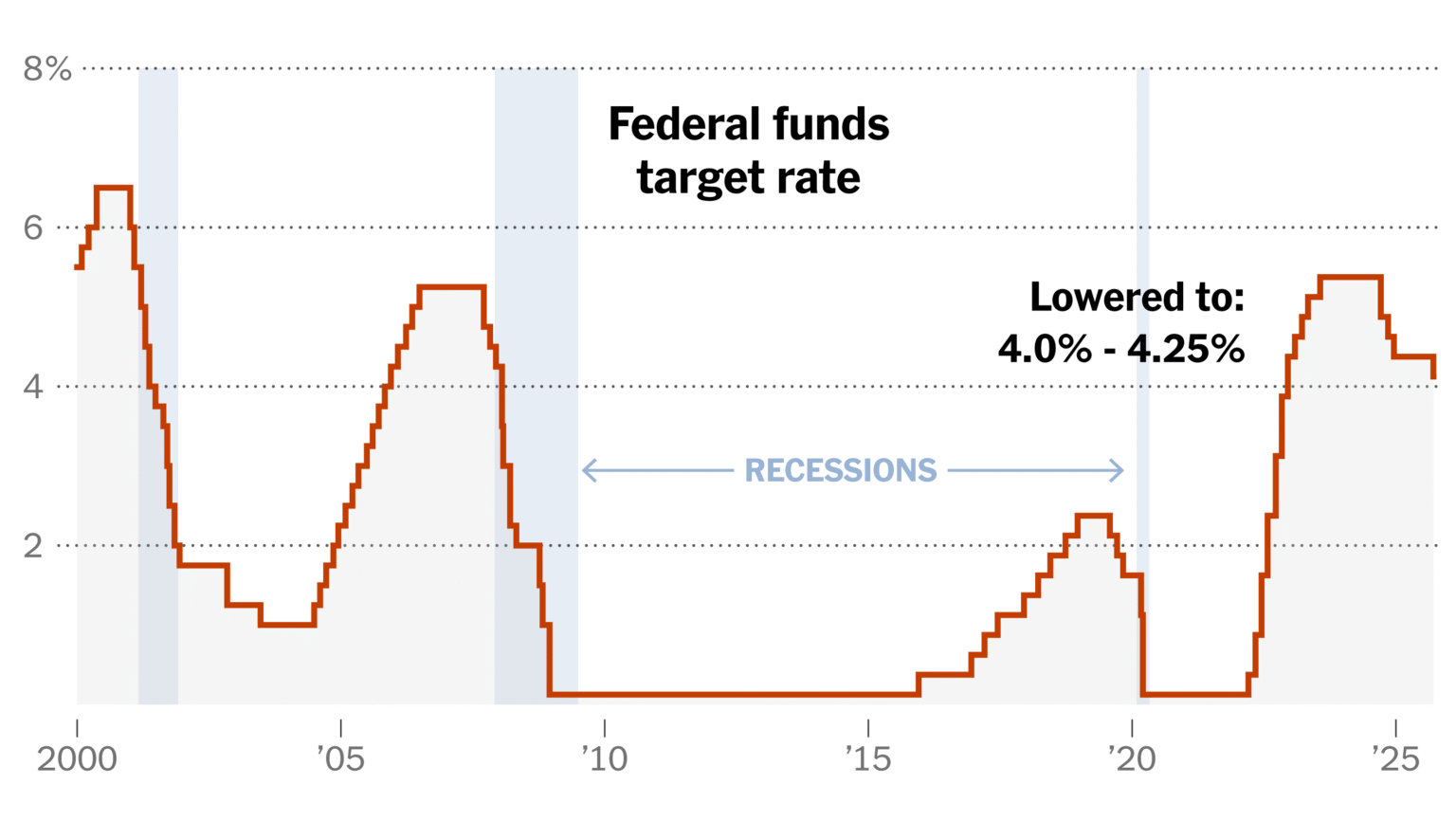
In recent weeks, the Federal Reserve rate cut has become a focal point of economic discussions, with growing market expectations indicating a significant likelihood of a reduction in December. The latest forecast shows that over 70% of traders now anticipate this interest rate cut, driven largely by comments from influential figures like New York Fed President John Williams. As the unemployment rate edged up to 4.4%, economists argue that these deteriorating labor market conditions justify a more accommodative monetary policy. Updates from the Fed regarding economic policy and potential adjustments to interest rates are closely watched, as they have a direct impact on investment strategies and overall financial market response. With such high stakes, the upcoming December decision is poised to set the tone for economic recovery and stability in the months ahead.
