Digital RMB is revolutionizing the landscape of currency by introducing a fully digital form of money poised to reshape how transactions are conducted. As the central bank digital currency of China, it incorporates innovative features such as smart contracts that differ significantly from Ethereum smart contracts, which rely heavily on blockchain technology. With digital currency interest steadily rising, the digital RMB offers a unique approach through its exclusive account system, managed jointly by the central bank and commercial banks. This design allows for programmability without compromising monetary functions, thereby enabling tailored payment solutions and seamless automatic execution. As the world explores blockchain alternatives, the digital RMB stands out as a formidable contender in the future of digital finance.
The concept of a digital version of currency has gained remarkable traction in recent years, often referred to as virtual money or electronic cash. Among various nations, the digital RMB has emerged as a pivotal player, representing China’s efforts in the domain of state-backed digital finance. Unlike traditional cryptocurrencies, which typically harness blockchain technologies, this digital currency operates on a sophisticated ledger system managed by financial authorities. Interest in this form of currency is increasing, fueled by its implications for payment systems and smart contract functionality. As the landscape evolves, understanding the distinctions and capabilities of assets like the digital RMB versus blockchain counterparts is essential for comprehending the future of monetary transactions.
Understanding Digital RMB Smart Contracts
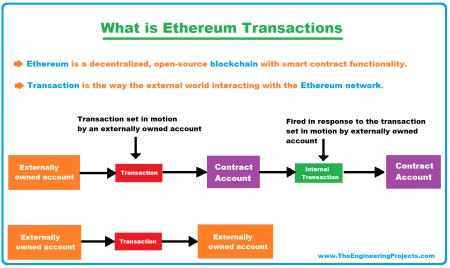
Digital RMB smart contracts are a groundbreaking shift in digital currency technology, differentiating themselves from popular Ethereum smart contracts. Unlike Ethereum’s contracts, which operate on a decentralized blockchain network and enable peer-to-peer transactions, digital RMB smart contracts are executed on a centrally managed system. This contrast raises compelling discussions about the efficiency of central bank digital currencies (CBDCs), particularly in how they handle security and transaction integrity without the common blockchain structure.
The unique architecture of digital RMB smart contracts means they can offer programmability without relying on the decentralized principles that characterize Ethereum. This allows for more controlled implementation of features, such as targeted payments and automated process execution, which are essential for government-related transaction oversight. Consequently, the digital RMB’s structure could pave the way for innovative financial products and services that utilize smart contracts while ensuring compliance with existing regulatory frameworks.
The Role of Digital RMB in Earning Interest
Starting January 1, the digital RMB will allow wallet balances to earn interest, which marks a significant enhancement in its usability compared to traditional fiat currencies. This feature aims to stimulate digital currency interest among users, especially considering that only specific classes of wallets (Class 1, 2, and 3) will qualify to earn interest. This measure is indicative of an increasing trend to make CBDCs more attractive and functional for everyday transactions, consequently embedding digital RMB in the financial ecosystem.
Importantly, the interest-earning feature for digital RMB wallets emphasizes the importance of the verification process. Only digitally verified wallets will be eligible to receive interest, highlighting the focus on security and ownership verification. This attribute may further influence the adoption rates of the digital RMB, as users will be encouraged to engage with wallet systems that prioritize financial accountability and ensure user rights in the digital currency landscape.
Comparative Advantages: Digital RMB vs Ethereum Smart Contracts
When comparing digital RMB smart contracts to those built on Ethereum, the centralized nature of digital RMB presents several advantages. For instance, by effectively managing transaction data through a centralized ledger, the digital RMB can prevent some of the scalability issues faced by Ethereum, especially during periods of high network congestion. Furthermore, with the backing of central banks, the digital RMB is likely to provide stability and trust, essential components for mass adoption in various financial transactions.
On the other hand, Ethereum smart contracts, while more flexible and empowering for developers, face challenges related to security and regularity due to their decentralized structure. Such complexity can deter businesses from fully embracing Ethereum’s capabilities due to fears of volatility and unpredictability. In this context, the digital RMB stands out as a viable alternative for enterprises seeking robustness, efficiency, and the ability to deploy smart contracts without the inherent risks associated with decentralized blockchain technologies.
