U.S. inflation expectations have notably risen, as highlighted in a recent survey from the New York Fed. As consumers project a 3.4% increase in prices over the upcoming year, this uptick creates a considerable stir regarding the economy’s trajectory. Coupled with a deteriorating employment outlook—where job opportunities are at their lowest in over a decade—these inflationary pressures pose significant challenges for the Federal Reserve’s interest rate adjustments. With the probability of securing new employment dropping to 43.1%, the disparity between inflation concerns and potential joblessness is growing. This scenario might complicate the Fed’s decision-making process in the forthcoming policy meeting, as they weigh both inflation rate hikes against the risk of increased unemployment.
In recent months, rising consumer price expectations have emerged as a critical issue in the U.S. economic landscape. Inflationary signals are now intertwining with a less favorable employment forecast, as many individuals express skepticism about available job opportunities. The Federal Reserve’s potential response to these inflation trends may be complicated by the decline in job market confidence reflected in consumer feedback. Additionally, as perceptions of wage growth and employment stability wobble, the central bank faces the challenge of balancing inflation control with the risks of exacerbating job losses. The ongoing dialogue around these economic indicators will be vital in shaping future monetary policy and addressing the concerns of American consumers.
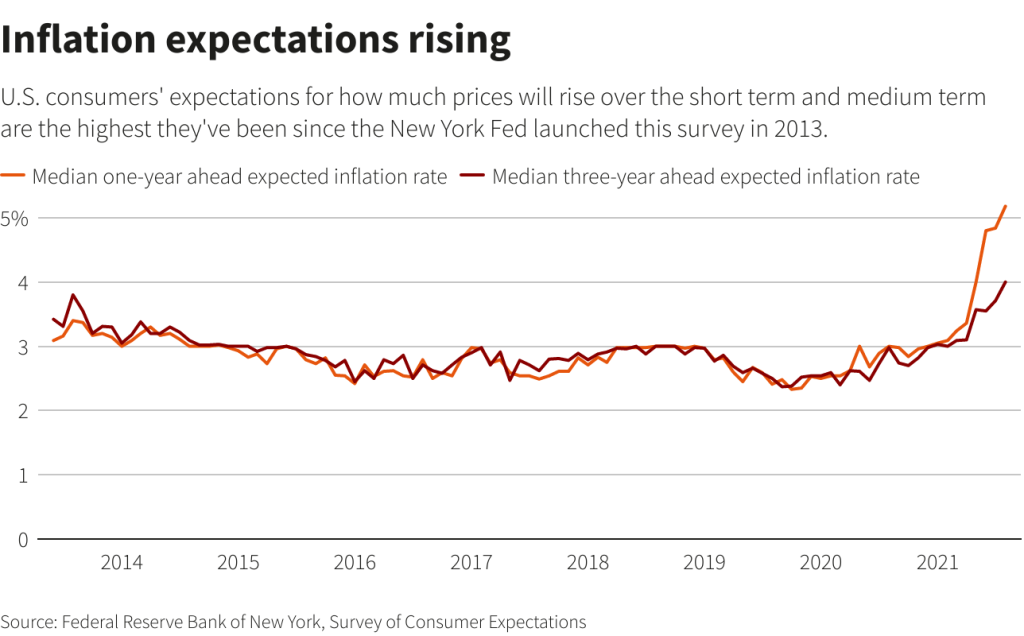
Rising U.S. Inflation Expectations and Their Impact
In December, U.S. inflation expectations saw an uptick, with consumers anticipating a 3.4% increase in prices over the next year. This rise from November’s 3.2% illustrates growing concern about the cost of living, which plays a crucial role in household budgeting and spending decisions. Inflation not only affects consumer purchasing power but also influences how the Federal Reserve formulates its monetary policy. As inflation expectations rise, there is an increasing pressure on the Fed to adjust interest rates accordingly to mitigate potential overheating of the economy.
However, expectations of rising inflation create a conflicting scenario for U.S. consumers and policymakers. While higher inflation signals a potential increase in prices, the accompanying deterioration in the employment outlook complicates matters. With fewer job opportunities available and a decline in consumer confidence reflected in survey data, the Federal Reserve faces a challenging landscape. Balancing the need to address inflation while ensuring job growth remains a vital issue, and the divergence in perceptions among Fed officials only adds to the intricacy of making timely and effective monetary adjustments.
