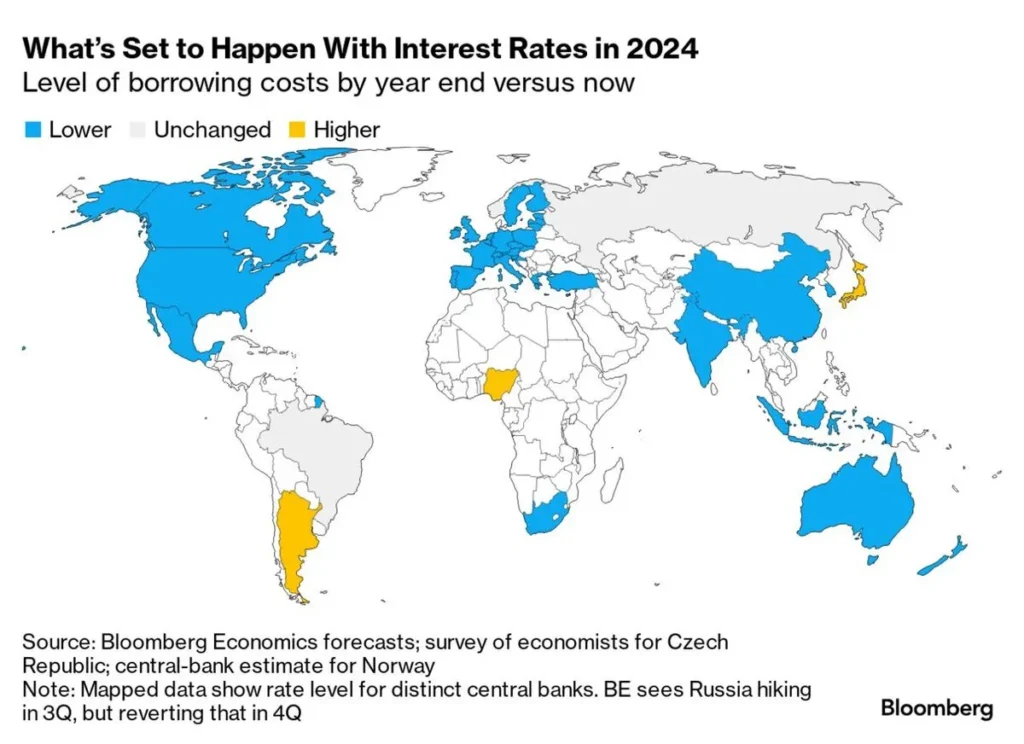
Over the past year, there has been a significant shift in monetary policy across the globe, as central banks have collectively cut interest rates 168 times. This trend reflects a broader strategy to stimulate economic growth in the face of various challenges, including inflationary pressures and economic slowdowns. Among the notable players in this monetary easing movement is the Federal Reserve, which has joined other central banks in lowering interest rates to support both businesses and consumers.
Interest rate cuts are typically employed by central banks to make borrowing cheaper, encouraging spending and investment. As businesses find it easier to secure loans, they are more likely to expand operations, hire additional staff, and invest in new projects. Similarly, consumers benefit from lower rates on mortgages and personal loans, which can enhance their purchasing power and promote economic activity.
The recent wave of rate cuts comes amid a backdrop of global uncertainty, with factors such as geopolitical tensions, supply chain disruptions, and the lingering effects of the COVID-19 pandemic affecting economic stability. By reducing interest rates, central banks aim to create a more favorable environment for growth, helping to mitigate the risks associated with these external pressures.
As we move forward, the effectiveness of these monetary policies will be closely monitored. Economists and analysts will be watching whether these cuts can successfully spur the economy and lead to a sustainable recovery. The actions taken by central banks today will shape the economic landscape for years to come.