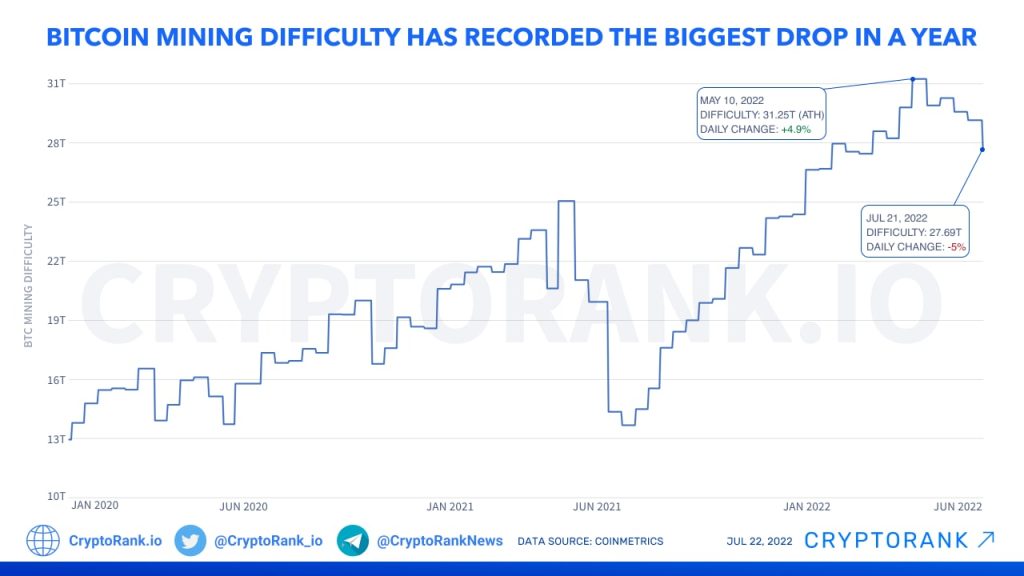
Recent developments in Bitcoin mining have seen a notable drop in mining difficulty, decreasing by approximately 11.16%. This substantial decline marks the sharpest adjustment since the significant mining challenges triggered by the China crypto mining ban in 2021. Currently, Bitcoin mining difficulty sits at 125.86 terahashes, reflecting broader challenges in the crypto market downturn where prices plummeted significantly. The adjustment, set to take effect at block 935,429, has coincided with a considerable decrease in the Bitcoin network hashrate, as miners faced operational difficulties, including disruptions caused by winter storms. As the landscape of cryptocurrency continues to evolve, upcoming adjustments may further impact mining dynamics, with forecasts suggesting another reduction in difficulty on February 23.
In recent trends, the complexity associated with Bitcoin mining operations has lessened, which some might refer to as a reduction in mining challenge. This situation has arisen in the context of numerous factors, including the aftermath of a significant ban on digital currency operations in China and fluctuations in the market’s overall health. As the ecosystem navigates through a crypto winter, the response from miners—which includes their hashrate and strategies—plays a crucial role in maintaining network stability. Additionally, seasonal weather events, such as winter storms, have added layers of operational hurdles, impacting how efficiently miners can perform. Understanding these dynamics is essential for anyone looking to grasp the intricate world of cryptocurrency mining today.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Bitcoin Difficulty Drop | The Bitcoin network’s mining difficulty has dropped by approximately 11.16%, the most significant decline since the 2021 China ban on crypto mining. |
| Current Difficulty | The current Bitcoin mining difficulty is 125.86 T, effective at block 935,429. |
| Average Block Time | The average block time has exceeded 11 minutes, which is longer than the intended 10-minute target. |
| Future Expectations | A further decrease in mining difficulty is anticipated around February 23, projected to be about 10.4% down to 112.7 T. |
| Impact of Winter Storm Fern | This severe winter storm reduced the total network hashrate due to power disruptions, resulting in a temporary loss of 60% hashing power for the Foundry USA mining pool. |
| Historical Context | The last major drop in Bitcoin mining difficulty was during the May-July 2021 period, with decreases ranging from 12.6% to 27.9% due to the China mining ban. |
Summary
The recent Bitcoin mining difficulty drop of over 11% represents the sharpest decline since the 2021 ban on crypto mining in China. This adjustment has significant implications for the mining ecosystem and the overall market, as it reflects ongoing challenges miners face, including extreme weather conditions and fluctuating energy consumption. With further decreases expected, understanding the factors contributing to these changes is crucial for stakeholders in the crypto space.