The Deteriorating Employment Outlook: Threats to Economic Stability
The employment outlook in the United States has weakened significantly, with recent data indicating that the perceived chances of finding a job have reached a twelve and a half year low. At just 43.1%, this probability suggests a shift in the labor market dynamics, raising concerns about economic stability and growth. A declining employment outlook not only impacts individual livelihoods but also bears broader implications for consumer spending, which is a crucial component of the economy. If consumers feel insecure about job prospects, they are less likely to make major purchases, thereby potentially stalling economic growth.
Furthermore, the implications of a poor employment outlook can directly affect the Federal Reserve’s policy decisions. As unemployment fears rise, the Fed may need to be more cautious in adjusting interest rates, as aggressive hikes could exacerbate job losses further. The delicate balance becomes even more evident when coupled with rising inflation expectations. These competing pressures from inflation and employment signal that any policy adjustments must carefully consider the prevailing economic conditions, as missteps could lead to heightened unemployment or runaway inflation.
Fed Rate Adjustments: A Delicate Balance Amid Economic Concerns
As inflation expectations rise, the Federal Reserve is tasked with the challenging responsibility of adjusting interest rates to maintain economic stability. The latest consumer expectations survey has revealed a mismatch between rising inflation sentiments and faltering job opportunities, which complicates the Fed’s decision-making process. If the Fed opts for a rate hike in response to inflation, it risks hindering job growth further, while maintaining lower rates may fuel the very inflation they aim to control. Thus, finding the right policy adjustment is critical in navigating this complex economic landscape.
The Fed’s interest rate decisions are closely monitored by markets and consumers alike, and any changes can have widespread implications. A cautious approach might be advocated by some Fed officials who perceive a greater risk of rising unemployment, making them wary of aggressive rate hikes. Conversely, the increasing inflation rate could lead others to push for immediate action to prevent further price increases. This divergence highlights the ongoing debate within the Federal Reserve, as officials work to align their strategies with the current economic indicators and the public’s expectations.
Consumer Expectations Survey: A Reflection of Economic Sentiment
The Consumer Expectations Survey conducted by the New York Fed serves as a vital tool for assessing public sentiment regarding inflation and employment. With a significant drop in the estimated probability of finding new job opportunities, this survey illuminates how economic conditions are perceived by everyday Americans. Such perceptions are crucial, as they can directly influence spending habits and overall economic activity. If consumers expect difficulties in finding work, they are more likely to curtail discretionary spending, further impacting economic growth.
In addition, the survey results prompt a deeper examination of the relationship between consumer expectations and the broader economic framework. Rising inflation expectations juxtaposed with declining employment probabilities indicate a rising sense of uncertainty among consumers. This growing sentiment poses challenges for the Fed and policymakers, as it necessitates responsive actions to both stabilize the economy and address consumer concerns. The insights gained from consumer expectations surveys highlight the importance of transparency and clear communication from the Federal Reserve to foster trust in economic policy.
Job Opportunities: The Key to Economic Recovery
Job opportunities form the backbone of a thriving economy, and their availability significantly influences consumer confidence and spending. The recent decline in perceived job prospects highlights a troubling trend for economic recovery. As consumers face reduced chances of employment, spending patterns are likely to shift, with an increased focus on savings over expenditures. This change can hinder overall economic growth and recovery, fueling a cycle of uncertainty that impacts both businesses and households.
Moreover, increasing job opportunities could serve as a remedy for elevating inflation expectations. As more individuals secure employment, consumer spending may rise, consequently driving demand for goods and services. However, this scenario hinges on the collaboration of various economic factors, including Federal Reserve interest rate policies, economic incentives for businesses, and the overall health of industry sectors. A revitalized job market is essential for turning around inflation trends and fostering sustainable economic growth.
The Interplay Between Inflation and Employment in Economic Policy
The interplay between inflation and employment presents a complex challenge for economic policymakers. Elevated inflation expectations can lead to higher interest rates, which may slow down job growth. Conversely, a deteriorating employment outlook can suppress consumer spending, which influences inflation. This cyclical relationship requires careful navigation by the Federal Reserve as it formulates economic policies. Understanding this dynamic is essential for crafting strategies that promote both stable prices and full employment.
In light of the current economic context, the Federal Reserve faces increasing pressure to strike a balance that supports job creation while managing inflation. Regulatory actions and monetary policy adjustments must consider longer-term implications on both fronts. Policymakers must remain vigilant and responsive, capable of adjusting their strategies based on evolving economic indicators amidst escalating consumer expectations. The effectiveness of their decisions will ultimately determine the trajectory of the economy moving forward.
