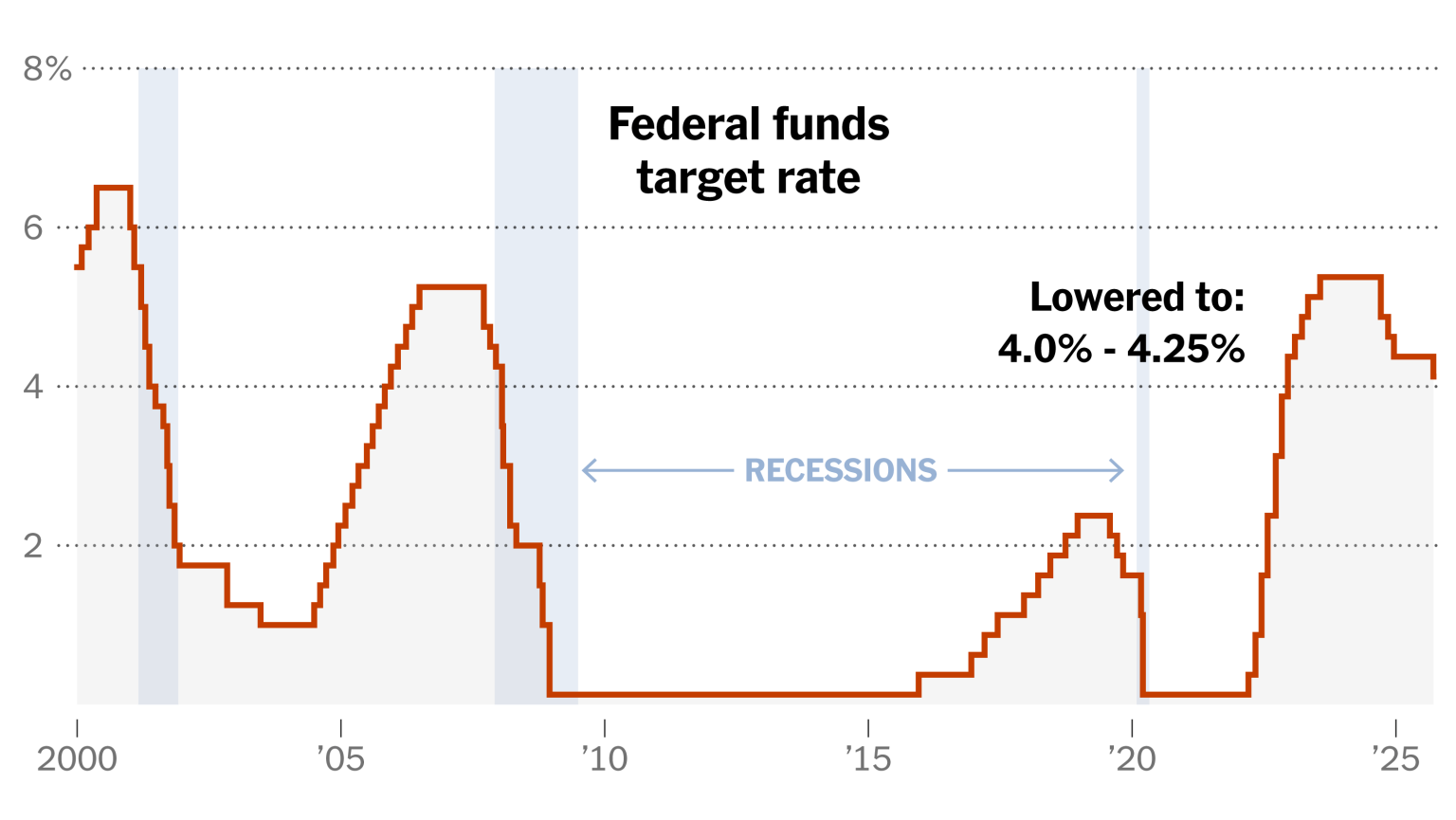
The anticipation surrounding a potential Federal Reserve rate cut has captured the attention of investors and economists alike. As the nation braces for the upcoming Federal Reserve meeting, discussions about the implications of an interest rate decision remain at the forefront of economic policy debates. With a December rate cut looking increasingly likely, participants in the market are weighing the effects on interest rates and their broader economic implications. Many experts agree that a cut could stimulate growth, particularly in light of current economic challenges. Understanding the ramifications of such a move is crucial for those navigating the complex landscape of finance and investment.
As we approach a pivotal moment in monetary policy, the prospect of a trimming of interest rates by the central banking system is on everyone’s lips. The forthcoming session of the Federal Reserve, set for December, holds significant weight for decision-makers and stakeholders in the economy. With the potential for a shift in these monetary guidelines, many are contemplating how such changes could influence economic conditions and consumer behavior. A reduction in such financial parameters could catalyze a wave of activity in various sectors, impacting lending rates and overall market confidence. Engaging in this discussion highlights the interconnectedness of fiscal strategies and their effects on economic growth.
