Tokenization is rapidly emerging as a transformative force in the realm of financial technology, with companies like BlackRock advocating for its potential to revolutionize market efficiency. By utilizing digital assets and blockchain technology, tokenization promises to streamline processes and widen access to various investment opportunities. However, warnings from the International Monetary Fund (IMF) highlight the potential dangers of adopting untested frameworks, emphasizing the risks of rapid market shocks and instability. This pivotal dialogue on tokenization underscores a critical juncture in finance, where the benefits of modernization may clash with the need for regulatory oversight. As stakeholders navigate this complex landscape, the future of tokenization will significantly impact how global financial systems operate and interact with emerging digital technologies.
The concept of asset digitalization, often referred to as tokenization, is at the forefront of discussions about modern finance. This innovative approach to recording asset ownership through decentralized networks and blockchain is transforming traditional practices and creating new avenues for economic participation. Leading institutions, including investment giants and international monetary authorities, are grappling with its implications—balancing the allure of immediate trade settlements and enhanced liquidity against the backdrop of systemic risks and unforeseen market volatility. As proponents tout the benefits of connecting conventional finance with digital asset infrastructure, skeptics raise valid concerns about the resulting speed and efficiency. Navigating this duality will be crucial as the future unfolds for integrated markets.
Understanding Tokenization in Financial Markets
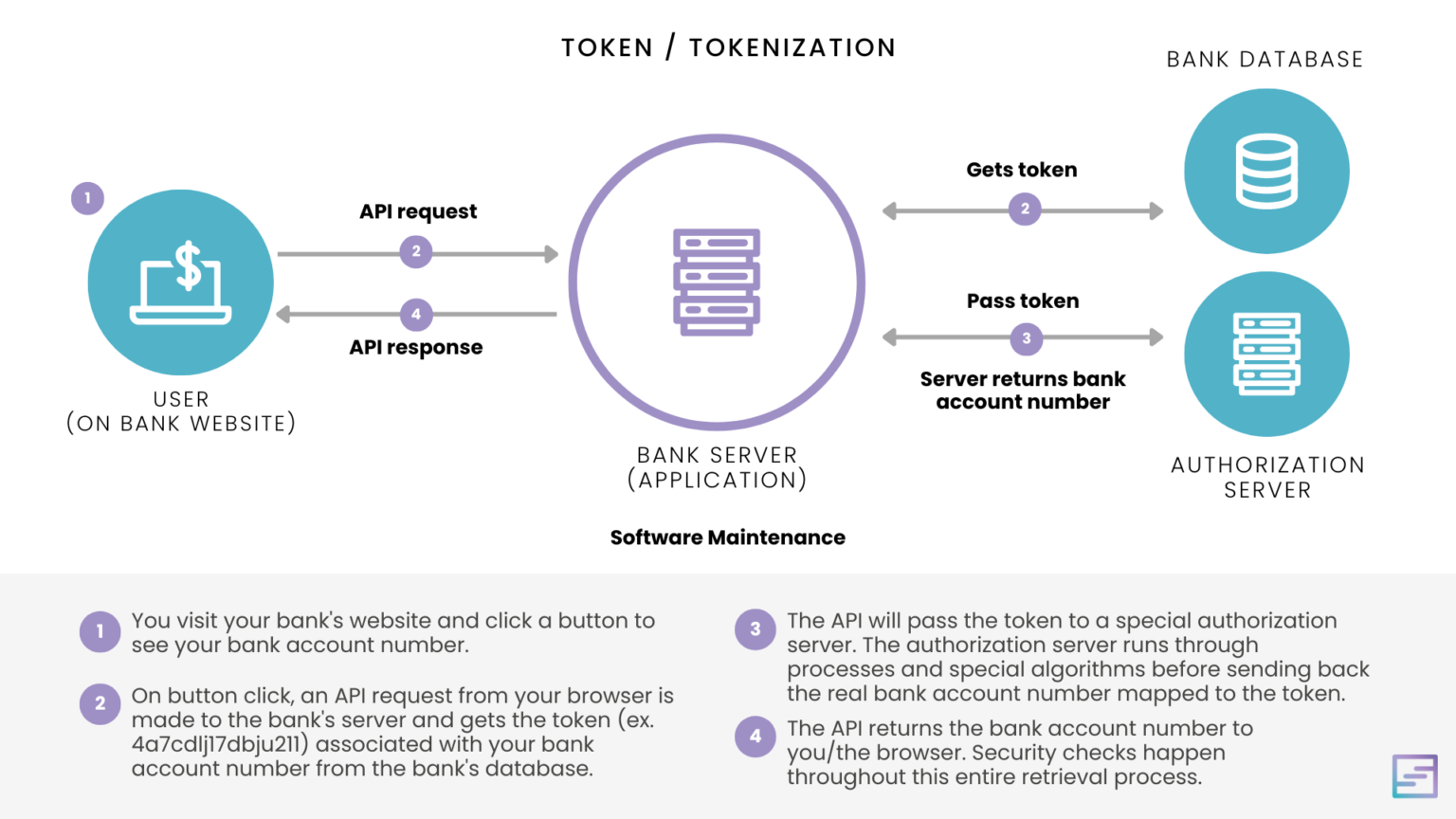
Tokenization in financial markets refers to the process of representing asset ownership through digital tokens on a blockchain. This innovation aims to modernize asset management and trading, making transactions faster, more transparent, and more efficient. By enabling the creation of tokenized versions of physical assets, it has the potential to streamline the transfer of ownership and reduce costs associated with traditional trading methods. Tokenization could revolutionize how assets are traded, providing investors with increased access to diverse asset classes, from equities and bonds to real estate and collectibles.
Organizations such as BlackRock view tokenization as a critical step towards enhancing market efficiency. They believe that by integrating digital assets into the investment landscape, workflows can be optimized to enable smoother transactions. As the tokenized ecosystem continues to grow, financial technology companies are developing solutions that facilitate quicker settlement cycles. In the context of BlackRock’s strategy, tokenization is a pathway to widen access to global financial markets and allows for the creation of innovative investment products tailored to a broader audience.
The IMF’s Perspective on Financial Technology Risks
