Canada’s CPI Expected to Rise in September: Inflation Concerns and Economic Implications
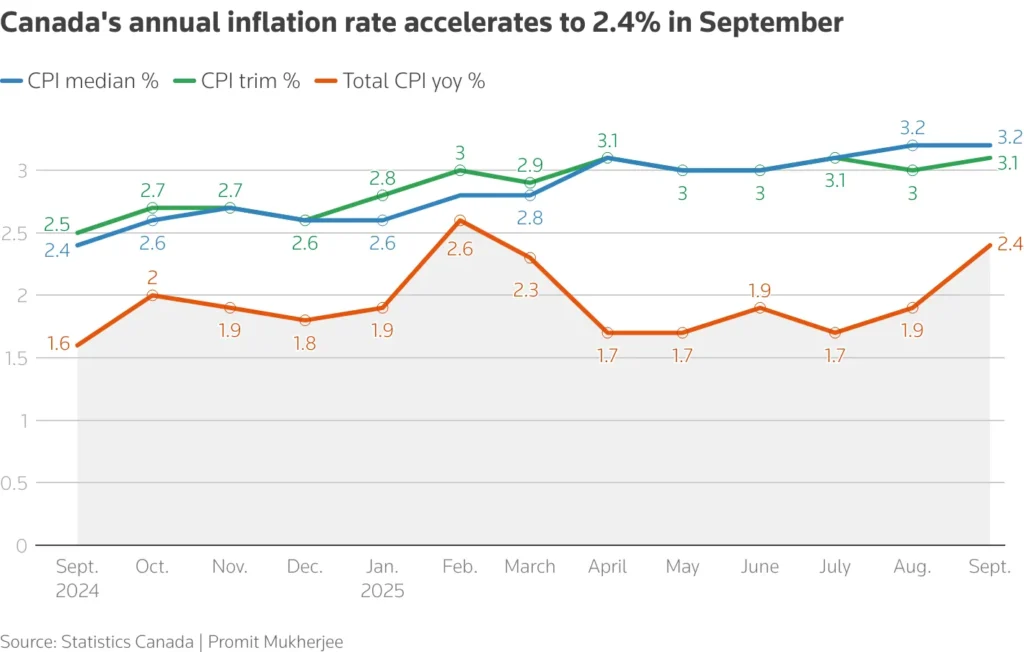
As September rolls around, economic analysts expect a rise in Canada’s Consumer Price Index (CPI), signaling a potential uptick in inflation that could impact consumers and the broader economic landscape. After a period of relatively stable prices, this anticipated increase raises concerns among consumers, policymakers, and market participants regarding the future of Canada’s financial stability and purchasing power.
Overview of CPI and Its Importance
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) is a critical economic indicator used to measure the average change over time in the prices paid by urban consumers for a market basket of consumer goods and services. As the principal measure of inflation, the CPI is used by economists and governments to set monetary policy and by businesses to predict consumer market behavior.
Factors Driving the Expected Rise
Several factors contribute to the anticipated increase in the CPI for September. Firstly, the energy sector has seen a noticeable surge in prices, particularly in oil and natural gas, partly due to international geopolitical tensions and trade dynamics. Additionally, food prices are expected to continue their upward trajectory, influenced by adverse weather conditions affecting crops and ongoing supply chain disruptions exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic recovery phase.
Housing costs, another significant component of the CPI, are also expected to rise due to increased demand and a relative shortage of housing supply in major urban centers. Furthermore, the depreciation of the Canadian dollar has made imports more expensive, contributing to higher consumer prices overall.
Economic Implications
The anticipated increase in the CPI has several implications for the Canadian economy. For consumers, rising inflation means decreased purchasing power, as higher prices could outpace wage growth. This scenario could lead to reduced consumer spending, which is a key driver of economic growth.
For policymakers, the rise in CPI will be a crucial factor in monetary decision-making processes. The Bank of Canada, which has a mandate to maintain price stability and target inflation at around 2 percent, might consider tightening monetary policy through interest rate hikes. While this could help curb inflation, higher interest rates would also increase borrowing costs for consumers and businesses, potentially slowing economic activity.
Market Reactions and Future Outlook
Financial markets are sensitive to changes in inflation and the corresponding shifts in monetary policy. As such, the expected rise in the CPI could lead to volatility in Canadian equity and bond markets. Investors and traders will likely monitor CPI releases closely, adjusting their portfolios to hedge against potential inflation risks.
Looking ahead, the trajectory of Canada’s CPI will depend on various global and domestic factors, including the pace of economic recovery post-pandemic, international commodity prices, and exchange rate fluctuations. Economic stakeholders will need to stay informed and agile, ready to adapt to the changing economic indicators that could affect their financial decisions and strategies.
Conclusion
The expected rise in Canada’s CPI in September is a development that carries significant implications for all sectors of the economy, from individual consumers to large corporations. As Canada navigates this challenging economic period, understanding and anticipating changes in the CPI will be crucial for effective economic planning and stability. Policymakers, businesses, and consumers alike must prepare for the potential impacts of rising inflation, which could shape Canada’s economic landscape in the coming months.