Impact of Bitcoin Mining Difficulty Drop on the Market
The recent drop in Bitcoin mining difficulty, which saw a decrease of approximately 11.16% in just 24 hours, has sent ripples through the crypto market. This significant adjustment is the steepest since the notorious China mining ban in 2021, highlighting the ongoing volatility inherent in Bitcoin mining operations. With the current difficulty level at 125.86 T, miners face a less challenging environment for block generation, which may lead to an increase in mining profitability. This shift can potentially attract more mining entities back to the network, stimulating activity as they attempt to capitalize on the favorable conditions.
Moreover, this decline in mining difficulty often corresponds with wider changes in the Bitcoin network hashrate – the cumulative computational power that miners contribute. When mining difficulty decreases, it suggests that fewer miners are currently operating or that a significant portion of the network’s hashing power has temporarily gone offline. Such fluctuations not only impact miner revenues but can also reflect broader market sentiments during prominent crypto downturns as traders and investors adjust their expectations regarding Bitcoin’s future pricing and stability.
Understanding Bitcoin Difficulty Adjustments
Bitcoin mining difficulty adjustments are intrinsic to the cryptocurrency’s protocol, automatically recalibrating approximately every two weeks based on the network’s total hashrate. As seen in the recent adjustment where the difficulty dropped by over 11%, these changes are crucial for maintaining the average block time of around 10 minutes. Historical patterns have demonstrated that during epochs of significant market fluctuation, such as the aftermath of the 2021 China crypto mining ban, Bitcoin’s difficulty can fluctuate drastically, allowing for a more sustainable mining ecosystem amidst unforeseen market pressures.
The mechanism ensures that as more miners join the network, the difficulty increases, maintaining that 10-minute block creation target. Conversely, if miners leave due to unfavorable conditions—like a winter storm or adverse market changes—the difficulty decreases to adapt. This continual balancing act reflects the dynamic nature of the cryptocurrency landscape, where miners must be agile to respond to external challenges, akin to the recent disruptions caused by both extreme weather conditions and fluctuations in the broader crypto market.
The Role of External Factors in Mining Operations
External factors, such as severe weather events and geopolitical regulations, play a significant role in shaping Bitcoin mining operations. The recent winter storm that swept across the United States exemplifies how environmental conditions can directly impact the Bitcoin network hashrate. With Foundry USA, the largest mining pool, losing nearly 60% of its hashing power, it becomes clear that natural disasters can momentarily stifle mining operations. Such disturbances lead to interruptions in power supply, forcing miners to halt operations, which in turn reduces the overall computational power securing the Bitcoin blockchain.
The ramifications of these disruptions extend beyond just the immediate effects on mining productivity. They highlight the fragile nature of Bitcoin’s decentralized architecture, which relies on consistent miner engagement. Furthermore, these fluctuations in hashrate can link back to broader market trends, with declines potentially leading to reduced miner profitability that exacerbates the already challenging conditions prompted by the current crypto market downturn. Therefore, miners must remain cognizant of both external challenges and their immediate impact on network operations.
Analyzing the Effects of the Crypto Market Downturn
The current crypto market downturn has resulted in diminished prices and reduced investment in Bitcoin mining operations. As Bitcoin fell from its all-time high of over $125,000 to lows around $60,000, many miners faced severe financial pressure, leading to temporary halts in operations and shifts of focus toward cryptocurrencies with potentially better returns. Consequently, the equilibrium of the Bitcoin network hashrate was disrupted, ultimately influencing the recent mining difficulty adjustment.