While BlackRock champions the benefits of tokenization, the IMF raises caution about its impact on financial stability. Their concerns stem from the recognition that the rapid pace of transactions in tokenized markets can lead to systemic risks. The IMF warns that the atomic nature of token settlement, which demands instant execution of trades, could amplify localized issues into widespread financial crises. This perspective highlights the potential for flash crashes or liquidity shortages to occur as automated trading strategies react unfavorably to market fluctuations.
Given the IMF’s crucial role in maintaining global economic stability, their skepticism is rooted in the challenges and unpredictable feedback loops that arise from high-speed trading environments. As these digital assets begin to integrate deeper into the financial system, the institution calls for careful consideration of regulations and risk management frameworks. It emphasizes the need for transparency and the establishment of robust safeguards that could prevent tokenized markets from exacerbating existing vulnerabilities during periods of market stress.
The Evolution of Asset Ownership and Financial Infrastructure
BlackRock’s viewpoint positions tokenization as the next evolutionary step in the modernization of financial infrastructure. Highlighting its transformative potential, the firm articulates that tokenization can elevate traditional asset management practices by leveraging blockchain technology. This evolution is comparable to significant advancements within the financial sector, such as the creation of electronic trading platforms and the implementation of global payment solutions like SWIFT. For investment firms, embracing tokenization means developing products designed to operate efficiently within this digital landscape, fostering innovation in asset management strategies.
On the flip side, the IMF’s perspective serves as a reminder of the ongoing challenges that accompany rapid technological advancements. Their analysis emphasizes that while tokenization holds the promise of enhancing operational efficiency, it also introduces unfamiliar risks. The potential for high volatility and interconnectedness within these markets could lead to unpredictable consequences. Therefore, balancing the benefits of innovation with prudent regulatory measures will be crucial to achieving a stable, efficient financial ecosystem.
Market Efficiency Versus Systemic Risk
The conversation surrounding tokenization inevitably leads to discussions about market efficiency and the potential for systemic risk. Proponents of tokenization assert that by reducing the time it takes to process transactions, there will be a notable increase in market efficiency. The ability to execute instantaneous trades without traditional delays represents a significant improvement in how financial assets are managed and sold. As the market becomes more efficient, it can facilitate a greater flow of investment and innovation, encouraging a new wave of growth in financial technology.