Understanding the Federal Reserve Rate Cut
The Federal Reserve, often referred to as the Fed, plays a crucial role in shaping economic policy in the United States. One of its primary tools is the adjustment of interest rates, which influence borrowing costs, consumer spending, and overall economic activity. As indicated in the recent meeting minutes, most participants within the Fed advocate for a rate cut in December. This decision is significant as it reflects the Fed’s proactive approach to support the economy amidst varying inflationary pressures and uncertainties in the financial markets.
However, the decision to lower interest rates is not made lightly. Many Federal Reserve officials expressed that their stance on a December rate cut was finely balanced. This suggests that while there are strong arguments in favor of cutting rates to stimulate growth, there are also valid concerns regarding inflationary risks and the potential impact on long-term economic stability. As we approach the December Federal Reserve meeting, keeping an eye on economic indicators will be essential for understanding how the committee may steer interest rates.
The Economic Implications of the December Rate Cut
The potential December rate cut by the Federal Reserve carries significant ramifications for various sectors of the economy. Lowering interest rates typically aims to boost economic activity by making borrowing cheaper, encouraging consumers and businesses to invest and spend more. This heightened demand can lead to improved employment levels and overall economic growth. Analysts closely monitor these interest rate decisions as they can heavily influence market trends and consumer confidence.
In addition to immediate economic effects, a Federal Reserve rate cut can reshape long-term investment strategies. For instance, when interest rates are lowered, bond prices tend to rise, prompting investors to shift their portfolios to take advantage of these fluctuations. Furthermore, consumer loans, such as mortgages and auto loans, often see reduced interest rates, making home and vehicle purchases more accessible to the average consumer. As such, understanding the potential outcomes of the upcoming interest rate decisions provides critical insights into future market conditions.
Factors Influencing the Federal Reserve’s Interest Rate Decision
Several elements play a critical role in shaping the Federal Reserve’s interest rate decisions. Key economic indicators such as inflation rates, employment figures, and consumer spending patterns inform the Fed’s perspective on whether to cut or maintain interest rates. The recent meeting minutes highlight a division among Fed officials, where some acknowledged the benefits of a rate cut while others debated the necessity of such action, weighing the potential risks against economic growth.
Moreover, external factors, including global economic conditions and geopolitical events, also impact the Federal Reserve’s decisions. The Fed must consider how international trade tensions or financial crises abroad can disrupt the U.S. economy. Therefore, the interplay between domestic and global markets is vital for understanding its monetary policy direction. This upcoming meeting emphasizes the complexity of the Fed’s role in navigating these multifaceted economic landscapes.
The Role of Federal Reserve Meetings in Setting Economic Policy
Federal Reserve meetings serve as a cornerstone for setting monetary policy and addressing the ever-changing economic landscape. These gatherings bring together members of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) to evaluate economic conditions and determine the appropriate course for interest rates. The recent minutes reveal a significant consensus among officials on the need to consider a rate cut as a proactive measure in light of current economic challenges, indicating how responsive the Fed can be in its approach.
During these meetings, various economic data reports are analyzed, including growth rates, inflation metrics, and employment statistics. These insights help the committee weigh the balance of risks associated with potential interest rate changes. Moreover, the transparency of the Fed’s discussions allows the public and investors to gauge future economic policies and adapt their strategies accordingly. It is a dynamic process that showcases the Fed’s commitment to maintaining economic stability.
Market Reactions to Potential Federal Reserve Rate Changes
Market reactions to Federal Reserve interest rate decisions can be swift and pronounced. Investors closely monitor any signals from the Fed about potential rate cuts or holds, as these decisions can dramatically affect stock prices, bond yields, and foreign exchange rates. The anticipation of a December rate cut has already stirred discussions among analysts regarding the potential for increased capital inflow into equities, as lower interest rates generally make stocks more attractive compared to fixed-income investments.
Additionally, the bond market reacts decisively to shifts in interest rates. Typically, when the Fed signals a willingness to lower rates, bond yields fall, leading to a rise in bond prices. This relationship prompts investors to reassess their positions and predict future movements based on the Fed’s policy outlook. Understanding these market dynamics is essential for stakeholders as they navigate through the possible ramifications of the Fed’s upcoming decisions.
Long-term Effects of Interest Rate Changes on the Economy
While short-term responses to interest rate changes may be more apparent, the long-term effects are equally crucial to consider. A successful Federal Reserve rate cut can help support economic recovery, especially during downturns, as it lowers borrowing costs for consumers and businesses. This liquidity boosts spending, which can lead to sustained economic growth. However, prolonged periods of low interest rates also pose risks, such as fueling asset bubbles and increasing debt levels.
As the Fed deliberates on the December rate cut, the potential impact on inflation should also be on the table. If economic growth accelerates due to lower rates, inflation might rise, prompting the Fed to eventually hike rates again to maintain equilibrium. Balancing these factors becomes critical in shaping the broader economic landscape. Understanding the historical context and potential future ramifications of interest rate changes equips individuals and businesses with the knowledge needed to navigate the evolving economic terrain.
