlight the significance of monetary adjustments, particularly in terms of increasing interest rates. Under the guidance of Governor Kazuo Ueda, the financial institution is evaluating how current price movements and economic stability might facilitate further hikes. Experts in the field are eager to dissect these changes, as they are intricately linked to forecasts for Japan’s economic performance. With growing discussions surrounding the intricacies of BoJ’s strategies, stakeholders are now deeply interested in the broader ramifications of these policy decisions. As we analyze the evolving scenario, it’s clear that the central bank’s actions are pivotal for shaping the future financial landscape in Japan.
Understanding Bank of Japan Interest Rate Hikes
The Bank of Japan (BoJ), under the leadership of Governor Kazuo Ueda, has signaled its intention to continue interest rate hikes if economic conditions satisfy their forecasts. The decision to increase rates reflects an ongoing effort to stabilize Japan’s economy, which has struggled with deflationary pressures and low growth for decades. By implementing a more aggressive monetary policy, the BoJ aims to counterbalance inflationary trends that have begun to emerge, ensuring that price levels are kept in check in line with the bank’s long-term targets.
Interest rate hikes are not merely a tool for curbing inflation; they also influence consumer spending, business investments, and overall economic activity in Japan. As rates rise, borrowing becomes more expensive, which can lead to reduced consumption and investment. Therefore, the BoJ is closely monitoring various economic indicators and price trends to determine the right pace at which to adjust rates, balancing the need for growth with the necessity of maintaining price stability.
The Economic Outlook of Japan in Relation to BoJ Monetary Policy
Kazuo Ueda’s outlook for the Japanese economy appears cautiously optimistic, provided that current economic and price trends remain consistent with the BoJ’s predictions. The governor has emphasized the importance of aligning monetary policy with real-time data to assess the health of the economy effectively. As Japan’s economy gradually transitions from deflationary pressures, the BoJ’s strategy seeks to foster sustainable growth while avoiding the pitfalls of rapid inflation.
With the potential for continued interest rate hikes, the Bank of Japan is tasked with navigating external pressures such as global economic instability and supply chain issues that could impact domestic markets. The intersection of these factors creates a delicate balance for the BoJ as it formulates its monetary policy. Observers will be keen to understand how these dynamics influence interest rate predictions and the overall economic outlook, directly affecting Japan’s competitiveness and financial stability.
Kazuo Ueda’s Vision for the BoJ and Interest Rate Predictions
Governor Kazuo Ueda has been vocal about the need for a nuanced approach to monetary policy as the Bank of Japan prepares to adjust interest rates in light of economic forecasts. His vision relies on comprehensive analysis and continuous updates to their strategies based on real-time economic data. Ueda believes that fostering transparency and clarity in the BoJ’s communications will help manage public expectations around future interest rate adjustments, thereby stabilizing the Japanese economy.
Going forward, interest rate predictions will likely reflect an adaptation to evolving economic conditions, including inflation rates, consumer behavior, and global market trends. Ueda’s leadership signifies a pivotal shift at the BoJ, where careful consideration is given to both immediate and long-term economic health. As the economic landscape evolves, the effectiveness of Ueda’s policies will be critical to shaping Japan’s financial future.
The Impact of BoJ Monetary Policy on Local Businesses
The Bank of Japan’s monetary policy, particularly regarding interest rate hikes, has direct implications for local businesses across the country. As borrowing costs rise, small and medium enterprises (SMEs) may find it more challenging to access funds for expansion or operational costs. Consequently, business owners must adapt their financial strategies to cope with these changes in monetary policy. Being aware of the BoJ’s decisions can help businesses prepare for any shifts in consumer demand or operational costs.
Conversely, some sectors may benefit from a more stable economic environment created by the BoJ’s actions. For instance, businesses focused on exports could see a more favorable landscape if interest rate hikes strengthen the yen against other currencies, making their products more competitive abroad. This dual impact emphasizes the importance of keeping abreast of Bank of Japan news to navigate the intricacies of the evolving market situation.
Global Comparisons: BoJ Interest Rate Hikes vs. Other Central Banks
When evaluating the Bank of Japan’s interest rate hikes, it’s essential to draw comparisons with other global central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the United States or the European Central Bank. Each institution faces unique economic circumstances and employs different strategies to stabilize their respective economies. As BoJ implements rate hikes, examining the policies of these counterparts offers valuable insight into potential economic outcomes and investor sentiments.
Additionally, global economic conditions, such as international trade dynamics and geopolitical influences, play a crucial role in shaping the monetary policies enacted by central banks around the world. The reactions of global market investors to the BoJ’s interest rate predictions may lead to shifts in capital flows, affecting exchange rates and economic stability in Japan. Understanding these comparative dynamics is critical for anticipating how domestic and foreign economies might respond to changes in the BoJ’s monetary policy.