In light of recent developments, discussions surrounding the upcoming monetary policy adjustments have intensified, particularly regarding the anticipated lowering of interest rates by the Federal Reserve. With the Fed’s December meeting approaching, analysts are closely monitoring the implications of potential cuts on market dynamics and broader economic conditions. Key indicators, such as the unemployment rate and financial market responses, play a crucial role in shaping Fed rate expectations. This sentiment is reflective of a larger trend in economic policy updates that aim to stabilize the economy amidst fluctuating labor market conditions. As we delve into the intricacies of these monetary policy shifts, understanding their broader impact is essential for both investors and policymakers alike.
Federal Reserve Rate Cut Expectations for December
With the Federal Reserve indicating a possible rate cut in December, market expectations have surged, now sitting at over 70%. This shift comes as many investors adjust their forecasts based on recent communications from key Fed officials. Historically, interest rate movements can serve as a powerful tool for economic policy adjustments, and markets are responding to these hints with increased investment activity. Analysts point to the recent remarks by New York Fed President John Williams, who has openly supported a reduction in rates, prompting many to reconsider their prior skepticism about the likelihood of a December cut.
Furthermore, Tom Porcelli’s insights on the deteriorating labor market underscore the necessity for a rate cut, given that the unemployment rate climbed to 4.4% in September. This rise signals potential vulnerabilities in the economy, revitalizing the debate surrounding the Fed’s current trajectory on interest rates. The combination of labor market challenges and optimistic Fed signals has led to a greater consensus among economists, predicating the intended rate cut as not just a possibility but a probable necessity to stabilize economic conditions.
Impact of Economic Policy Updates on Financial Markets
Economic policy updates, particularly regarding interest rates, wield substantial influence over financial markets. As reports circulate about a potential December rate cut by the Federal Reserve, the market has reacted with marked enthusiasm, elevating stock prices in anticipation of cheaper borrowing costs. Investors frequently interpret such changes as signals for future financial stability, consequently driving market activity as they position themselves to capitalize on potential growth. As noted by Josh Hirt from Vanguard, the coalition of influential Fed officials advocating for easing presents a strong likelihood that the upcoming policy changes will have far-reaching implications across various sectors.
Additionally, the current discussions surrounding the Federal Reserve’s stance reflect broader economic concerns, particularly the looming uncertainty from the ongoing government shutdown. Without access to the latest employment and inflation data, the Fed’s decisions might be perceived with caution. This uncertainty can trigger volatility in financial markets, as traders react to speculative thoughts rather than hard data. Any shifts in the Fed’s monetary policy will be keenly scrutinized by market participants, making it paramount for the central bank to communicate its actions and underlying reasons effectively.
Analyzing Unemployment Rate Shifts and Fed Rate Expectations
The increase in the unemployment rate to 4.4% has reinvigorated discussions surrounding the Federal Reserve’s upcoming decisions on interest rates. As economists examine these shifts, they acknowledge a clear connection between labor market performance and the Fed’s monetary policy. With the job market in a precarious state, as articulated by several Fed officials and economists, the potential for a rate cut emerges as a plausible remedy for mitigating unemployment. Economic policy updates from the Fed will likely reflect a neighborhood of cautious optimism aimed at fostering job growth while tackling inflation concerns.
Moreover, the interplay between unemployment statistics and Fed rate expectations raises questions about the central bank’s future strategies. Rates are not merely tools for controlling inflation but also instruments to stimulate economic activity. As the Fed weighs the implications of rising unemployment against their commitment to fostering economic stability, the decisions made at the upcoming December meeting will serve as critical indicators of the Fed’s approach in the context of shifting economic conditions. Hence, analysts will closely monitor how the Fed maneuvers through these complex economic signals.