Conversely, the concerns raised by the IMF regarding systemic risks must not be underestimated. As markets operate at accelerated speeds due to tokenization, the prospect of liquidity crises or market disruptions becomes a tangible concern. For example, should a tokenized asset experience sudden volatility, the cascading effects might lead to a series of rapid sell-offs, triggering market panics. Thus, understanding and addressing these risks is vital for building a resilient financial ecosystem that can integrate digital assets while safeguarding against unintended consequences.
Tokenization: A Double-Edged Sword
Tokenization presents a unique duality in the context of modern finance. On one hand, it promises to democratize investment opportunities and enhance market participation through the creation of fungible, divisible digital assets. This democratization aligns with the goals of financial technology firms aiming to provide accessible solutions for a broader investor base. Innovations like tokenized private credit and real estate share offerings can attract both institutional and retail investors, paving the way for greater market inclusion and financial literacy.
However, this transformation also carries implications that could destabilize traditional market structures. With the rapid movement of digital assets, the associated risks—like potential market runs or unexpected liquidity shortages—could jeopardize the very investments and innovations tokenization seeks to enable. The balancing act between harnessing the benefits of tokenization and addressing the inherent risks is crucial as financial markets evolve in this digital age.
The Future of Tokenization and Market Accessibility
The future of tokenization holds significant promise for increasing market accessibility. By eliminating barriers such as high fees and lengthy registration processes, tokenization allows for the fractionalization of high-value assets. This means that investors can engage with assets that were previously out of reach, such as real estate or private equity, by purchasing only a fraction of these assets through tokenized structures. Consequently, as more asset classes become tokenized, the investment landscape could become increasingly democratized, fostering inclusivity within global markets.
Nonetheless, achieving this future relies on effective regulation and the establishment of clear operational standards. The contrasting views of BlackRock and the IMF underscore the need for a balanced approach to leveraging technology while ensuring systemic safeguards are in place. As the industry continues to innovate and evolve, collaboration between regulatory bodies and market players will be essential to realize the full benefits of tokenization in a safe, stable manner.
Adoption Challenges for Tokenization in Traditional Finance
Although the benefits of tokenization are clear, the challenges that impede broader adoption within traditional finance cannot be overlooked. Issues such as regulatory uncertainty, interoperability between different blockchain networks, and resistance from established financial institutions all pose significant hurdles. Many stakeholders in the financial sector are cautious about committing to tokenization due to the potential risks highlighted by the IMF, particularly concerns about untested frameworks that lack a regulatory backbone.
Moreover, as regulatory bodies contemplate the future of digital assets, they must navigate the fine line between fostering innovation and protecting investors. For extensive adoption of tokenization to take root, a conducive environment needs to be established, where asset protection is assured alongside operational transparency. This endeavor will require cooperation among financial institutions, tech innovators, and regulators with a shared vision for the future of finance.
Global Collaboration for Effective Tokenized Markets
The successful integration of tokenization into global markets hinges on international collaboration among financial institutions and governing bodies. Establishing coherent standards and frameworks that address interoperability, disclosure, and risk management will be essential for navigating the complexities associated with tokenized assets. Both BlackRock and the IMF recognize that without mutual agreements and well-defined guidelines, tokenization could lead to fragmentation in the market, where different jurisdictions may enforce disparate regulations.
Moreover, fostering open lines of communication will enable the sharing of best practices and risk mitigation strategies that can be integral in shaping the tokenization landscape. By working together, global stakeholders can promote a secure and efficient marketplace that balances innovation with responsibility. Such collaboration will enhance market confidence in digital assets, preparing the financial sector for a future where tokenization becomes a cornerstone of transactional practices.
Regulatory Frameworks: The Key to Tokenization Success
Regulatory frameworks will play a pivotal role in determining the success of tokenization in financial markets. As BlackRock pushes for adoption, there is a clear need for regulations that can accommodate the unique characteristics of digital assets while ensuring robust investor protection. The establishment of well-defined regulatory guidelines would provide clarity for asset managers, investors, and emerging fintech companies, fostering a healthy ecosystem for tokenized markets.