The Connection Between Interest Rates and Consumer Behavior
Interest rates play a pivotal role in shaping consumer behavior. When the Federal Reserve announces a rate cut, consumers often respond by increasing spending on big-ticket items, such as homes and cars, due to lower borrowing costs. This surge in consumer confidence can contribute significantly to overall economic activity. The December rate cut, if implemented, could encourage spending just in time for the holiday season, reflecting the urgency of timely monetary interventions.
Conversely, higher interest rates tend to restrain consumer spending, as individuals face increased costs associated with borrowing. In recent months, the Fed has grappled with how best to manage this delicate balance between stimulating growth through lower rates while keeping inflation in check. Observing trends in consumer purchasing patterns in reaction to the Federal Reserve’s decisions provides insight into the broader economic implications of such policies.
Analyzing the Impact of Federal Reserve Meetings on Financial Markets
Federal Reserve meetings are a focal point for financial market analysis, as traders and investors closely monitor any updates regarding interest rates and other economic indicators. The decisions made during these sessions can significantly influence stock market performance, with sectors such as banking and real estate being particularly sensitive to changes in interest rate policies. The anticipation of a December rate cut has already prompted shifts in market strategies, highlighting the importance of Fed announcements.
Furthermore, the financial markets are not just reactive; they also attempt to predict outcomes based on economic data and Federal Reserve communications. A signal from the Fed suggesting a rate cut can lead to increased trading activity as market participants adjust their positions. These scenarios underscore the intricate connection between the Federal Reserve’s policy decisions and the overall behavior of financial markets.
The Historical Perspective on Federal Reserve Rate Changes
Understanding the historical context of Federal Reserve rate changes can offer valuable insights into the potential outcomes of forthcoming decisions. Looking back at previous instances when the Fed opted to cut rates reveals patterns that can help predict market reactions and economic impacts. Historical data shows that rate cuts often coincide with boosts in consumer spending and investment, reflecting the central bank’s role in economic stabilization.
Moreover, analyzing past Federal Reserve meetings emphasizes the interplay between interest rate decisions and external economic shocks. For instance, during economic downturns, rate cuts have typically been employed as a tool to stimulate recovery. As the current economic landscape evolves, drawing lessons from history will be instrumental for both policymakers and investors in anticipating how a December rate cut could shape future economic trajectories.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of the Federal Reserve rate cut in December?
The Federal Reserve rate cut in December is significant as it reflects the central bank’s response to current economic conditions. Participants in the December Federal Reserve meeting suggested a rate cut to stimulate economic growth, although some members felt that maintaining current interest rates could also be justified.
How does the Federal Reserve’s interest rate decision impact the economy?
The Federal Reserve’s interest rate decision, including any rate cut, impacts borrowing costs for consumers and businesses. Lower interest rates typically encourage spending and investment, which can help boost economic activity, while higher rates may slow it down.
What are the possible outcomes of the Federal Reserve’s December rate cut?
Possible outcomes of the Federal Reserve’s December rate cut include increased consumer spending, growth in business investment, and a potential boost in the stock market. However, the effectiveness of a rate cut depends on various factors, including overall economic conditions and consumer confidence.
How does the Federal Reserve meeting influence interest rates?
The Federal Reserve meeting influences interest rates through discussions and decisions made regarding monetary policy. If a majority of participants favor a rate cut, as seen in recent meetings, it can lead to an official reduction in interest rates, impacting loans and saving rates across the economy.
What factors do the Federal Reserve consider before making an interest rate decision?
Before making an interest rate decision, the Federal Reserve considers several factors, including inflation rates, employment statistics, economic growth forecasts, and global economic conditions. These elements help determine whether an adjustment, such as a December rate cut, is necessary to promote economic stability.
Why might some Federal Reserve members oppose a rate cut despite support from others?
Some Federal Reserve members may oppose a rate cut despite support from others due to concerns about potential inflationary pressures, the risks of taking an aggressive easing approach, or a belief that the current economic conditions do not warrant such a shift in interest rates.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Rate Cut Support | Most Federal Reserve participants support a rate cut in December. |
| Decision Balance | Some participants indicated the decision was finely balanced. |
| Support for Current Rates | A few participants could have also supported maintaining current interest rates. |
Summary
The discussion surrounding the Federal Reserve rate cut reveals significant insights from the recent meeting minutes. The overall sentiment among participants leans towards implementing a rate cut in December, though there is a recognition of the delicate balance in making this decision. Importantly, some members expressed that they could also advocate for keeping the interest rates unchanged, emphasizing the ongoing debates within the Federal Reserve regarding optimal monetary policy.
Related: More from Market Analysis | Earnings season is wrapping up with a mixed bag of results across | Polymarket Bet Fails to Catch Insider Traders