Such downturns not only lead to diminished miner activity but also set a precedent for market behavior in response to adverse conditions. With rising electricity costs and regulatory environments becoming more stringent, miners must adapt while keeping a close watch on the volatility of the crypto market. Additionally, a decrease in mining engagement in times of lower prices often leads to lesser overall market confidence, potentially setting off a chain reaction that affects mining difficulty and the stability of the Bitcoin ecosystem.
The Aftermath of the China Crypto Mining Ban
The China crypto mining ban instigated unprecedented changes within the Bitcoin mining landscape, resulting in significant impacts on both mining difficulty and network hashrate. Following the ban, miners were forced to evacuate, leading to immediate downward adjustments in Bitcoin mining difficulty ranging from 12.6% to 27.9%. Such volatility reminds us of the direct correlation between regulatory actions and miner behavior, profoundly affecting market stability and pricing.
As miners relocated to more favorable jurisdictions, the overall hashrate began to stabilize, yet the chaos initiated by China’s decision remains a pivotal reference point for understanding current market dynamics. It demonstrates how geopolitical events can sway miner participation substantially, leading to bottlenecks in new block additions and influencing the general trajectory of the Bitcoin network. Moreover, as we reflect on these historical events, ongoing concerns about future regulatory actions loom, potentially shaping the mining landscape once again.
Future Projections for Bitcoin Mining Difficulty
Looking ahead, projections suggest that Bitcoin mining difficulty may continue to witness declines, particularly as miner operations pivot in response to both market conditions and external factors. As noted, experts anticipate further difficulty adjustments of around 10.4% expected on February 23, which may encourage renewed interest from miners hoping to capitalize on a less competitive environment. Such adjustments offer a glimpse into the fluid nature of the mining landscape while also reinforcing the necessity for adaptability regarding operational strategies.
However, future challenges are on the horizon, including potential regulatory scrutiny and ongoing market fluctuations. As the Bitcoin ecosystem evolves, miners must be vigilant in monitoring emerging trends, such as the rise of AI data centers and the integration of high-performance computing as alternative solutions. These innovations may not only alter operational tactics but will redefine the parameters of profitability within Bitcoin mining in an increasingly interconnected global economy.
The Importance of Adaptability in Mining Operations
In the ever-evolving realm of Bitcoin mining, adaptability stands as a crucial factor for survival and success. As miners navigate through environmental disruptions like winter storms or face regulatory challenges similar to those imposed by China’s crypto mining ban, the ability to pivot quickly can determine long-term viability. Mining operations that embrace changes—whether it means reducing energy consumption during peak outages or transitioning infrastructure to accommodate market demands—are more likely to sustain profitability and resilience.
Moreover, as external factors continue to shape the crypto space, the ability of miners to respond effectively will become increasingly essential. Those who invest in innovative technologies and infrastructures, such as green energy or diversified operational hubs, will find themselves better positioned against future volatility. The mining sector’s ability to adapt will ultimately dictate its longevity and reliability in contributing to the broader Bitcoin network, amid the uncertainties presented by the landscape of cryptocurrency.
Regulatory Implications on Bitcoin Mining
The regulatory scrutiny that Bitcoin mining faces remains a significant aspect influencing operational stability and mining difficulty. As governments around the globe grapple with the implications of cryptocurrency, policies enacted can either promote or stifle mining activities. The instances of China’s 2021 ban serve as a critical reminder of how sudden regulatory changes can reshape entire ecosystems, leading to immediate difficulty adjustments and lapses in miner engagement. This serves as a cautionary tale for miners in regions where regulations are still being formed.