Conversely, the IMF’s cautionary stance highlights the importance of prudent oversight to avert potential crises stemming from unregulated tokenized assets. Striking a balance between fostering innovation and implementing effective controls is essential to prevent systemic disruptions. As financial institutions and regulators come together to design comprehensive standards, the messaging must clearly convey the safety nets in place, ensuring that all participants in tokenized markets can navigate them with confidence.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is tokenization and how does BlackRock see it impacting financial technology?
Tokenization refers to the process of converting rights to an asset into a digital token on a blockchain. BlackRock views tokenization as a revolutionary upgrade to financial technology, akin to major innovations in finance like the introduction of SWIFT, believing it will enhance market efficiency, widen global market access, and shorten asset settlement times.
How does the IMF view the risks associated with tokenization of digital assets?
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) warns that the tokenization of digital assets may lead to significant financial instability. They highlight concerns such as susceptibility to rapid market crashes, liquidity shortages, and the potential for ‘atomic’ settlement dangers, which could exacerbate financial shocks and disrupt global markets.
What are the advantages of tokenization in improving market efficiency according to BlackRock?
BlackRock argues that tokenization can significantly improve market efficiency by digitizing asset ownership on blockchain networks, thus eliminating manual processes and facilitating instant settlement. This evolution is expected to reduce costs and delays common in traditional finance, leading to a more accessible and streamlined investment ecosystem.
What innovations are driving the growth of tokenized financial products?
The growth of tokenized financial products is fueled by innovations in blockchain technology that enable secure, peer-to-peer transactions and programmable settlements. BlackRock’s tokenized funds, along with products like tokenized real estate shares and private credit instruments, exemplify how tokenization is broadening the scope of investable assets beyond traditional markets.
What concerns does the IMF raise about liquidity in tokenized markets?
The IMF raises concerns that the shift to tokenized markets could lead to liquidity crises, especially under stress conditions. They emphasize that the immediate funding requirements of atomic settlements might cause a sudden demand for liquidity that could disappear, potentially resulting in localized problems escalating into wider financial crises.
How might tokenization transform traditional financial systems according to BlackRock’s perspective?
From BlackRock’s perspective, tokenization could transform traditional financial systems by enhancing automation, shortening settlement times to ‘T+0’, and integrating various asset classes into a cohesive digital ecosystem. This change is expected to drive major efficiencies across financial infrastructure, ultimately benefiting investors.
What is the role of regulatory clarity in the future of tokenization according to financial experts?
Regulatory clarity is seen as crucial for the future of tokenization. Experts highlight that until regulations distinguish between volatile cryptocurrencies and regulated tokenized securities, traditional investors like banks and pension funds may be hesitant to delve fully into this new ecosystem, thus stalling potential growth in the tokenized asset market.
Could tokenization lead to systemic risks in financial markets as suggested by the IMF?
Yes, the IMF suggests that while tokenization brings substantial benefits, it also introduces systemic risks due to its high-speed operations and interconnected contracts. These risks could create feedback loops in volatile markets, leading to rapid and uncontrolled market disruptions far beyond what traditional risk management can handle.
| Key Points | BlackRock’s Perspective | IMF’s Concerns |
|---|---|---|
| Tokenization seen as major market upgrade since internet | Views it as an opportunity for modernization and efficiency | Sees it as a volatile framework leading to financial shocks |
| Aims to widen market access and enhance infrastructure | Tokenized funds already launched, leading in digital asset ETFs | Cautions against flash crashes and liquidity issues |
| Compares to past financial innovations like SWIFT | Believes in bridging traditional and digital finance | Highlights potential for cascading failures in crises |
| Tokenization could reach $30 trillion in RWAs by 2034 | Moderate growth seen in tokenized instruments and real estate | Fears of hidden leverage and complex interdependencies |
| Envisions a more efficient and inclusive market structure | Focus is on creating innovative investment products | Concerned with systemic vulnerabilities due to speed |
Summary
Tokenization is solidifying its presence in global financial markets, showcasing its potential to revitalize traditional structures while sparking significant debate among stakeholders. BlackRock advocates for its transformative capacity, emphasizing modernization and greater access to financial resources. In contrast, the IMF highlights the attendant risks of rapid market dynamics, warning of potential destabilization in financial systems. As institutions move towards a future shaped by tokenization, the critical challenge will be achieving consensus on regulatory frameworks that ensure both innovation and stability.