Exploring Blockchain Alternatives for Digital Currency
While blockchain technology serves as the backbone of many cryptocurrencies, alternatives like the digital RMB showcase that digital currencies can operate effectively without extensive blockchain infrastructure. The digital RMB leverages a unique account system that facilitates transactions through a ‘single ledger’ managed by both the central bank and commercial banks, thus eliminating some of the common pitfalls of traditional blockchain systems, such as high energy consumption and slow transaction speeds.
Exploring these blockchain alternatives opens a dialogue on the future of digital currency development. With various innovations emerging in this space, including enhanced transaction verification processes and adaptable smart contracts, national digital currencies like the digital RMB represent a significant step toward a future where digital transactions can be more easily integrated into everyday banking and consumer experience, potentially reshaping global finance.
Security Protocols of Digital RMB Smart Contracts
The implementation of security protocols in digital RMB smart contracts is critical in ensuring user trust and system integrity. Given that these contracts operate on a centralized framework, security measures emphasized by the central bank and commercial entities are designed to prevent unauthorized access and fraudulent activities. This contrasts with decentralized models, where the responsibility of security often falls on individual users, which can be less reliable.
Moreover, by utilizing a digitally verified wallet system, the digital RMB enhances user protection, ensuring that only authorized wallets can participate in transactions and eligible for benefits like earning interest. These robust security measures not only fortify the digital RMB’s appeal but also align closely with the increasing demand for safe and reliable financial interaction in the digital age.
How Digital RMB is Shaping Future Financial Transactions
The introduction of digital RMB is not just a significant development in China’s financial landscape but also a harbinger of changes to global financial transactions. With features such as smart contracts that enable targeted payments, the digital RMB allows for enhanced financial efficiency, potentially revolutionizing how businesses and consumers interact with money. This shift may influence the broader global landscape, prompting other nations to explore their own digital currencies.
As cash transactions decline worldwide, the digital RMB represents a progressive step towards utilizing digital currencies in everyday financial scenarios. The capability to streamline cross-border payments and create direct pathways for financial services through digital means can foster economic growth both domestically and internationally, marking a pivotal moment in the evolution of financial transactions.
Challenges Facing Digital RMB Adoption
Despite the promising features of digital RMB, there are several challenges that could impact its adoption. User education remains crucial; many individuals are still not familiar with how digital currencies operate, especially in comparison to traditional fiat currencies. A lack of understanding may hinder the willingness of users to transition from cash-based systems to digital platforms.
Additionally, concerns regarding privacy and data security may pose threats to widespread acceptance. As the digital RMB requires verification processes and centralized oversight, users may fear surveillance of their financial transactions. Addressing these concerns through transparent policies and robust protections is essential for fostering trust and encouraging a more significant adoption of digital currencies.
The Global Impact of Central Bank Digital Currencies
The rise of central bank digital currencies (CBDCs), including digital RMB, has global implications that could reshape the international monetary system. With countries around the world exploring similar options, the introduction of the digital RMB may push for a new paradigm where CBDCs facilitate smoother cross-border transactions, lower remittance costs, and more effective monetary policy transmission.
As central banks realize the benefits of adopting digital currencies, this could lead to a competitive landscape where nations strive to enhance their versions of CBDCs. Such dynamics may not only affect international trade and finance but also demand significant adaptations in regulatory frameworks to ensure clarity as multiple digital currencies begin to coexist in the global marketplace.
Future Prospects for Digital RMB and Financial Innovation
The digital RMB’s future is intrinsically linked to ongoing financial innovations that leverage technology to enhance user experience and transaction effectiveness. As the digital currency ecosystem continues to evolve, the digital RMB could integrate more advanced features that utilize cutting-edge technology such as artificial intelligence and machine learning to anticipate user needs, monitor transaction patterns, and provide real-time fraud detection.