Future regulations will likely continue to adapt, reflecting society’s responsiveness toward cryptocurrencies. Such policies could involve environmental mandates aimed at reducing carbon footprints or capital taxation measures for mining operations. Regardless of the direction, continued vigilance and proactive engagement with regulatory bodies will be essential for industry stakeholders. By establishing constructive dialogues and demonstrating a commitment to responsible mining, the Bitcoin community can shape regulations that foster a thriving mining environment while addressing social concerns.
Technological Advances in Bitcoin Mining
As cryptographic technology progresses, Bitcoin mining operations are witnessing transformational changes that could redefine efficiency and profitability. The introduction of advanced mining hardware and software solutions not only enhances computational power but also promotes energy-efficient practices. Miners are now able to extract Bitcoin at lower difficulties, especially during periods of decline, providing opportunities to stabilize revenues amid fluctuating market conditions.
Additionally, leveraging AI and blockchain technology can enable miners to predict difficulty adjustments more accurately, optimizing operational efficiency. Staying ahead of technological trends is crucial as the sector evolves alongside global dynamics, including shifts in consumer demand, regulatory frameworks, and environmental considerations. Ultimately, embracing innovation will allow mining participants to adapt seamlessly, ensuring the sustainability of mining operations in the highly competitive arena of cryptocurrency.
Frequently Asked Questions
What caused the recent Bitcoin mining difficulty drop?
The recent Bitcoin mining difficulty drop of approximately 11.16% was primarily influenced by a decrease in the Bitcoin network hashrate, exacerbated by adverse conditions such as the winter storm in the US that temporarily disrupted power supply for miners. Furthermore, the broader crypto market downturn indicated less competitive mining conditions.
How does the Bitcoin difficulty adjustment affect miners?
Bitcoin difficulty adjustments, like the recent drop, impact miners significantly by altering the challenge associated with adding new blocks to the blockchain. A decrease in difficulty, such as the recent adjustment to 125.86 T, typically allows miners to find blocks more easily, potentially increasing profitability, especially during market downturns when mining revenues may decline.
What was the significance of the mining difficulty drop during the 2021 China crypto mining ban?
During the 2021 China crypto mining ban, Bitcoin mining difficulty experienced declines ranging from 12.6% to 27.9%. The recent 11.16% drop marks the most substantial adjustment since then, highlighting how external factors can lead to rapid fluctuations in Bitcoin mining difficulty based on changes in the Bitcoin network hashrate.
How does a winter storm impact Bitcoin mining operations?
A winter storm can significantly impact Bitcoin mining operations by disrupting power supply and causing miners to temporarily shut down. As seen with winter storm Fern, major mining pools like Foundry USA experienced a loss of approximately 60% in their hashrate, leading to a decrease in the overall Bitcoin network hashrate.
What is the relationship between Bitcoin mining difficulty and the crypto market downturn?
The relationship between Bitcoin mining difficulty and the crypto market downturn is intertwined; as the market faces downturns, mining profitability can decrease, leading to reduced miner participation and, consequently, a lower network hashrate. This can prompt difficulty adjustments such as the recent drop of over 11%, which reflects the reduced competitiveness among miners.
When is the next expected Bitcoin difficulty adjustment?
The next Bitcoin difficulty adjustment is expected to occur on February 23, with predictions indicating a further decrease of about 10.4% to a difficulty level of approximately 112.7 T. Such adjustments respond to changes in the Bitcoin network hashrate as miner activity fluctuates.
What role does the Bitcoin network hashrate play in mining difficulty?
The Bitcoin network hashrate represents the total computational power being utilized by miners to secure the network. A decline in hashrate can trigger a downward adjustment in Bitcoin mining difficulty, making it easier for miners to add new blocks and impacting overall mining profitability, especially during adverse market conditions.
How did the China crypto mining ban impact global Bitcoin mining?
The China crypto mining ban in 2021 led to a massive exodus of miners, impacting the global Bitcoin mining landscape. The immediate consequence was a sharp decline in the Bitcoin network hashrate and significant difficulty adjustments. This has reshaped mining operations worldwide, leading to shifts in where and how Bitcoin mining takes place.