Fed Leadership Support for Rate Cuts
The strong endorsement of a rate cut by key figures like Fed Chair Powell and New York Fed President Williams illustrates a unified front among Federal Reserve leadership. The camaraderie among these influential policymakers can significantly impact market perceptions and expectations. With their synergy creating a powerful narrative, investors find themselves more inclined to trust in the proposed shifts in monetary policy. This eagerness is reflected in the aggressive market positioning around December, as stakeholders bet on a favorable outcome during the upcoming meeting.
Further, Williams’ advocacy for a rate cut, alongside Powell’s leadership, fosters an environment where the Fed’s actions are perceived as coherent and predictable. The notion of a ‘weighty coalition’ within the Fed, where major decision-makers align on maintaining support for the economy through rate adjustments, strengthens market confidence. Should rates be lowered in December, markets could see a surge of investment driven by optimism, as indicated by the rapid increase in the probability of a cut attracting investment activity from those previously hesitant.
Potential Dissent at the December FOMC Meeting
While prevailing expectations suggest a favorable outlook for a December rate cut, it is essential to recognize that dissent within the Fed remains a possibility. Officials like Boston Fed President Collins and Dallas Fed President Logan have made public comments expressing apprehension about additional rate reductions. This division illuminates the complexities of navigating monetary policy in a climate rife with economic uncertainty. As these dissenting voices emerge, they reflect ongoing debates about the efficacy of further easing and the potential risks associated with such decisions.
Moreover, the potential for dissent highlights the magnitude of the upcoming Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) meeting. With significant implications for interest rate trajectories, dissenting opinions may augment broader conversations regarding economic policy sustainability. Former Cleveland Fed President Mester’s notions of the rate cut serving as an ‘insurance cut’ add a layer of nuance, as this perspective might signal a cautious approach rather than a definitive shift towards aggressive easing. Understanding these dynamics will be crucial for economists and market participants as December approaches.
Market Response to Fed’s Potential Rate Cuts
The financial markets have shown a robust response to increasing speculation regarding a potential Federal Reserve rate cut in December. As market participants attempt to anticipate the Fed’s forthcoming actions, fluctuations in stocks, bonds, and other instruments have displayed pronounced volatility. Recent commentary from Fed officials, particularly regarding the necessity to respond swiftly to labor market changes, has prompted investors to pivot strategies, banking on the possibility of lower borrowing costs and a less restrictive economic environment.
The response from the financial markets is a classic example of the interplay between expectations and reality in economic policy. In scenarios where the Fed communicates a strong inclination towards easing, as evidenced by the statements from Williams and Powell, investors often react positively due to the perceived benefits of rate cuts on corporate profitability and consumer spending. Monitoring these shifts not only sheds light on market confidence but also illustrates how interconnected economic fundamentals and policy expectations can shape broader financial landscapes.
The Role of Inflation Data in Fed Decisions
As the Federal Reserve prepares for its December meeting, the lack of access to the latest inflation data due to the government shutdown amplifies the complexity of its monetary policy decisions. Understanding how inflation interacts with economic growth and unemployment will be vital for the Fed in formulating appropriate actions. Economists constantly weigh the risks of inflation against those of unemployment, knowing that ineffective policy measures could exacerbate underlying economic challenges.
In this climate, clearing the fog surrounding inflation metrics before the meeting could shape the Fed’s narrative. If inflation remains subdued, the central bank could proceed more confidently with a rate cut. Conversely, if inflation data suggest rising consumer prices, it may deter officials from making significant adjustments. These intricate connections between inflation, unemployment, and potential Fed rate cuts underscore the delicate balance the Fed must maintain as it navigates economic uncertainties.
Long-term Implications of Rate Cuts on Economic Conditions
The long-term implications of a Federal Reserve rate cut extend beyond immediate market reactions. While such cuts are often perceived as short-term solutions to bolster economic activity, their effectiveness can influence broader economic conditions over time. Lower interest rates can lead to increased borrowing and spending by consumers and businesses, potentially invigorating growth patterns. However, there are concerns about the sustainability of this growth and the risks of fostering asset bubbles in a low-rate environment.