Collaboration between tech companies and financial institutions will be crucial in realizing these prospects. By fostering an environment conducive to innovation, the digital RMB could not only maintain its relevance in the fast-paced digital economy but also set a benchmark for other digital currencies looking to establish themselves in the financial landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Digital RMB and how does it differ from traditional currencies?
The Digital RMB, or digital Renminbi, is China’s central bank digital currency (CBDC) that operates independently of blockchain technology. Unlike traditional currencies, it is controlled by the People’s Bank of China and offers features like programmability through smart contracts, allowing for targeted payments and automatic execution.
How do Digital RMB smart contracts differ from Ethereum smart contracts?
Digital RMB smart contracts are fundamentally different from Ethereum smart contracts. While Ethereum’s contracts operate on a decentralized blockchain network, Digital RMB smart contracts use a unique account management system based on a single ledger maintained by the central bank and commercial banks, ensuring security and compliance with monetary policy.
Will Digital RMB wallets earn interest?
Yes, starting January 1, Digital RMB wallet balances eligible under certain categories can earn interest. Only Class 1, 2, and 3 wallets, which can be digitally verified, are allowed to accrue interest, while Class 4 wallets, which lack ownership verification, will not earn interest.
What are the benefits of using Digital RMB over traditional digital currencies?
The Digital RMB offers several advantages over traditional digital currencies, including interest accrual for verified wallets, enhanced programmability through non-blockchain smart contracts, and increased control over monetary functions, all aimed at maintaining financial stability.
Why is the Digital RMB not built on blockchain technology?
The Digital RMB is designed to function independently of blockchain to ensure a stable monetary system managed by the central bank. This approach allows for a tailored account system that provides flexibility and efficiency without the limitations posed by decentralized blockchain networks.
What role do central banks play in the Digital RMB ecosystem?
Central banks, specifically the People’s Bank of China, play a crucial role in the Digital RMB ecosystem by maintaining a unified ledger and overseeing the issuance and regulation of the currency, ensuring compliance with financial policies and stability in the digital currency landscape.
How can I open a Digital RMB wallet?
To open a Digital RMB wallet, users will need to go through the mobile banking services of participating banks or payment platforms like WeChat and Alipay, which will gradually gain the ability to facilitate wallet creation starting January 1.
What functionalities do Digital RMB smart contracts enable?
Digital RMB smart contracts enable various functionalities, including targeted payments, automatic execution of transactions, and programmability, providing users with enhanced control over their digital currency activities without compromising monetary policy.
What implications does the Digital RMB have for digital currency interest?
The Digital RMB introduces a novel dynamic to digital currency interest by allowing eligible wallets to earn interest, thereby incentivizing users to adopt this digital currency while enhancing the utility and attractiveness of digital financial services.
Are there any blockchain alternatives for the Digital RMB?
While the Digital RMB itself does not utilize blockchain technology, it represents an alternative approach to digital currencies, focusing on centralized control and regulatory compliance as opposed to decentralized blockchain alternatives used by cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Digital RMB Wallet Interest | Starting January 1, wallet balances will earn interest. |
| Non Block-chain Smart Contracts | Unlike Ethereum, digital RMB smart contracts are not blockchain-dependent and are supported by a unique account system. |
| Interest Eligibility | Only verified Class 1, 2, and 3 wallets can earn interest; Class 4 wallets are ineligible. |
| Implementation of Smart Contracts | Allows targeted payments and automatic execution without interfering with monetary functions. |
| Launch of Digital Wallets | Operational banks and apps like WeChat and Alipay will support digital RMB wallet creation starting January 1. |
Summary
Digital RMB is a progressive digital currency initiative that stands apart from other cryptocurrencies, particularly in its approach to smart contracts and its underlying infrastructure. Unlike Ethereum’s blockchain-based smart contracts, Digital RMB utilizes a new account system managed by the central and commercial banks, representing a modernized financial strategy for programmable payments while ensuring monetary stability. As it rolls out wallet interest and expands accessibility through mainstream banking platforms, Digital RMB promises to reshape financial transactions in China.
Related: More from Ethereum News | Stock Drops on Mixed Q4 Results | Google Cloud, MoneyGram Join New Privacy Network Bank Initiative