Consumer Confidence and Its Link to BoJ Rate Decisions
Consumer confidence is a pivotal factor influencing the effectiveness of the Bank of Japan’s monetary policy, especially in light of interest rate hikes. When confidence declines, consumer spending typically decreases, which can stifle economic growth. Conversely, a robust consumer sentiment can stimulate demand, fortifying the economy against the adverse effects of rising borrowing costs. Kazuo Ueda’s administration must consider these dynamics when assessing the timing and magnitude of interest rate adjustments.
The BoJ has a vested interest in fostering a favorable consumer outlook as it navigates its monetary policy. This involves not only managing interest rates effectively but also ensuring the public understands the rationale behind these changes. A well-informed populace is more likely to respond positively to the BoJ’s actions, thus enhancing the overall efficacy of its economic strategies.
Analyzing Japan’s Inflation Trends and Monetary Policy Responses
The interplay between inflation rates and the Bank of Japan’s monetary policy forms a complex narrative critical to understanding the nation’s economic health. The BoJ’s interest rate hikes are often a reaction to rising inflation, aimed at curbing excessive price increases and maintaining purchasing power for consumers. As price trends continue to evolve, the BoJ’s analysis and response mechanisms become vital in determining future interest rate policies.
Ueda’s administration is tasked with carefully monitoring these inflation trends to prevent a resurgence of the deflation that Japan has struggled with over the years. Policymakers must balance the necessity for rate hikes with the risk of discouraging economic growth. An astute response to inflationary pressures is essential for safeguarding Japan’s economic stability while supporting a vibrant consumer market.
Future Projections of Japan’s Economic Landscape
Considering the current trajectory of global markets and domestic economic indicators, projections of Japan’s economic landscape are increasingly nuanced. With ongoing interest rate hikes from the Bank of Japan, expectations for growth and inflation are under constant reassessment. Analysts and policymakers alike are urged to examine both short-term fluctuations and long-term trends to form a comprehensive economic outlook.
The efficacy of Japan’s responses to future economic challenges will hinge upon the adaptability of its monetary policy as led by Kazuo Ueda. By focusing on flexible monetary strategies that respond to emerging economic realities, the BoJ can foster a stable economic environment that promotes sustainable growth amid global uncertainties. As such, stakeholders will remain attentive to the bank’s decisions, with high expectations set for the implications of upcoming interest rate changes.
Strategic Implications of BoJ’s Interest Rate Decisions
The strategic implications of the Bank of Japan’s interest rate decisions extend beyond domestic borders, affecting foreign investors and trade partners alike. As the BOJ considers further rate hikes, other central banks will monitor these changes closely, adjusting their own policies accordingly. This interconnectedness highlights the global nature of economic policy-making and the potential ripple effects stemming from Japan’s financial strategies.
Additionally, Ueda’s leadership signals a shift towards a more responsive monetary policy that may prioritize collaboration with other economies. As interest rates rise, the strategic implications for foreign investment, trade relations, and capital flows will be critical for understanding Japan’s role in a rapidly changing global economy. Policymakers will need to remain vigilant to maximize the potential benefits of BoJ decisions while minimizing any adverse impacts on Japan’s economic position.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the latest Bank of Japan interest rate hikes announced by Kazuo Ueda?
As of recent announcements, Bank of Japan Governor Kazuo Ueda indicated that interest rate hikes would continue if the economy and price trends align with their predictions. This suggests a gradual tightening of monetary policy in response to Japan’s economic conditions.
What is the outlook for the Japan economy amid Bank of Japan interest rate hikes?
The Japan economy outlook amid the Bank of Japan’s interest rate hikes appears cautiously optimistic. The BoJ is carefully monitoring economic indicators to guide future monetary policy decisions, aiming to stabilize growth while managing inflation.
How do Bank of Japan interest rate hikes impact consumers in Japan?
Bank of Japan interest rate hikes can lead to higher borrowing costs for consumers as banks may pass on the increased rates. This could impact spending and investment decisions, affecting overall economic activity in Japan.
What factors influence the Bank of Japan’s interest rate predictions?
Bank of Japan’s interest rate predictions are influenced by various factors, including inflation rates, economic growth, and global economic conditions. Governor Kazuo Ueda emphasizes the need for the economy and price trends to align with their forecasts to justify ongoing rate hikes.
How is BoJ monetary policy changing under Governor Kazuo Ueda?
Under Governor Kazuo Ueda, BoJ monetary policy is shifting towards a more cautious approach, with a focus on balancing economic growth with inflation control. The recent interest rate hikes are part of this strategic adjustment, aimed at responding to evolving economic conditions.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Bank of Japan’s policy on interest rates |
| Governor Kazuo Ueda’s statement |
| Predictions for the economy and price trends |
| Continued interest rate hikes expected |
Summary
The Bank of Japan interest rate hikes are anticipated to continue under the guidance of Governor Kazuo Ueda, provided that the economic and price trends align with their forecasts. This indicates a responsive monetary policy that aims to adapt to ongoing financial conditions, with implications for both domestic and global economic landscapes.