Monitoring U.S. Economic Indicators: The Role of Surveys
Surveys play an instrumental role in monitoring U.S. economic indicators, providing valuable insights into consumer expectations, inflation, and employment. These tools allow economists and the Federal Reserve to gauge public sentiment, helping to inform their decisions with real-time data. By analyzing trends in consumer expectations, policymakers can more effectively anticipate future economic conditions, preparing for potential shifts that may require intervention.
Moreover, maintaining an ongoing dialogue with consumers through such surveys fosters public trust in economic institutions. When individuals feel their voices are heard through these assessments, it enhances their engagement with the economy, potentially leading to increased spending and investment. For the Federal Reserve, harnessing the insights from these surveys is crucial in formulating effective policy measures that align with the evolving economic landscape.
Future Projections: Navigating Economic Uncertainties
Looking ahead, navigating economic uncertainties becomes paramount for both consumers and policymakers. The fluctuations in inflation expectations and employment levels signal a need for adaptive strategies that can respond to rapid changes in the economic environment. As the Federal Reserve prepares for its next move, assessing future projections based on current data will be essential in stabilizing the economy.
These projections must take into account potential economic shocks, changes in consumer sentiment, and shifts in global economic trends. Policymakers should be prepared to pivot their strategies based on real-time assessments of the economy. Engaging with various economic indicators continues to facilitate a well-rounded approach that aims to support growth while keeping inflation in check. Ultimately, the ability to adapt to these ongoing changes will determine the resilience and health of the U.S. economy in the coming months.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the current U.S. inflation expectations for the coming year?
As of December, U.S. inflation expectations rose to 3.4%, indicating a slight increase from 3.2% in November. This rise reflects consumer sentiment about price changes over the next year.
How do U.S. inflation expectations affect Federal Reserve interest rates?
U.S. inflation expectations play a crucial role in determining Federal Reserve interest rates. Higher expectations may lead the Fed to increase rates to combat inflation, while lower expectations could allow for sustained low rates.
What impact do U.S. inflation expectations have on job opportunities?
Falling U.S. inflation expectations often correlate with deteriorating job opportunities, as indicated by the recent consumer expectations survey, where the probability of finding a new job after unemployment has dropped to 43.1%.
How do employment outlook changes relate to U.S. inflation expectations?
Changes in employment outlook can significantly influence U.S. inflation expectations. A weak employment outlook may lead consumers to anticipate lower inflation due to reduced spending power and economic activity.
How does the consumer expectations survey reflect U.S. inflation expectations?
The consumer expectations survey provides insights into U.S. inflation expectations by gathering data on how consumers foresee price changes, job opportunities, and economic sentiment affecting their financial outlook.
Why might the Federal Reserve hesitate to adjust interest rates amidst rising U.S. inflation expectations?
The Federal Reserve may hesitate to adjust interest rates due to rising U.S. inflation expectations alongside a deteriorating employment outlook. This dual concern makes it challenging to determine the best course of action for the economy.
What is the relationship between the inflation rate and the employment outlook in the U.S.?
The relationship between the inflation rate and the employment outlook in the U.S. is intricate; rising inflation can lead to increased costs of living, while a poor employment outlook often hinders consumer spending, thus affecting inflation.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Inflation Expectations | Expectations rose to 3.4% for the upcoming year, up from 3.2%. |
| Employment Outlook | Perceptions of job opportunities dropped to the lowest in 12.5 years, with only a 43.1% chance of finding a new job after unemployment. |
| Fed Officials’ Concerns | Division among Fed officials regarding inflation concerns vs. rising unemployment. |
| Impact on Interest Rates | The divergence in outlook may hinder interest rate adjustments during the upcoming Fed meeting. |
Summary
U.S. inflation expectations are rising as consumers anticipate a 3.4% increase in prices over the next year. This uptick in inflation expectations, combined with a troubling decline in employment prospects, creates a complex scenario for the Federal Reserve. With job opportunity perceptions at a record low and uncertainty about wage growth, the Fed faces significant challenges in balancing inflation control with employment stabilization. Concerns over these conflicting indicators may lead to a more cautious stance on interest rate adjustments in the immediate future.
Related: More from Market Analysis | Barclays Looks at Blockchain for Payments, Deposits | PayPal USD Powers New PYUSDx App