Furthermore, the potential for a rate cut as ‘insurance’ against economic downturns must be viewed within the context of overall policy. The Fed’s commitment to monitoring the evolving economic landscape suggests a cautious approach to rate adjustments, as historical precedents illustrate that premature easing can lead to unintended consequences. Hence, understanding these dynamics is essential for stakeholders contemplating the long-term success of monetary policy interventions.
Strategic Communication and Its Impact on Fed Credibility
Strategic communication plays a crucial role in the Federal Reserve’s ability to manage market expectations and credibility. As the Fed considers potential rate cuts, effectively conveying the rationale behind these decisions will be paramount for maintaining trust among investors and consumers alike. The opinions of influential leaders such as Williams and Powell are instrumental in shaping perceptions, ensuring that their messaging resonates through various channels. By emphasizing the interconnectedness of economic conditions, the Fed can bolster its credibility and foster confidence in the ongoing economic recovery.
Moreover, the timing of communications, particularly before critical meetings like the December FOMC gathering, can profoundly impact market behavior. A well-timed acknowledgment of economic challenges, coupled with proactive measures, will likely reinforce public trust in the Fed’s decision-making process. As recent dynamics illustrate, clear and consistent messaging can mitigate volatility while preparing the markets for potential shifts, emphasizing the importance of communication as a powerful tool in the Fed’s broader economic strategy.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the likelihood of a Federal Reserve rate cut in December?
The likelihood of a Federal Reserve rate cut in December has surged to over 70% following supportive comments from New York Fed President John Williams. Market expectations have shifted dramatically, largely due to the deteriorating labor market conditions and a rising unemployment rate of 4.4%, which has bolstered the case for an interest rate cut.
How do Fed rate expectations affect financial markets?
Fed rate expectations significantly impact financial markets as they influence investment decisions, risk appetite, and asset valuations. The recent increase in the likelihood of a December rate cut has triggered a strong response in financial markets, with investors adjusting their positions based on anticipated economic policy updates.
What economic indicators are prompting the Federal Reserve to consider a rate cut?
The Federal Reserve is considering a rate cut mainly due to indicators such as the rising unemployment rate, which reached 4.4% in September—the highest level in nearly four years. Economists highlight the current precarious state of the job market as a key reason for a potential interest rate cut in December.
Will a Federal Reserve rate cut lead to immediate economic improvement?
While a Federal Reserve rate cut may provide short-term economic stimulation by increasing access to lower borrowing costs, its effectiveness can depend on various factors, including the overall economic climate and consumer confidence. Economists suggest that the cut may serve as an ‘insurance cut’ to support the economy, pending further developments in economic performance.
What are the potential implications of a December Fed rate cut on the unemployment rate?
A December Fed rate cut could lead to lower borrowing costs, which might stimulate business investment and consumer spending, potentially reducing the unemployment rate over time. However, the current rise in unemployment reflects existing economic challenges, and it remains unclear how quickly rate cuts will influence job growth.
What key messages might the Fed convey after a rate cut in December?
After a December rate cut, Federal Reserve officials may emphasize that the decision was made as a precautionary measure or ‘insurance cut’ while they monitor the economy’s response. This communication strategy aims to clarify that future rate decisions will be contingent on incoming economic data and performance.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Expectations | Over 70% chance of a rate cut in December as indicated by market sentiment. |
| Influential Voices | New York Fed President Williams supports a rate cut, impacting market views. |
| Labor Market Conditions | Unemployment rose to 4.4%, marking a significant indicator for the Fed’s decision. |
| Support from Key Officials | Powell, Williams, and Waller are in favor of a new round of easing. |
| Potential Dissenting Votes | Some officials, like Boston Fed President Collins, may oppose the rate cut. |
| Communication Strategy | The December meeting could convey that the rate cut is an “insurance cut”. |
| Impact of Government Shutdown | Fed lacks access to recent employment and inflation data due to the shutdown. |
Summary
The Federal Reserve rate cut is increasingly likely as market expectations soar, influenced by supportive remarks from key officials and worsening labor market conditions. With the unemployment rate at its highest in nearly four years, the prevailing sentiment suggests that a rate cut may be on the horizon, despite some dissenting opinions within the Fed. As the December meeting approaches, all eyes will be on the Fed’s decision-making process and the communication strategies they employ to convey their intentions to the market.